Conceptual Physics Practice Final Exam, Semester 1
advertisement

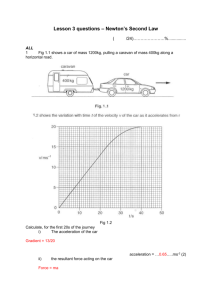
Conceptual Physics Practice Final Exam, Semester 1 Tips for Successful Test-­‐Taking: 1. Take a few deep breaths and relax. The calmer you feel, the more you will remember. 2. Before beginning a problem, identify the topic (forces, kinematics, momentum, energy, or skills). That way you know what study guide to look at if you get stuck. 3. For numerical problems, list the information you’ve been given and what you need to find. If you get stuck, refer to the tips listed on the study guide. 4. If you get really stuck, refer to #1. Then skip the problem and come back to it later. 5. Before you turn in your exam, be sure to go back and finish any questions you’ve skipped. It’s also a good idea to check your answers – you can catch careless mistakes this way. 1. What is the direction of the net force on the following car? a. b. c. d. Left Right There is no net force It is impossible to know 2. A 4.0-­‐kg cat is running along a fence 2.0 meters above the ground. The cat has 130 joules of total mechanical energy. The speed of the cat is closest to a. 2.0 m/s b. 5.0 m/s c. 8.0 m/s d. 12 m/s For questions 3-­‐5: Thor, God of Thunder jumps into flight. He is initially at rest and accelerates at 1000 m/s2 until he reaches a speed of 5000 m/s. How long does it take him to reach 5000 m/s? 3. What is the problem asking you to find? a. Initial velocity b. Final velocity c. Time d. Distance e. Acceleration 4. What formula should you use to solve the problem? a. 𝑑 = 𝑣! 𝑡 + !! 𝑎𝑡 ! ! ! ! b. 𝑑 = ! ! ! 𝑡 c. 𝑣! = 𝑣! + 𝑎𝑡 d. 𝑣!! = 𝑣!! + 2𝑎𝑑 5. What is the correct answer? e. 10 s f. 5 s g. 0.25 s h. 1 s For questions 6-­‐7: 6. During which interval(s) does the object have the greatest average speed? a. 1-­‐3 seconds b. 3-­‐7 seconds c. 7-­‐9 seconds d. 9-­‐12 seconds 7. What is the average speed during the interval between 3 and 7 seconds? a. 0 m/s b. 5 m/s c. 2.5 m/s d. 10 m/s 8. A 2-­‐kg seagull flies at a velocity of 3 m/s. What is its momentum? a. 1 kgm/s b. 1.5 kgm/s c. 5 kgm/s d. 6 kgm/s 9. You are standing on a skateboard at rest. Choose the best statement about what happens when you jump off to the left. a. The skateboard moves to the left because its momentum and your momentum must be in the same direction. b. The skateboard moves to the left, but at a slower velocity than you jump. c. The skateboard moves to the right, but a little bit of momentum is lost to friction. d. The skateboard moves to the right, but slowly because of its mass. For questions 10-­‐11: A boy on a sled slides on a smooth track without friction. The combined mass of the boy and the sled is 50.0 kg. 10. What is the total mechanical energy of the boy-­‐sled system at point E? a. 5,000 J b. 8,000 J c. 9,000 J d. 11,000 J 11. What is the speed of the boy-­‐sled system at point D? a. 4 m/s b. 9 m/s c. 14 m/s d. 19 m/s For questions 12-­‐14 A 70 kg skater is at rest on the ice when someone tosses her a 10 kg medicine ball at a velocity of 4 m/s. 12. What happens when the skater catches the ball? a. She does not move because he is much larger than the ball. b. She moves forwards so he doesn’t fall. c. She moves backwards at a velocity greater than 4 m/s. d. She moves backwards at a velocity less than 4 m/s. 13. What is the momentum of the medicine ball before the skater catches it? a. 10 kgm/s b. 40 kgm/s c. 70 kgm/s d. 80 kgm/s 14. What is the final velocity (vf) of the skater and the medicine ball? a. 0.5 m/s b. 1 m/s c. 4 m/s d. 8 m/s 15. An African elephant has a mass of 6000 kg. What is its weight? a. 6,000 kg b. 6,000 N c. 60,000 kg d. 60,000 N 16. Suppose that a sled is accelerating at a rate of 2 m/s2. If the net force is doubled and the mass is halved, what is the new acceleration? a. 8 m/s2 b. 4 m/s2 c. 2 m/s2 d. 1 m/s2 For questions 17-­‐19: A basketball player starts down the court with an initial velocity of 2 m/s. She accelerates at 1 m/s2 for 3 seconds. How fast is she going at the end of the 3 seconds? 17. What does the problem ask you to find? a. Initial velocity b. Final velocity c. Time d. Distance e. Acceleration 18. What formula should you use to solve the problem? a. 𝑑 = 𝑣! 𝑡 + !! 𝑎𝑡 ! ! ! ! b. 𝑑 = ! ! ! 𝑡 c. 𝑣! = 𝑣! + 𝑎𝑡 d. 𝑣!! = 𝑣!! + 2𝑎𝑑 19. What is the correct answer? a. 3 m/s b. 5 m/s2 c. 5 m/s d. 3 m/s2 For questions 20-­‐22 Refer back to questions 3-­‐5. How far does Thor travel during his acceleration? 20. What are you being asked to find? a. Initial velocity b. Final velocity c. Time d. Distance e. Acceleration 21. What formula should you use to solve the problem? a. 𝑑 = 𝑣! 𝑡 + !! 𝑎𝑡 ! ! ! ! b. 𝑑 = ! ! ! 𝑡 c. 𝑣! = 𝑣! + 𝑎𝑡 d. 𝑣!! = 𝑣!! + 2𝑎𝑑 22. What is the correct answer? e. 50,000 m f. 100,000 m g. 125,000 m h. 12,500 m 23. Which graph(s) represent an object at rest? 24. How many sig figs in: 100 a. One b. Two c. Three d. Four 25. How many sig figs in: 205 a. One b. Two c. Three d. Four 26. How many sig figs in the answer to: 2.01 x 3.5 a. One b. Two c. Three d. Four 27. Which object in the answer choices below has the greatest total mechanical energy? a. A 2,000-­‐kg elephant sitting next to a stream b. A 500-­‐kg car rolling at a speed of 1.0 m/s c. A 0.001-­‐kg penny on the ledge of a building 100 meters above the ground d. A 3.0-­‐kg seagull flying at a speed of 2.0 m/s while it is 4.0 meters above the ground For questions 28-­‐30: A 2000 kg car is moving to the right at a velocity of 10 m/s when it collides with an 8000 kg truck at rest. After the collision, both vehicles stick together. 28. What is the total initial momentum (pi) of both the car and the truck? a. 20,000 kgm/s b. 100,000 kgm/s c. 0 kgm/s d. 200 kgm/s 29. What is the final velocity (vf) of the two vehicles? a. 10 m/s b. 5 m/s c. 2 m/s d. 1 m/s 30. What is the momentum of the truck, after the collision? a. 8,000 kgm/s b. 16,000 kgm/s c. 40,000 kgm/s d. 0 kgm/s 31. If the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the object: a. Must not be moving b. Must be moving with a constant velocity c. Must not be accelerating d. None of these For questions 32-­‐34: You wake up on a mysterious planet and decide you want to find the acceleration from gravity there. You drop a small rock from 35 meters and measure the time it takes to fall as 5.0 seconds. What is the acceleration from gravity on the planet? 32. What is the problem asking you to find? a. Initial velocity b. Final velocity c. Time d. Distance e. Acceleration 33. What formula should you use to solve the problem? a. 𝑑 = 𝑣! 𝑡 + !! 𝑎𝑡 ! ! ! ! b. 𝑑 = ! ! ! 𝑡 c. 𝑣! = 𝑣! + 𝑎𝑡 d. 𝑣!! = 𝑣!! + 2𝑎𝑑 34. What is the correct answer? a. 2.8 m/s2 b. 5.6 m/s2 c. 14 m/s2 d. 0.7 m/s2 35. If you push on a wall with 100 N of force, how much force does the wall exert on you? a. 50 N b. 100 N c. 150 N d. 200 N time time position time time 37. Which one of the following graphs describes an object that is moving at a constant speed to the right (+ direction)? time Graph C time Graph D position Graph B position Graph A position position position position position 36. Which one of the following graphs describes an object that is moving from slow to fast? Graph A Graph B Graph C Graph D time time For questions 38-­‐41: In a study measuring the influence of different quantities of fertilizer on plant growth, 38. The independent variable would be ___________ a. Amount of fertilizer b. Plant height growth c. Type of Plant d. Amount of sunlight 39. The dependent variable would be the ______________. a. Amount of fertilizer b. Plant height growth c. Type of plant d. Amount of sunlight 40. Examples of controlled variables would be ___________________________ a. Amount of fertilizer b. height growth c. Type of Plant d. Amount of sunlight 41. A good increment for plant growth would be ______________ a. centimeters b. meters c. kilometers d. nanometers For questions 42-­‐43: 1 inch = 2.54 centimeters (cm) one day = 24 hours 39.4 inches = 1 meter one mile = 5280 feet 12 inches = 1 ft 1 hour =3600 seconds (s) 42. Which of these conversion factors should be used to convert 20 miles/hour into meters/second? 5280 ft a. 1mile 1mile b. 5280 ft 1hr c. 3600s 3600s d. 1hr 43. Convert 20 miles/hour to meters/second. a. 18 m/s b. 20 m/s c. 9 m/s d. 60 m/s 44. Consider the plot shown below. Which description below is consistent with the graph? a. The object accelerates in the positive direction and then in the negative direction. b. The object moves upwards, reaches its peak and then falls with an acceleration. c. The object moves in the positive direction and then moves in the negative direction. 45. Consider the plot shown below. Which description below is consistent with the graph? a. The object moves slowly at a constant speed and then faster at a constant speed. b. The object accelerates in the positive direction and then accelerates more rapidly. c. The object moves forward, changes direction and then accelerates more rapidly.