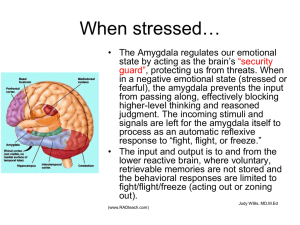
Outline The Yerkes-Dodson Law One
advertisement
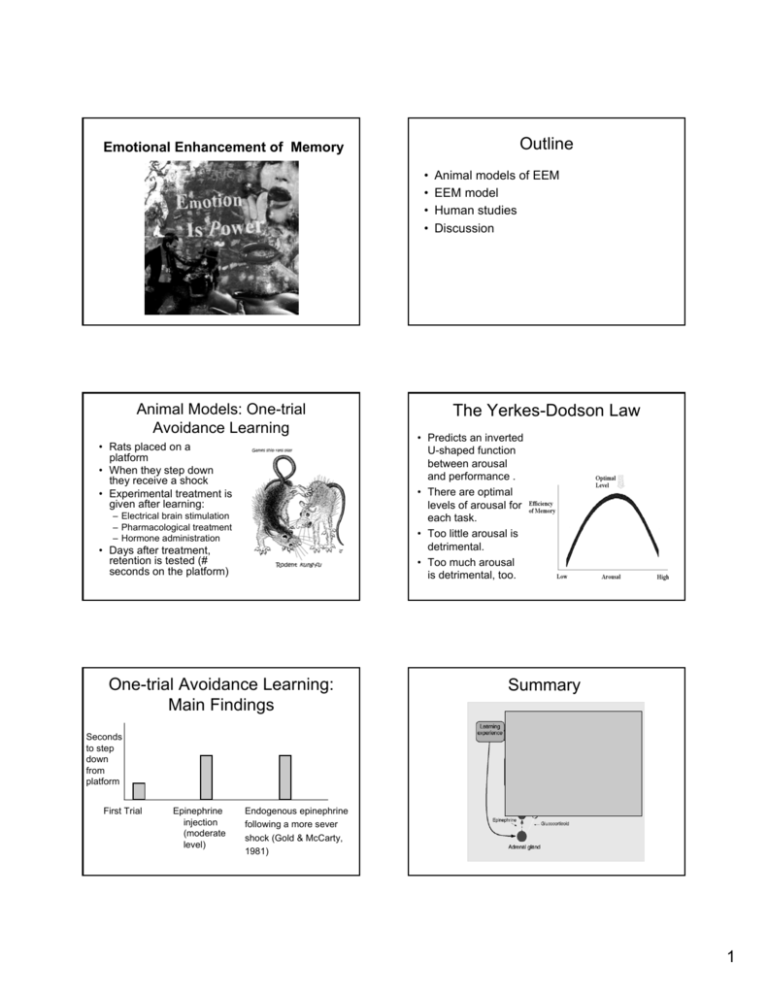
Outline Emotional Enhancement of Memory • • • • Animal Models: One-trial Avoidance Learning • Rats placed on a platform • When they step down they receive a shock • Experimental treatment is given after learning: – Electrical brain stimulation – Pharmacological treatment – Hormone administration • Days after treatment, retention is tested (# seconds on the platform) One-trial Avoidance Learning: Main Findings Animal models of EEM EEM model Human studies Discussion The Yerkes-Dodson Law • Predicts an inverted U-shaped function between arousal and performance . • There are optimal levels of arousal for each task. • Too little arousal is detrimental. • Too much arousal is detrimental, too. Summary Seconds to step down from platform First Trial Epinephrine injection (moderate level) Endogenous epinephrine following a more sever shock (Gold & McCarty, 1981) 1 Summary One-trial Avoidance Learning: Post-encoding treatment Seconds to step down from platform First Trial Hippocampal damage Amygdala damage 5 seconds 5 days 5 seconds 5 days Summary One-trial Avoidance Learning: Post-encoding treatment Seconds to step down from platform First Trial Peripheral b-blockers 5 seconds 5 days Vagal nerve damage 5 seconds 5 days Epinephrine doesn’t cross the blood-brain barrier Mcgaugh 2000 Adrenal Demedullation Studying Emotion & Memory • Animal models • Field studies – Eye-witness – “Red outs” – Childhood abuse • Laboratory studies Passive Avoidance E: Epinephrine injection; Active Avoidance – Simulations – Experimental manipulations • Patient studies Sal: Saline injection 2 Encoding Emotions Hamman 1999 Encoding Emotions Hamman 2002 PET study shows increased amygdala activation for positive, negative, or interesting pictures relative to neutral pictures. Subliminal Registration Retrieving emotions • Backward masking by neutral faces. • 8/10 participants reported not seeing the emotional faces. Whalen 1998 The Subsequent Memory Effect The Story Paradigm: Section 1 (Neutral) • PET study: Cahill et al. (1996) presented neutral and emotional films to participants in the PET • Imaging studies show correlation of amygdala activation with subsequent memory after delayed testing 3 The Story Paradigm: Section 2 (Critical) The Story Paradigm: Section 3 (Neutral) Effects of Amygdala Damage I Effects of Amygdala Damage II • Participants exposed to the emotional version of the story. • Contradictory results • Patient DR had damage resulting from operations to control epilepsy • Potentially related to location of damage in the amygdala • DR has abnormal perception of fear – dissociation of perceptual and mnemonic consequences of amygdala damage • Patient BP has Urbach-Wiethe disease • Memory measured following 1-week delay. (Cahill et al., 1995) Controls Patient Effect of Beta-Blockers Effect of Beta-Blockers Arousing, Placebo • Participants received beta-blocker treatment 1 hour prior to encoding. • Treatment did not affect emotional experience. Neutral, Placebo Neutral Neutral Arousing Arousing Placebo Beta-B Placebo Beta-B Arousing, BetaBlockes Neutral, BetaBlockes Results: Betablockers eliminate enhancement of memory for an emotional portion of a story (Cahill et al., 1994) 4 Post-encoding induction of arousal • Clark et al. (1999) • Stimuli: Neutral words • Post-training vagal stimulation (3 levels) • Recognition memory test Normalized word recognition score after 3 levels of vagal nerve stimulation Amygdala Effects on Multiple Memory Systems Spatial task Cued task The Modulation Hypothesis • Animal & human evidence • Correspondence between animal and human evidence • “Converging evidence” from lesion, pharmacological, and behavioral studies • New directions – effects on nondeclarative memory Problems with the Modulation Hypothesis • EEM in immediate testing Hippocampus Amygdala Caudate Packard, Cahill & Mcgaugh 1994 Short/Long-Term Consolidation Problems with the Modulation Hypothesis • EEM in immediate testing • Memory enhancement specific to emotional items? • Cognitive mediation mechanisms • Serial vs. parallel short and long-term Izquierdo 1998 consolidation • Each can be disrupted independently of the other • McGaugh’s model currently addresses LTM only 5 Amygdala and Experience • “emotion center in the brain” • Production in bilateral amygdala lesioned patients • Phenomenology in bilateral amygdala lesioned patients • Amygdala activation for subliminal material Patient Boswell • 63-year old man • Extensive bilateral lesions in the MTL (including hippocampus, PHG and the amygdala) and the temporal cortex • No perceptual, language, or motor impairment • Severely amnesic for 15 years • Cannot identify or report as familiar the faces of people (e.g. caregivers) he met since the onset of his amnesia – either explicitly or implicitly (SCR) Patient Boswell’s Affective Memory Good guy-Bad guy experiment: – no explicit knowledge (free/cued recall), – but chose the “good guy” as the person he would go to for a treat Good guy-Bad guy followup after 4 years: – No explicit knowledge – Clearly chose the “real-life” good guys more than others – Generated SCR to good guy’s face 6