1 Early events in synapse formation
advertisement
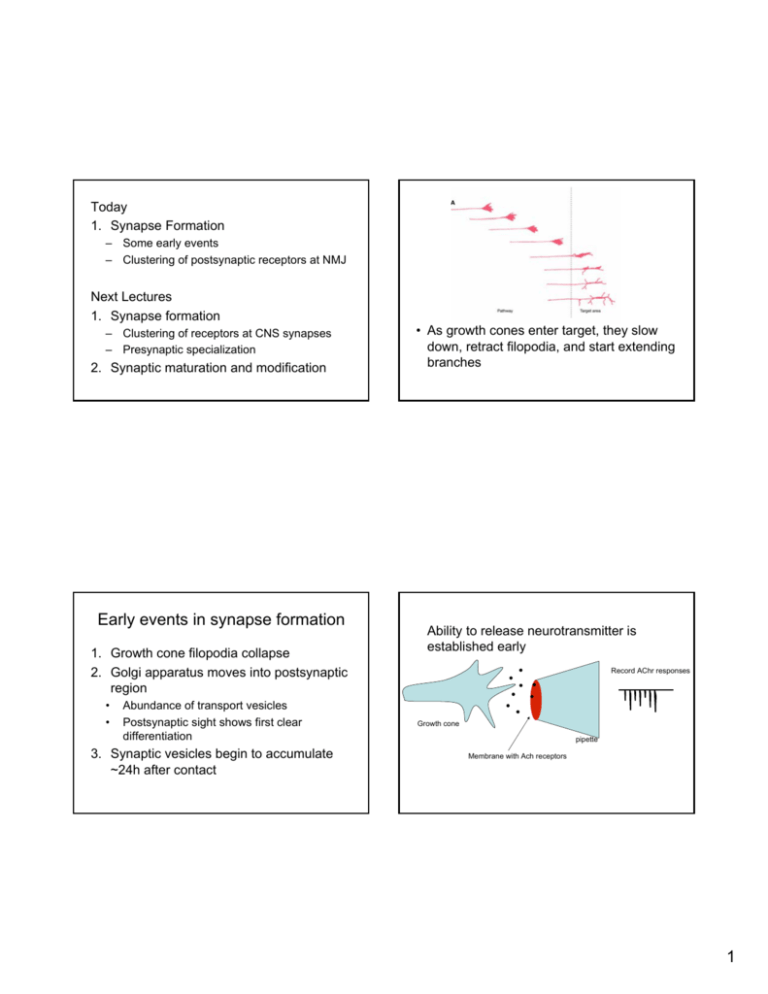
Today 1. Synapse Formation – Some early events – Clustering of postsynaptic receptors at NMJ Next Lectures 1. Synapse formation – Clustering of receptors at CNS synapses – Presynaptic specialization 2. Synaptic maturation and modification Early events in synapse formation 1. Growth cone filopodia collapse 2. Golgi apparatus moves into postsynaptic region • • Abundance of transport vesicles Postsynaptic sight shows first clear differentiation 3. Synaptic vesicles begin to accumulate ~24h after contact • As growth cones enter target, they slow down, retract filopodia, and start extending branches Ability to release neurotransmitter is established early Record AChr responses Growth cone pipette Membrane with Ach receptors 1 • Early events in synaptogenesis also use second messenger systems 1. Calcium 2. cAMP/Protein Kinase A 3. Protein Kinase C • Calcium is seen to rapidly increase in the growth cone when appropriate contact is made Growth cone filled with Ca-sensitive dye Experimentally ↑ Calcium or cAMP • – Can induce retraction of filopodia Appropriate contact inappropriate contact Synapse Formation 1. Postsynaptic receptor clustering • Initially muscles have even distribution of AchRs • In the mature synapse: – 10,000 AchRs / μm2 – Outside synapse 10 AchRs / μm2 1. neurotransmitters cause similar response over entire muscle 2. Visualized • With presynaptic contact receptors cluster 2 Apply Ach A A B B • Shift from uniform response → large and small muscle • Suggests receptors cluster with nerve contact A A B B Postsynaptic Potentials Postsynaptic Potentials There is a AchR prepattern prior to innervation • AchRs labelled with α-bungarotoxin (component of cobra snake venom label is radioactive or fluorescent) Failure to innervate diaphragm muscles prepattern Frog NMJ 3 Is Neurotransmitter Activation Required for Clustering? • The ability to induce clustering requires the correct neuron / target pair Spinal Cord Motor Neuron Plus bungarotoxin no difference Spinal Cord Motor Neuron Dorsal Root Ganglion Sensory Neuron No, neurotransmitter action is not required muscle Clustering involves both: • After innervation clustering involves: 1. Movement of receptors within membrane 2. Insertion of new receptors Movement of receptors: 1. Apply Ach to small patch and measure response 2. Apply bungarotoxin to same patch and measure response (smaller) 3. Wait 4. Apply Ach again (recovers) 4 Movement of receptors Insertion of new receptors Control Red fluorescent label apply Bungtx Bungarotoxin AchR ~5 minutes green fluorescent label Y Y Y Y 1. Measure red and green light Y 1. Bungarotoxin is permanent inhibitor of Ach receptor 2. Since response recovers → suggests receptors can move into patch Antibody that recognizes AchR How do AchRs cluster • Agrin, a cluster inducing molecule 1. Applied agrin can induce clustering of receptor 2. Blockade of agrin function blocks clustering in the presence of neurons Without neurons • With neurons added green > red indicates new receptors – Multiple agrin isoforms from neurons and muscle – Neural agrin specifically required for clustering 5 How does agrin induce clustering? Background observations: • Agrin induces phosphorylation of AchR β subunit • Inhibition of tyrosine kinase activity inhibits clustering Block agrin function X P P P P How does agrin signal? Add agrin Add agrin P P • Aside… – Receptor tyrosine kinase • Receptor that has intrinsic signaling abilities • agrin binds to a lot of candidate molecules – ie. can directly phosphorylate targets • Unlike G-protein coupled receptors that activate kinases indirectly – Including CAMs, ECM • Identification of MuSK Receptor Tyrosine Kinase G-protein couple receptor – Muscle Specific Kinase – Transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase target target-P target target-P 6 Evidence MuSK involved in agrindependent clustering • MuSK knockout mice have no postsynaptic differentiation – Neither do agrin KO mice • Inactive MuSK blocks agrin signalling • MuSK KO muscles unresponsive to agrin • Does agrin bind MuSK directly? – Agrin can activate MuSK in muscle – but not when MuSK is expressed in nonmuscle cell – Suggests an additional muscle derived factor is required Agrin binds MuSK – So far unidentified, called Masc What links MuSK to AchR? • Rapsyn, a AchR binding protein essential for clustering • Rap and AchR will co-cluster in non-neural cells – Means rap has ability to cluster indepently • In rapsyn mouse KO, – agrin can activate MuSK but AchR don’t cluster. – Suggests Rapsyn is required to link agrin activation of MuSK to AchR receptor clusters • No AchR clusters in rapsyn KO mice 7 Neural agrin secreted Masc clustering MuSK P AchR rapsyn 8