KUWAIT - heritage.org
advertisement

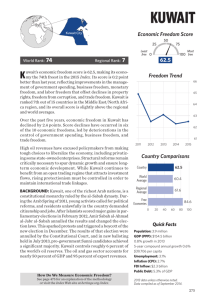
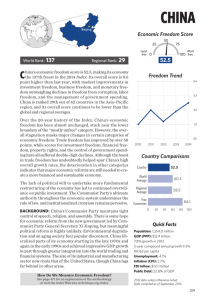
KUWAIT Economic Freedom Score 25 World Rank: 74 Regional Rank: 7 Least free 0 espite efforts to modernize and diversify Kuwait’s D economy, oil production remains dominant. The private sector is largely dependent on government spend- 50 75 Most 100 free 62.7 Freedom Trend 65 ing and expatriate labor, and the labor market is highly segmented. The public sector employs about 80 percent of the labor force; expatriates are employed mostly in the small private sector. ECONOMIC FREEDOM SNAPSHOT • 2016 Economic Freedom Score: 62.7 (up 0.2 point) • Economic Freedom Status: Moderately Free • Global Ranking: 74th • Regional Ranking: 7th in the Middle East/North Africa Region • Notable Successes: Trade Freedom and Monetary Freedom • Concerns: Rule of Law, Business Freedom, and Labor Freedom • Overall Score Change Since 2012: +0.2 Kuwait performs relatively well in promoting many aspects of economic freedom, but institutional deficiencies stemming from state bureaucracy and an entitlement culture still stifle economic dynamism. The judicial system remains vulnerable to political influence, lacks transparency, and cannot defend property rights effectively. BACKGROUND: Kuwait, the first Arab country in the Gulf to create an elected parliament, is a constitutional monarchy ruled by the al-Sabah dynasty. After Islamists scored major gains in parliamentary elections in February 2012, Amir Sabah al-Ahmad al-Jabr al-Sabah annulled the results and changed the election laws. This sparked protests and triggered a boycott of the new election in December, the results of which were annulled by the Constitutional Court. In new balloting in July 2013, pro-government Sunni candidates achieved a significant majority. Political tensions remain high, and economic policymaking has been constrained by disputes between the royal family and parliament. Kuwait controls roughly 6 percent of the world’s oil reserves. Oil and gas account for nearly 60 percent of GDP and 95 percent of export revenues. How Do We Measure Economic Freedom? See page 467 for an explanation of the methodology or visit the Index Web site at heritage.org/index. 64 63 62 61 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Country Comparisons Country 62.7 World Average 60.7 Regional Average 62.6 Free Economies 83.9 0 20 40 60 80 100 Quick Facts Population: 4.0 million GDP (PPP): $284.0 billion 1.3% growth in 2014 5-year compound annual growth 3.3% $71,020 per capita Unemployment: 3.0% Inflation (CPI): 2.9% FDI Inflow: $485.8 million Public Debt: 7.1% of GDP 2014 data unless otherwise noted. Data compiled as of September 2015. 267 KUWAIT (continued) THE TEN ECONOMIC FREEDOMS Score RULE OF LAW Property Rights Freedom from Corruption Country World Average 45.0 44.0 0 20 40 60 80 Rank 1–Year Change 65th 69th 0 +1.0 100 The opposition is pressuring the government to address corruption, but the ruling family has obstructed parliamentary efforts to investigate it. Inadequate transparency in government spending and operations is exacerbated by the weak rule of law. The legal system is not well developed, and foreigners face difficulties enforcing contract provisions in local courts. Only citizens of Gulf Cooperation Council countries may own land. Fiscal Freedom 97.7 GOVERNMENT Government Spending 57.7 SIZE 6th 116th 0 20 40 60 80 0 –3.4 100 Kuwait does not tax individual income. In practice, foreign-owned firms and joint ventures are the only businesses subject to the corporate income tax, which is a flat 15 percent. Duties on international trade and transactions account for most other tax revenue. Government spending equals 37.5 percent of GDP, and public debt is less than 10 percent of GDP. Oil revenues allow tax rates to be kept low while maintaining government revenue. REGULATORY EFFICIENCY Business Freedom Labor Freedom Monetary Freedom 63.4 62.7 74.2 96th 77th 119th 0 20 40 60 80 +4.8 –1.5 +0.2 100 Progress in regulatory reform has been gradual and uneven. Bureaucratic hurdles add to the cost of completing licensing requirements. Labor regulations lack flexibility, and the labor market remains highly segmented. Reflecting the reality of long-term lower oil prices, the government has initiated a five-year (2015–2019) development plan to phase out Kuwait’s extensive system of subsidies, currently 9 percent of GDP. OPEN MARKETS Trade Freedom Investment Freedom Financial Freedom 77.2 55.0 50.0 89th 102nd 72nd 0 20 40 60 80 +1.0 0 0 100 Kuwait’s average tariff rate is 3.9 percent. Government procurement processes favor domestic firms. The government screens new foreign investment and restricts investment in some sectors of the economy. The financial sector continues to evolve. The number of non-performing loans is declining, and the banking sector remains well capitalized. The Capital Markets Authority took on a supervisory role in September 2011. Long-Term Score Change (since 1996) RULE OF LAW Property Rights Freedom from Corruption 268 –45.0 –26.0 GOVERNMENT SIZE Fiscal Freedom Government Spending –2.2 +46.8 REGULATORY EFFICIENCY OPEN MARKETS Business Freedom –21.6 Labor Freedom –17.5 Monetary Freedom –7.5 Trade Freedom +0.2 Investment Freedom +25.0 Financial Freedom 0 2016 Index of Economic Freedom