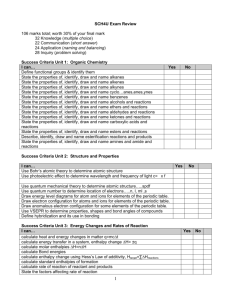
1. Calculate the equilibrium pH and pOH of the following solutions a
advertisement

1. Calculate the equilibrium pH and pOH of the following solutions
a. 0.100 M HCl
pre equilibrium !
0.100
0
equilibrium !
0
HCl """
! H +
0
0.100
100%
+
pH = - log [H + ] = - log (0.100) = - (-1.00)
pH + pOH = 14.00 or pOH = 14.00 - pH
or
K w = [H + ][OH - ] ;
[OH - ] =
Cl0.100
& pH = 1.00
& pOH = 13.00
1.00 X 10 -14 = [0.100][OH - ]
1.00 X 10 -14
, [OH - ] = 1.00 X 10 -13
[0.100]
& pOH = 13.00
b. 2.50 M H2SO4 (assume 100% dissociation)
pre equilibrium !
equilibrium !
2.50
0
H 2SO 4 "100%
""
! 2 H+ +
0
2 (2.50)
pH = - log [H + ] = - log (5.00) = - (0.699)
pH + pOH = 14.00 or pOH = 14.00 - pH
or
K w = [H + ][OH - ] ;
[OH - ] =
0
SO-24
2.50
& pH = - 0.699
& pOH = 14.699
1.00 X 10 -14 = [5.00][OH - ]
1.00 X 10 -14
, [OH - ] = 2.00 X 10 -15
[5.00]
& pOH = 14.70
c. 5.25 M Ca(OH)2 ((assume 100% dissociation)
pre equilibrium !
5.25
0
0
Ca(OH)2 "100%
""
! Ca +2 +
equilibrium !
0
5.25
pOH = - log [OH - ] = - log (10.5) = - (1.021)
pH + pOH = 14.00 or pH = 14.00 - pOH
2 OH 2 (5.25)
& pOH = - 1.021
& pH = 15.021
or
K w = [H + ][OH - ] ;
1.00 X 10 -14 = [H + ][10.5]
1.00 X 10 -14
[H ] =
, [H + ] = 9.52 X 10 -16
[10.5]
+
& pH = 15.021
d. 4.25 X10-3 M NaOH
pre equilibrium !
4.25 X 10 -3
0
0
NaOH "100%
""
! Na +
equilibrium !
4.25 X 10 -3
0
OH -
+
4.25 X 10 -3
pOH = - log [OH - ] = - log (4.25 X 10 -3 ) = - (-2.372)
& pOH = 2.372
pH + pOH = 14.00 or pH = 14.00 - pOH
& pH = 11.628
or
K w = [H + ][OH - ] ;
[H + ] =
1.00 X 10 -14 = [H + ][4.25 X 10 -3 ]
1.00 X 10 -14
, [H + ] = 2.35 X 10 -12
[4.25 X 10 -3 ]
& pH = 11.628
2. Calculate the pre-equilibrium concentration the acid or base:
a. A solution of HCl with an equilibrium pH of 2.156
pre equilibrium !
X
0
0
HCl "100%
""
! H+ +
0
X
equilibrium !
pH = - log [H + ] = 2.156
ClX
or log [H + ] = - 2.156 & [H + ] = 10 -2.156 = 6.98 X 10 -3
Since the [H + ] is X and X is the initial (pre-equilibrium) concnetration of HCl
The original concentration of HCl is 6.98 X 10 -3 M
b. A solution of NaOH with an equilibrium pH of 10.853
pre equilibrium !
0
NaOH "100%
""
! Na +
0
X
equilibrium !
pH = 10.853
X
0
+
OH X
but since pH + pOH = 14.00 then pOH = 3.147
pOH = - log [OH - ]
or log [OH - ] = - pOH [OH - ] = 10 -3.147 = 7.13 X 10 -4
& The initial concentration of NaOH = 7.13 X 10 -4 M
3. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of H+, OAc-, OH- and HOAc for a solution that has
an initial HOAc concentration of 2.50 M [Ka (HOAc) = 1.80 X 10-5]
pre equilibrium !
2.50
0
HOAc Ä
2.50 - x
equilibrium !
H
x
+
0
+ OAcx
[H + ][OAc- ]
[x][x]
x2
-5
Ka =
" 1.80 X 10 =
=
[HOAc]
[2.50 - x] (2.50)
x2
1.80 X 10 =
" x 2 = 4.50 X 10 -5
x = 6.71 X 10 -3
(2.50)
Checking the assumption: (2.50 - x) = 2.50 - 0.007
2.49 # 2.50 (1/250 = 0.4 %)
-5
[H + ] = x
[OH - ] = K w /x
[OAc- ] = x
& [HOAc] = 2.50 - x
[H + ] = 6.71 X 10 -3 M
[OAc- ] = 6.71 X 10 -3 M
[OH - ] = (1.00 X 10 -14 )/(6.71 X 10 -3 ) = 1.49 X 10 -12 M
& [HOAc] = 2.50 - 6.71 X 10 -3 = 2.49 M
4. What pre-equilibrium concentration of HOAc is necessary for the solution to have an
equilibrium pH of 2.755?
pre equilibrium !
HOAc Ä
x-y
equilibrium !
Ka =
x
0
H
y
0
+
+ OAcy
[H + ][OAc- ]
[y][y]
y2
" 1.80 X 10 -5 =
=
[HOAc]
[x - y] (x-y)
However, it is mentioned in the problem that the equilibrium pH is 2.755
since pH = - log[H + ] the log[H + ] = -2.755 & [H + ] = 1.76 X 10 -3 and
for the reaction, that means y = 1.76 X 10 -3 and
1.80 X 10 -5 =
y2
(1.76 X 10 -3 )2
3.09 X 10 -6
=
=
(x-y) (x - 1.76 X 10 -3 ) (x - 1.76 X 10 -3 )
3.09 X 10 -6
(x - 1.76 X 10 ) =
" (x - 1.76 X 10 -3 ) = 0.1717 " x = 0.1717 + 1.76 X 10 -3
-5
1.80 X 10
-3
x = the original (pre-equilibrium) concentration of HOAc = 0.173 M
5. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of H+, NH4+, OH- and NH3 for a solution that has
an initial NH3 concentration of 0.450 M [Kb (NH3) = 1.78 X 10-5]
pre equilibrium !
0.450
0
NH 3 + H 2O Ä
equilibrium !
0.450 - x
NH
0
+
4
x
+ OH x
[NH +4 ][OH - ]
[x][x]
x2
-5
Kb =
" 1.78 X 10 =
=
[NH 3 ]
[0.450 - x] (0.450)
x2
1.78 X 10 =
" x 2 = 8.01 X 10 -6
x = 2.83 X 10 -3
(0.450)
Checking the assumption: (0.450 - x) = 0.450 - 0.003
0.447 # 0.450 (3/450 = 0.6 %)
-5
[H + ] = K w /x
[NH +4 ] = x
[OH - ] = x
& [NH 3 ] = 0.450 - x
[[H + ] = K w /(2.83 X 10 -3 ) = (1.00 X 10 -14 )/(2.83 X 10 -3 ) = 3.53 X 10 -12 M
[NH +4 ] = 2.83 X 10 -3 M
[OH - ] = 2.83 X 10 -3 M
& [NH 3 ] = 0.450 - 2.83 X 10 -3 = 0.447 M
6. A solution has pre equilibrium concentrations of HCl = 1.50 M and HOAc = 2.50 M.
Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of HCl, HOAc, Cl- and OAc-. Also calculate the
equilibrium pH.
0.150
0
0
HCl !100%
!!
" H + + Cl0
0.150
0.150
0.250
0.150
HOAc Ä
0.250 - x
Ka =
0
+
H
+ OAc0.150 + x
x
[H + ][OAc- ]
[0.150 + x][x]
# 1.80 X 10 -5 =
If (0.250 - x) can be considered 0.250, is it not
[HOAc]
[0.250 - x]
logical that (0.150 + x) can be considered 0.150
1.80 X 10 -5 =
[0.150 ][x]
[0.250]
& x=
(1.80 X 10 -5 )(0.250)
(0.150)
or x = 3.00 X 10 -5 (check the assumptions and you can see they were acceptable)
[HCl] = 0
[HOAc] = 0.250 - x = 0.250 M
[Cl] = 0.150 M
[OAc- ] = x = 3.00 X 10 -5 M
[H + ] = 0.150
[OH - ] = K w /(0.150)
pH = 0.824
[OH - ] = (1.00 X 10 -14 )/(0.150) = 6.66 X 10 -14 M
pOH = 13.176
(note: pH + pOH = 14.000)
{I know [OH - ] and pOH were not asked for, but .....}
7. A solution has an initial concentration of NaOAc = 0.500 M and an initial concentration of
HOAc of 1.50 M. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of H+, OH-, Na+, OAc- and
HOAc.
0.500
0
0
NAOAc !100%
!!
" Na + +
0
0.500
1.50
HOAc
1.50 - x
0
Ä
H
x
OAc0.500
0.500
+
+ OAc0.500 + x
[H + ][OAc- ]
[x][0.500 + x]
[x][0.500]
Ka =
# 1.80 X 10 -5 =
=
[HOAc]
[1.50 - x]
[1.50]
1.80 X 10
-5
[x][0.500]
=
[1.50]
(1.80 X 10 -5 )(1.50)
& x=
(0.500)
or x = 5.40 X 10 -5
[H + ] = 5.40 X 10 -5
[OH - ] = K w /(0.150)
pH = 4.268
[OH - ] = (1.00 X 10 -14 )/(5.40 X 10 -5 ) = 1.85 X 10 -10 M
pOH = 9.732
[Na + ] = 0.500 M
[OAc- ] = 0.500 + x = 0.500 M
[HOAc] = 1.50 - x = 1.50 M
8. How many grams of NH3 must be dissolved to make 250.0 mL of a solution that has an
equilibrium pH of 12.250?
x
0
0
NH 3 + H 2O Ä
x-y
NH +4 + OH y
y
[NH +4 ][OH - ]
[y][y]
y2
! 1.78 X 10 -5 =
=
[NH 3 ]
[x - y] (x - y)
Kb =
{When faced with two unknowns (x & y) you can either give up or reread the question
to see what other information has been given}
Here your were given pH = 12.250 this means pOH = 14.000 - pH = 14.000 - 12.250
pOH = 1.750 & [OH - ] = 1.77 X 10 -2 M
1.78 X 10 -5 =
y2
(1.77 X 10 -2 )2
(3.14 X 10 -4 )
=
=
(x - y)
(x - 1.77 X 10 -2 )
(x - 1.77 X 10 -2 )
(x - 1.77 X 10 -2 ) =
and
3.14 X 10 -4
= 17.6
1.78 X 10 -5
or x = 17.6 + 1.77 X 10 -2
x = 17.6 M
17.6 moles/Liter X 0.2500 Liters = 4.04 moles & 4.04 moles X 17.03 g/mole
gives 75.0 grams of NH 3
BTW this is about the same concentration has "household ammonia"
9. Ferric hydroxide {Fe(OH)3} is a strong base. Determine the pH of a 2.45 X 10-3 M solution
of Fe(OH)3.
2.45 X 10 -3
0
0
Fe(OH)3 !100%
!!
" Fe +3
0
x
(2.45 X 10 -3 )
+
3 OH 3x
3 (2.45 X 10 -3 )
[OH - ] = 7.35 X 10 -3 pOH = - log [OH - ] = - log (7.35 X 10 -3 )
pOH = 2.134
pH = 14.000 - pOH &
pH = 11.66
10. A solution is prepared that contains the following materials:
NaCl 0.150 M
NaOAc 0.250 M
HOAc 0.200 M (Ka = 1.80 X 10-5)
Determine the equilibrium concentrations of Na+, Cl-, H+, OH-, HOAc and OAc-.
0.150
0
0
0.250
NaCl !100%
!!
" Na + + Cl0
0.150
0.200
HOAc Ä
0.200 - x
Ka =
0
0
Na + +
OAc-
(0.150 + 0.250)
0.250
0.250
+
H + OAcx
0.250 + x
[H + ][OAc- ]
[HOAc]
# 1.80 X 10 -5 =
0.250 x
0.200
1.80 X 10 -5 =
x = 1.44 X 10
NaOAc !100%
!!
"
0.150
0
0.150
-5
[Na + ] = 0.400,
#
(x)(0.250 + x)
(0.200 - x)
(1.80 X 10 -5 )(0.200)
= x
0.250
+
= [H ]
Kw
1.000 X 10 -14
K w = [H ][OH ] # [OH ] = + =
[H ]
1.44 X 10 -5
[Cl- ] = 0.150,
[OH - ] = 6.94 X 10 -10 ,
+
-
-
[H + ] = 1.44 X 10 -5 ,
[HOAc] = 0.200,
[OAc- ] = 0.250
11. The following solutions are mixed together.
150.0 mL of 0.600 M NaOH (Kb = ∞)
300.0 mL of 2.400 M NH3 (Kb = 1.78 X 10-5)
150.0 mL of 2.600 M NH4Cl
Since these are all mixed together, the concentrations must be adjusted to account for the dilution
V2 = 600.0 mL (the total volume)
NaOH: C1V1 = C2V2 ! (0.600)(150.0) = C2 (600.0) ! C2 = 0.150 M
NH 3 : C1V1 = C2V2 ! (2.400)(300.0) = C2 (600.0) ! C2 = 1.200 M
NH 4 Cl: C1V1 = C2V2 ! (2.600)(150.0) = C2 (600.0) ! C2 = 0.650 M
0.150
0
0
0.650
NaOH "100%
""
# Na + + OH 0
0.150
NH 4 Cl "100%
""
#
0.150
1.200
0
Ä
NH
+
4
""
#
x
(0.800 + x)
Kb =
[NH +4 ][OH - ]
[NH 3 ]
x =
(1.78 X 10 -5 )(1.350)
= 3.00 X 10 -5 = [OH - ]
0.800
! 1.78 X 10 -5 =
[H + ] = 3.33 X 10 -10 ,
[Cl- ] = 0.650,
0.650
(0.800+x)(x) (0.800)(x)
=
(1.350 + x)
(1.350)
[OH - ] = 3.00 X 10 -5 ,
[NH 3 ] = 1.350,
pH = 9.478
Cl-
OH -
+
0
(1.350 - x)
0
0.150
100%
(1.200 + 0.150) $""
" (0.650 - 0.150)
x
NH +4 +
0.650
0.650
NH 3 + H 2O
0
[Na + ] = 0.150 ,
[NH 4 Cl] = 0,
&
pOH = 4.522
[NH +4 ] = 0.800,
[NaOH] = 0.
12. A solution is prepared that has the following initial concentrations:
NH3 (Kb = 1.78 X 10-5) = 0.500 M
NaOH (Kb = ∞) = 0.250 M
HCl (Ka = ∞) = 0.150 M
Determine the equilibrium concentrations of H+, OH-, Na+, NH4+, Cl-, NH3, NH4Cl, & NaOH. Also
calculate the equilibrium pH.
0.250
0
0
0.150
NaOH !100%
!!
" Na + + OH 0
0.250
0.250
0.150
0
0
HCl !100%
!!
" H+ +
0
0.150
Cl0.150
0.250
H+ +
0
OH - !100%
!!
" H 2O
0.150
0.500
0
NH 3 + H 2O Ä
NH
(0.500 - x)
x
0.150
+
4
+ OH 0.150 +x
Kb =
[NH +4 ][OH - ]
[NH 3 ]
x =
(1.78 X 10 -5 )(.500)
= 5.93 X 10 -5 = [NH +4 ]
0.150
# 1.78 X 10 -5 =
[H + ] = 6.67 X 10 -14 ,
[Cl- ] = 0.150,
[OH - ] = 0.150 ,
[NH 3 ] = 0.500,
pH = 13.176
(x)(0.150 + x) (x)(0.150)
=
(0.500 - x)
(0.500)
[Na + ] = 0.250 ,
[NH +4 ] = 5.93 X 10 -5 ,
[NH 4 Cl] = 0,
pOH = 0.824
13. The following solutions are mixed together. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of
NH3, NH4+, and the equilibrium pH
125.0 mL of 1.920 M NH3 (Kb = 1.78 X 10-5)
100.0 mL of 1.200 M NaOH (Kb = ∞)
75.00 mL of water
Determine the equilibrium concentrations of H+, OH-, Na+, NH4+, Cl-, NH3, & NH4Cl. Also
calculate the equilibrium pH.
Since these solutions (including the water) are all mixed together, the concentrations
must be adjusted to account for the dilution & V2 = 300.0 mL (the total volume)
NH 3 : C1V1 = C2V2 ! (1.920)(125.0) = C2 (300.0) ! C2 = 0.8000 M
NaOH: C1V1 = C2V2 ! (1.200)(100.0) = C2 (300.0) ! C2 = 0.4000 M
0.4000
0
0
NaOH "100%
""
# Na + + OH 0
0.4000
0.4000
0.8000
0
NH 3 + H 2O
(0.8000 - x)
Ä
[NH +4 ][OH - ]
Kb =
[NH 3 ]
x =
0.4000
NH +4 + OH x
0.4000 + x
! 1.78 X 10 -5 =
(x)(0.4000+x) (x)(0.4000)
=
(0.8000 - x)
(0.8000)
(1.78 X 10 -5 )(0.8000)
= 3.56 X 10 -5 = [NH +4 ]
0.4000
[H + ] = 2.500 X 10 -10 , pH = 13.6021,
+
4
-5
[NH ] = 3.56 X 10 ,
[OH - ] = 0.4000 ,
[NH 3 ] = 0.8000,
pOH = 0.3979,