Boolean Expres..
advertisement

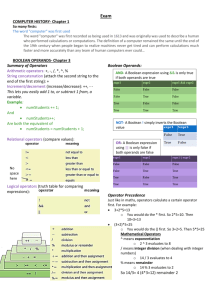
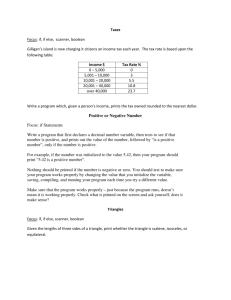
: 3B - Boolean Expressions Boolean expressions are used to compare two values and get a true-or-false answer: value1 relational_operator value2 The following relational operators are used: < less than > greater than = equal to <= less than or equal to >= greater than or equal to <> not equal to More complex Boolean expressions are formed by using the Logical Boolean operators: not negation (~) and conjunction (^) or disjunction (v) xor NOT exclusive-or is a unary operator — it is applied to only one value and inverts it: not true = false not false = true if (not found) then writeln(‘does not exist’); AND yields TRUE only if both values are TRUE: TRUE and FALSE = FALSE if (mark >= 90) and (mark <=100) then OR TRUE and TRUE = TRUE grade:= ‘A’ yields TRUE if at least one value is TRUE: TRUE or TRUE = TRUE TRUE or FALSE = TRUE FALSE or TRUE = TRUE FALSE or FALSE = FALSE if (rank >=5) or ( age >50) then writeln(‘Car Park allocated ‘); When combining two Boolean expressions using relational and Boolean operators, be careful to use parentheses. (a>b) or (x<=1) This is because the Boolean operators are higher on the order of operations than the relational operators: 1. 2. 3. 4. not * / div mod and + - or < > <= >= = <> Selection: The If statement The general format for the IF statement is as follows : IF (Boolean expression) then Statement; In the case where more than one statement needs to be executed the format is as follows; if (Boolean expression) then Begin Statement_1; Statement_2; Statement_3 End Else Begin Statement_1; Statement_2; End;