Outline of the U.S. Constitution
advertisement
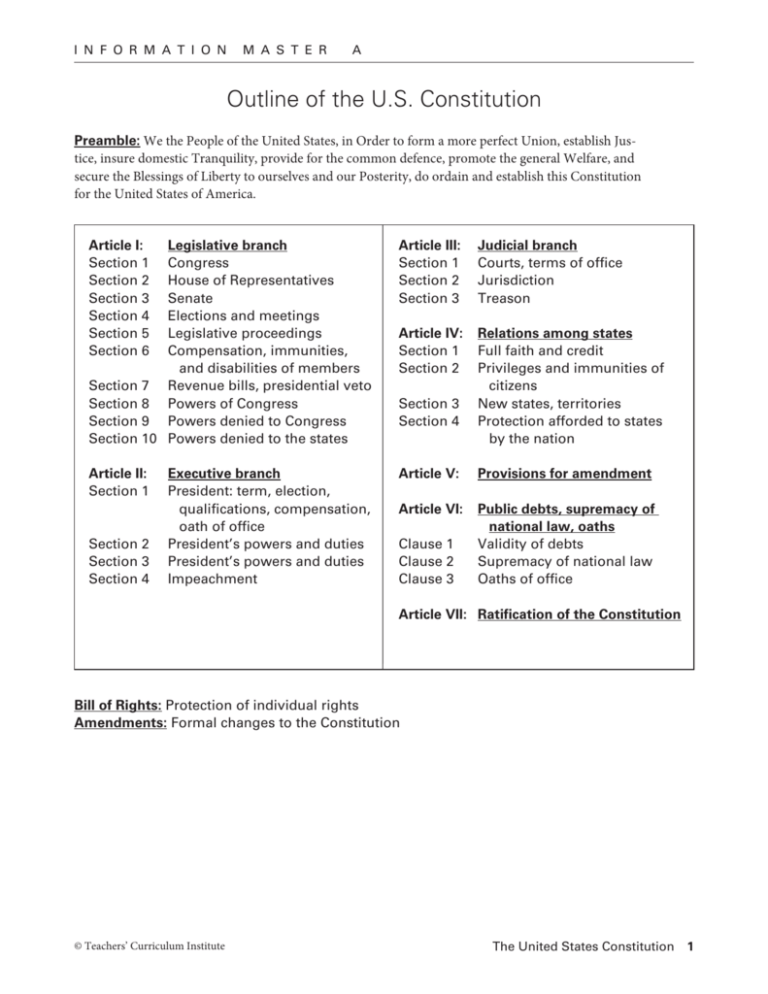
i n f o r m a t i o n m a s t e r a Outline of the U.S. Constitution Preamble: We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America. Article I: Legislative branch Section 1 Congress Section 2 House of Representatives Section 3Senate Section 4Elections and meetings Section 5 Legislative proceedings Section 6 Compensation, immunities, and disabilities of members Section 7Revenue bills, presidential veto Section 8 Powers of Congress Section 9 Powers denied to Congress Section 10 Powers denied to the states Article III: Judicial branch Section 1 Courts, terms of office Section 2 Jurisdiction Section 3Treason Article II: Executive branch Section 1 President: term, election, qualifications, compensation, oath of office Section 2 President’s powers and duties Section 3 President’s powers and duties Section 4Impeachment Article V: Provisions for amendment Article IV: Relations among states Section 1Full faith and credit Section 2 Privileges and immunities of citizens Section 3New states, territories Section 4 Protection afforded to states by the nation Article VI: Public debts, supremacy of national law, oaths Clause 1 Validity of debts Clause 2Supremacy of national law Clause 3Oaths of office Article VII: Ratification of the Constitution Bill of Rights: Protection of individual rights Amendments: Formal changes to the Constitution © Teachers’ Curriculum Institute The United States Constitution 1 i n f o r m a t i o n m a s t e r b Completed Constitutional Law 1 Matrix Card 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Article Section I 2 I I I II II Yes 3 6 years 7 the House of Representatives 8 Congress 2 the president, with approval of the Senate 2 II Answer to Question 2 Constitutional Provision with Key Words Underlined “No Person shall be a Representative who shall not have attained to the Age of twenty five Years.” “The Senate of the United States shall be composed of two Senators from each State . . . for six Years.” “All Bills for raising Revenue shall originate in the House of Representatives.” “The Congress shall have power . . . to declare War.” “He shall have Power, by and with the Advice and Consent of the Senate, to make Treaties.” the Senate “He shall nominate, and by and with the Advice and Consent of the Senate, shall appoint Ambassadors.” the president “He shall nominate, and by and with the Advice and Consent of the Senate, shall appoint . . . Judges of the supreme Court.” “. . . attained to the Age of thirty five Years.” 8 II 1 35 years old 9 II 1 four years 2 and 3 the House of Representatives can impeach; the Senate tries the impeachment 10 I © Teachers’ Curriculum Institute “He shall hold his Office during the Term of four Years.” “The House of Representatives . . . shall have sole Power of Impeachment.” “The Senate shall have sole Power to try all Impeachments.” The United States Constitution 2 i n f o r m a t i o n Card 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Article m a s t e r Section I I III III II II © Teachers’ Curriculum Institute Constitutional Provision with Key Words Underlined 8 Congress 3 president of the Senate “The Vice President of the United States shall be President of the Senate, but shall have no Vote, unless they be equally divided.” 2 1 1 2 federal courts “The judicial Power shall extend to all Cases . . . arising under this Constitution . . . to Controversies between two or more States.” for life “The judges, Both of the supreme and inferior Courts, shall hold their Offices during good Behaviour.” the states the president the congressional law 3 V I Answer to Question “The Congress shall have Power . . . To regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States.” VI III b no Congress 7 the president “Each State shall appoint . . . a Number of Electors.” “The President shall be Commander in Chief of the Army and Navy of the United States.” “This Constitution, and the Laws of the United States . . . shall be the supreme Law of the Land.” “Treason against the United States, shall consist only in levying War against them, or in adhering to their Enemies, giving them Aid and Comfort.” “The Congress, whenever two-thirds of both Houses shall deem it necessary, shall propose Amendments to this Constitution.” “Every bill which shall have passed the House of Representatives and the Senate, shall, before it becomes a Law, be presented to the President of the United States; If he approve, he shall sign it, but if not he shall return it.” The United States Constitution 3 i n f o r m a t i o n m a s t e r c Guiding Principles of the Constitution The limited government envisioned in the Constitution is based upon six guiding principles. Popular Sovereignty Because the government is created by and for the people, power resides not with the government or its leaders but with the people. In a representative democracy, the people vote to elect leaders to represent their interests. GOV_LM_04-1_v1.eps B/W 1st Proof 6-18-2007 GOV_LM_04-2_v1.eps B/W 1st Proof 6-18-2007 GOV_LM_04-3_v2.eps B/W 2ndProof 6-20-2007 GOV_LM_04-4_v2.eps B/W 2nd Proof 8-29-2007 GOV_LM_04-4_v2.eps B/W 2nd Proof 6-20-2007 GOV_LM_04-6_v1.eps © Teachers’ Curriculum Institute B/W 1st Proof 6-18-2007 Rule of Law The people and their government must abide by a set of laws, rather than by arbitrary rules set down by any individual or group. The Constitution sets limits to governmental power and establishes how leaders who overstep their power can be removed. Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances Powers and responsibilities are divided among three government branches to prevent any one person or group from having too much power. A system of checks and balances allows each branch to monitor and check the power of the others to prevent any abuse of government power. Federalism Power is divided between the central government and the individual state and local governments. Independent Judiciary The judicial branch is established as an independent entity, free of pressures and influences from the other two branches. The Supreme Court is the highest authority in the federal court system. Individual Rights Individual rights and liberties are protected against government encroachment. The United States Constitution 4 i n f o r m a t i o n m a s t e r d Completed Constitutional Law 2 Matrix Card 1 2 3 4 5 Relevant Excerpt from the Constitution Article IV, Section 2, Clause 1: Privileges and immunities. The Citizens of each State shall be entitled to all privileges and immunities of Citizens in the Several States. Principle or Principles Exemplified Individual rights Rule of law Explanation of How These Principles Are Exemplified States cannot discriminate against citizens of other states. This limits the power of state governments and guarantees the rights of individuals. Separation of powers and checks and balances No treaty signed by the president can go into effect unless two-thirds of the Senate approves it. This acts as a check on the president’s power. The president’s nominees for judges, ambassadors, and other offices must also be confirmed by the Senate. Article I, Section 7, Clause 2: The veto. Every Bill which shall have passed the House of Representatives and the Senate, shall, before it become a Law, be presented to the President of the United States; If he approve he shall sign it, but if not he shall return it. Separation of powers and checks and balances The power of Congress to make laws is checked by the president, who can approve or veto them. Tenth Amendment: Powers reserved to the states. The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution . . . are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people. Federalism Any powers not specifically given to the federal government or denied to the states are reserved for the states and thus the people. Article I, Section 2, Clause 1: Direct election of the House of Representatives. The House of Representatives shall be composed of Members chosen every second Year by the People of the several States, and the Electors in each State shall have the Qualifications requisite for Electors of the most numerous Branch of the State Legislature. Popular sovereignty Article II, Section 2, Clause 2: The Senate checks and balances the president’s power to make treaties and appointments to office. He [the president] shall have Power, by and with the Advice and Consent of the Senate, to make Treaties, provided two thirds of the Senators present concur; and he shall nominate, and by and with the Advice and Consent of the Senate, shall appoint Ambassadors, other public Ministers and Consuls, Judges of the supreme Court, and all other Officers of the United States. © Teachers’ Curriculum Institute Individual rights Federalism Members of the House of Representatives are elected by the people every two years. The states set the qualifications for voting. The United States Constitution 5 i n f o r m a t i o n Card m a s t e r d Relevant Excerpt from the Constitution Principle or Principles Exemplified Explanation of How These Principles Are Exemplified Federalism 6 Article I, Section 8, Clause 3: Interstate Commerce Clause. Congress has the power to regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States, and with the Indian Tribes. The power to regulate interstate commerce is given to the federal government. This is an example of a delegated power. Individual rights 7 Preamble. We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America. The opening words of the Constitution state that the Constitution is established by the people to protect the rights and well-being of all citizens. These words also suggest that the Constitution is the basis of law. Rule of law 8 Article VI, Section 2: Supremacy Clause. This Constitution, and the Laws of the United States which shall be made in Pursuance thereof; and all Treaties made, or which shall be made, under the Au­ thority of the United States, shall be the supreme Law of the Land; and the Judges in every State shall be bound thereby, any Thing in the Constitution or Laws of any State to the Contrary notwithstanding. Federalism 9 Article IV, Section 4: Republican form of government and protection against invasion. The United States shall guarantee to every State in this Union a Republican Form of Government, and shall protect each of them against Invasion; and on Application of the Legislature, or of the Executive (when the Legislature cannot be convened), against domestic violence. Checks and balances 10 Article III, Section 1: Supreme Court, lower courts, judges serve for life or good behavior. The judicial Power of the United States, shall be vested in one supreme Court, and in such inferior Courts as the Congress may from time to time ordain and establish. The Judges, both of the supreme and inferior Courts, shall hold their Offices during good Behavior, and shall, at stated Times, receive for their Services a Compensation, which shall not be diminished during their Continuance in Office. © Teachers’ Curriculum Institute Rule of law Federalism Individual rights Popular sovereignty Independent judiciary The Supremacy Clause establishes the Constitution as the highest authority in the country, to which all leaders must adhere. It also establishes the authority of federal law over state law. This provision guarantees representative government for the states, as well as federal protection from invasion. Implied within that guarantee are the protection of rights and liberties and rule by the people. Supreme Court justices hold their terms for life (subject to good behavior). Their pay cannot be reduced while they serve. This creates a judiciary less likely to be influenced by the other branches of government—an additional check. The United States Constitution 6








