Watercolor Color Polygons Lesson - Mrs. Guest
advertisement

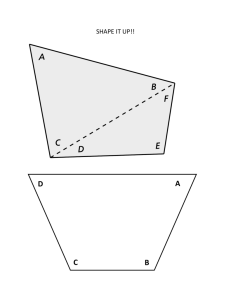
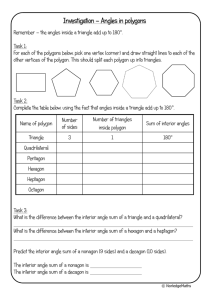
Color Theory (n − 2)180 = Degree of each angle in a regular polygon. 1 n For this activity, you will explore regular polygons and color theory. A regular polygon has congruent (equal) sides and congruent (equal) angles. Part I-­‐ Primary Colors +100 points Step 1 Use your ruler and protractor to create a regular triangle (3 equal sides and 3 equal angles). Use the side (n − 2)180 to find the degree of each angle in a regular polygon. The variable n length of five inches. Use n represents the number of sides in the polygon. Step 2 Find the angle bisector of each angle using your protractor and ruler. An angle bisector cuts an angle in half and is drawn from the vertex to any point on that angle. Each triangle has 3 angle bisectors. The point where they intersect is called the incenter of a triangle. Separate your regular triangle into three triangles. (See image below) Red Yellow Blue Then, use watercolor paint the primary colors (red, yellow, and blue) in triangles. When your painting is dry, label the side length and find the length of the radius then label the radius length on your diagram. 2 Part II-­‐ Secondary Colors + 200 points Step 1 Use your ruler and protractor to create a regular hexagon (polygon with 6 equal sides and 6 equal angles). (n − 2)180 to find the degree of each angle in a regular polygon. Use the side length of 3 inches. Use n Step 2 Separate your hexagon into six regular triangles (see image below). o y r g p b Then, use watercolor and paint primary colors and secondary colors in triangles. When your painting is dry, label the side length and find the length of the radius then label the radius length on your diagram. Part III-­‐ Tertiary Colors + 500 points Step 1 Use your ruler and protractor to create a regular dodecagon (polygon with 12 equal sides and 12 equal (n − 2)180 to find the degree of each angle in a regular angles). Use the side length of 1.5 inches. Use n polygon. The variable n represents the number of sides in the polygon. Step 2 Separate your regular dodecagon into 12 triangles (see image). ro r o rp Then, use watercolor paint and paint in primary colors, secondary oy colors, and tertiary colors in triangles. p When your painting is dry, label the side length and find the length of the radius then label the radius length on your diagram. y pb b bg g yg Part IV + 100 points Use your ruler to create two columns that are 2X 2 with 6 squares (similar to tonal, crosshatching, and linear). Create value from Black watercolor to white watercolor and the grays in between. In the second column, create black color from red, blue, and yellow, and use this black to create grays in between white and black. Part V + 500 points B1 3 Create a regular octagon with a side length of 2 inches. Draw all the diagonals in your octagon. A diagonal is a line segment connecting non-­‐adjacent vertices of a polygon. There are 20 diagonals in an octagon. Y Z D1 V C1 Use complementary colors (opposite colors on the color wheel) to create a color scheme with the shapes your diagonals create in your octagon. W X A1 Part VI + 500 points Create a regular decagon (10 sided polygon) with a side length of 2 inches. Draw all the diagonals in your decagon. A diagonal is a line segment connecting non-­‐adjacent vertices of a polygon. There are 35 diagonals in a decagon. Use analogous colors (3 colors next to each other on the color wheel) to create a color scheme with the shapes your diagonals create in your decagon. R=red B=blue G=green Y=yellow O=orange P = purple