Investigating Eukaryotes KEY

Investigating Eukaryotes
KEY
Biology
HS/Science
Unit: 04 Lesson: 01
Student answers will vary slightly, but should be similar to those below.
Eukaryotic Cells Questions:
1. What is the basic definition of a eukaryotic cell?
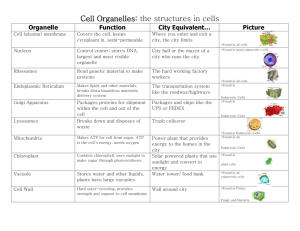
A eukaryotic cell has a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles like mitochondrion, chloroplasts, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum.
2. What is the meaning of the word parts “eu-” and “karyo-”, and how can these word meanings help you understand what a eukaryotic cell is?
Eu- means “good, well, or true”, and “karyo-“ means nucleus or nut. This means a eukaryotic cell has a true nucleus.
3. What specialized structures, if any, are present in eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells always have a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles such as: chloroplasts, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondrion, plastids, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, and vesicles.
4. What are examples of eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells include plant cells, animal cells, fungi, and protists.
5. How do eukaryotic cells reproduce?
Eukaryotic cells reproduce through mitosis or meiosis.
6. What are some ways that eukaryotic cells obtain energy?
Eukaryotic cells can obtain energy through photosynthesis or from digesting organic compounds.
©2012, TESCCC 08/15/12 page 1 of 1