Chapter 5 Study Guide and Practice
advertisement
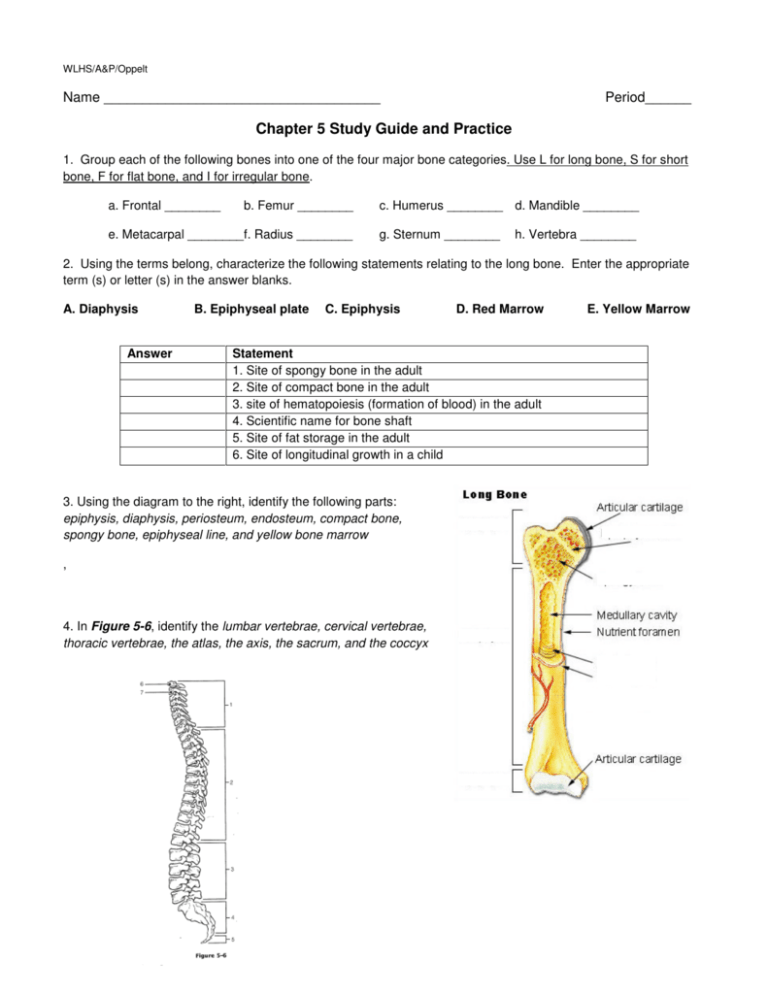
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name ____________________________________ Period______ Chapter 5 Study Guide and Practice 1. Group each of the following bones into one of the four major bone categories. Use L for long bone, S for short bone, F for flat bone, and I for irregular bone. a. Frontal ________ b. Femur ________ e. Metacarpal ________f. Radius ________ c. Humerus ________ d. Mandible ________ g. Sternum ________ h. Vertebra ________ 2. Using the terms belong, characterize the following statements relating to the long bone. Enter the appropriate term (s) or letter (s) in the answer blanks. A. Diaphysis Answer B. Epiphyseal plate C. Epiphysis D. Red Marrow Statement 1. Site of spongy bone in the adult 2. Site of compact bone in the adult 3. site of hematopoiesis (formation of blood) in the adult 4. Scientific name for bone shaft 5. Site of fat storage in the adult 6. Site of longitudinal growth in a child 3. Using the diagram to the right, identify the following parts: epiphysis, diaphysis, periosteum, endosteum, compact bone, spongy bone, epiphyseal line, and yellow bone marrow , 4. In Figure 5-6, identify the lumbar vertebrae, cervical vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae, the atlas, the axis, the sacrum, and the coccyx E. Yellow Marrow 5. In Figure 5-3, identify the following bones or sutures (NOTE: Ingore the lines pointing to the skull): Frontal Bone, Parietal Bone, Zygomatic Bone, Occipital Bone, Maxilla, Mandible, Coronal Suture, and Sagittal Suture 6. The following statements provide distinguishing characteristics of the vertebrae composing the vertebral column. Match the key terms with the statements below. A. Atlas B. Axis C. Cervical Vertebra E. Lumbar Vertebra F. Sacrum G. Thoracic Vertebra Answer D. Coccyx Description 1.Type of vertebra(e) containing foramina in the transverse processes, through which the vertebral arteries ascend to reach the brain 2. Its dens provides a pivot for rotation of the first cervical vertebra 3. Transverse processes have facets for articulation with rib, spinous process points sharply downward 4. Composite bone; articulates with the hip bone laterally 5. Massive vertebrae; weight sustaining 6. Tailbone; vestigial fused vertebra 7. Supports the head; allows the rocking motion of the occipital condyles 8. Seven components; unfused 9. Twelve components; unfused 7. Circle the term that DOES NOT belong in each of the following groupings. A. Tibia B. Skull C. Ischium D. Mandible E. Calcaneus Ulna Rib Cage Scapula Frontal Bone Tarsals Fibula Pelvis Ilium Temporal Bone Carpals Femur Vertebral Column Pubis Occipital Bone Talus 8. In Figure 5-11, identify the ilium, ishcium, sacrum, pubis, coccyx, and symphysis pubis 9. Describe the differences between a male and female cocae (hipbones). 10. Describe the following joint movements. Movement Description Flexion Extension Adduction Abduction Rotation Circumduction Pronation Supination Protraction Retraction Eversion Inversion 11. Describe the process of growth and development of a bone from fetus to adult. 12. Complete the following chart of joint types. Type of Joint Description Amount of movement allowed Where is this joint type found in the body? Fibrous joints Cartilaginous joints Synovial joints 13. Complete the following chart of synovial joint types. Synovial Joint Classification Description Example Ball-and-socket Condylar Plane Hinge Pivot Saddle 14.Terms to know Osteon Osteoblast Osteoclast Osteocyte Fontanel Articulation Bursae Lacunae Long Bone Short Bone Flat Bone Irregular Bone Epiphysis Diaphysis Compact Bone Spongy Bone Axial Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton False Rib True Rib Floating Rib Haversian Canal Osteoporosis Fracture 15.**Make sure to review ALL 4 lecture notes on bones, Reading Guide Chapter 5, and all colorings. 16. Identify as many bones as you can on the skeleton below.







