Mathcad - lesson1.mcd
advertisement
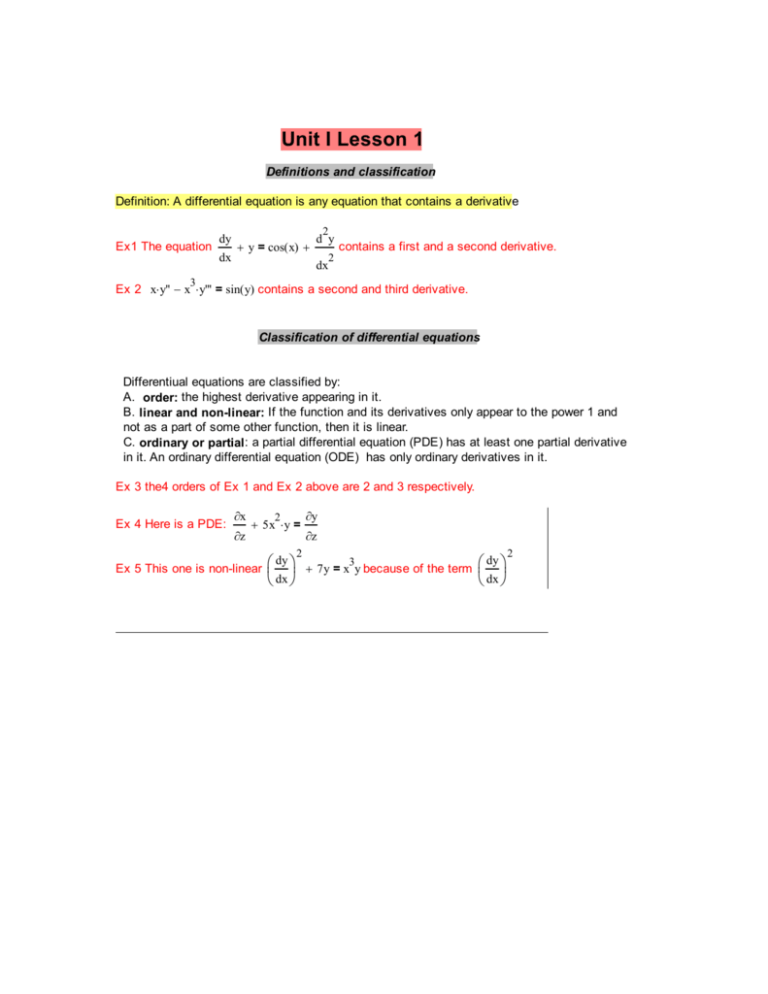
Unit I Lesson 1 Definitions and classification Definition: A differential equation is any equation that contains a derivative Ex1 The equation dy dx 2 + y = cos( x) + d y contains a first and a second derivative. 2 dx 3 Ex 2 x⋅ y'' − x ⋅ y''' = sin( y) contains a second and third derivative. Classification of differential equations Differentiual equations are classified by: A. order: the highest derivative appearing in it. B. linear and non-linear: If the function and its derivatives only appear to the power 1 and not as a part of some other function, then it is linear. C. ordinary or partial: a partial differential equation (PDE) has at least one partial derivative in it. An ordinary differential equation (ODE) has only ordinary derivatives in it. Ex 3 the4 orders of Ex 1 and Ex 2 above are 2 and 3 respectively. Ex 4 Here is a PDE: ∂x ∂z 2 + 5x ⋅ y = 2 Ex 5 This one is non-linear ∂y ∂z dy + 7y = x3y because of the term dx dy dx 2





















