Liver Enzyme Lab
advertisement

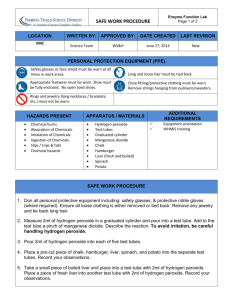
Name: _______________________ Block: ______ Liver Enzyme Lab Identify the Problem: What is produced when liver enzymes come in contact with hydrogen peroxide? Background Information: • Hydrogen Peroxide: A colorless, odorless liquid that is created during reactions in the cells of the human body. It must be broken down to prevent damage to cell tissue. Hydrogen peroxide will kill cells if it isn’t broken down. • Enzyme: A chemical that speed up reactions. Enzymes are not used up during the reaction, and can be used over and over again. Example: an enzyme in the body called catalase is responsible for breaking down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. Catalase is found in many cells in the body, including the liver. Catalase separates hydrogen peroxide into two substances: water and oxygen. • Oxygen: A colorless, odorless gas. It is an oxidizer, which means that it supports combustion or “feeds the fire”. Materials: Goggles, small beaker, beef/ chicken liver, 20 ml of 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, (2) test tubes, candle, splint, matches, green tray Procedure: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Spread your materials out on the table. Place the small beaker inside the green tray. Place about 10 grams of liver into a test tube. Place the test tube in the beaker. Take a second test tube, but place no liver in the test tube. With goggles on, measure 20 ml of hydrogen peroxide and pour it into each test tube. Carefully use a match to light the candle. Leave the candle lit. Hold a splint over the candle flame until the splint lights. Blow out the splint and place it near the bubbles inside the test tube with the liver. Repeat this for the test tube with no liver. Record observations in the space below. Data/Observations: 1. What do you see when the liver comes into contact with the H2O 2? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 2. What happens when you place the splint near the bubbles in the test tube? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 3. What happens when you place the splint into the test tube with no liver? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 4. What did the data from the oxygen probe show? Give specific numbers ( in percent) in your answer. _________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Conclusions: 1. Below is the chemical equation for this reaction: ( challenge: balance the equation) H2O 2 H2O + O2 2. Looking at the formula, what two products are formed from the breakdown of H2O 2? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 3. Looking at your background info, what gas do you think is contained in the bubbles that are formed? Give evidence from your observations. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 4. Why or how is catalase (the enzyme) important in this reaction? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 5. Was this an example of a physical change or a chemical change? (Use your observations, and your notes on chemical and physical changes to support your answer). ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________