Handout with solution
advertisement

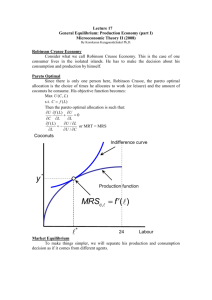
ECON 101: Principles of Microeconomics – Discussion Section Week 2 TA: Kanit Kuevibulvanich This week, you will learn: - Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) - Opportunity Cost - Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage - Range of Trading Prices Things you should know: - What is Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)? How to find PPF? - What is opportunity cost? How is it related to PPF? How to find joint PPF? - What is the definition of absolute advantage and comparative advantage? - How to find the range of trading prices? Exercises (Now you should be very organized in working through all problems!) Question 1 Crusoe finds himself stranded on an island. He devotes 10 hours each day to either gathering coconuts (C) or catching puffer fish (F). Crusoe can gather 4 coconuts in an hour, but he needs 5 hours to catch a puffer fish. On the other side of the island is Friday. Friday also devotes 10 hours each day to gathering coconuts and fishing. He can gather 3 coconuts per hour and needs only 3 1/3 hours to catch a puffer fish. 1. Draw Crusoe’s production possibilities frontier with coconuts on the y-axis. Give its equation. On a separate graph, do the same for Friday. 2. What is the opportunity cost of gathering a coconut for Crusoe? For Friday? 3. What is the opportunity cost of catching a puffer fish for Crusoe? For Friday? One day, Crusoe and Friday befriend each other and they decide to work together. 4. For maximum output, who should specialize in coconuts? In puffer fish? Justify your answer using the language of comparative advantage. 5. Draw a new joint PPF and label the kink point. 6. Determine the range of trading prices that both of them can agree for each good. 7. With trade, would it be possible for each person to consume two fishes and 10 coconuts? Without trade? 8. Suppose Friday takes half as much time to catch a puffer fish, what would happen to his PPF? Answer briefly. Question 2 Abby and Gale make xylophones (x) and yarn (y). The equations below list their output capacity per work shift in performing each task. Abby: y = 18 – 3x Gale: y = 12 – 6x 1. List the opportunity costs each of them face. 2. Describe the comparative and absolute advantages each person possesses. How do the two concepts relate? 3. Draw the joint PPF. What do the slopes signify? 4. Write down the equation(s) of the joint PPF. 5. Abby and Gale would like to trade. What would be mutually beneficial range of trading prices? Give your answer as a price for xylophones in terms of yarn. 1 ECON 101: Principles of Microeconomics – Discussion Section Week 2 TA: Kanit Kuevibulvanich Solution Question 1 1. Crusoe can gather 40 coconuts or catch 2 fishes. PPF of Crusoe is a line given by C = 40 – 20F. Friday can do 30 coconuts and 3 fishes, so PPF is C = 30 – 10F. 2. Crusoe: 1/20 fish for a coconut, Friday: 1/10 fish per coconut 3. Crusoe: 20 coconuts per fish, Friday: 10 coconuts per fish 4. Coconut: Crusoe, Fish: Friday 5. Joint PPF is two line segments given by C = 70 – 10F when 0 ≤ F ≤ 3 C = 100 – 20F when 3 ≤ F ≤ 5. Kink point is (F, C) = (3, 40). 6. Price of a fish: between 10 and 30 coconuts Price of a coconut: between 1/30 to 1/10 fish 7. With trade: both need to gather 20 coconuts and catch 4 fishes, which are on the joint PPF; thus, it is attainable. Without trade, each person has to gather 10 coconuts and 2 fishes for himself. It is on the PPF of Friday, but not on the PPF of Crusoe. Thus, it is attainable for Friday, but not Crusoe. 8. Friday can catch twice as many fishes, i.e. 6 fishes instead of 3 fishes. Slope of his PPF is flatter. Question 2 1. Abby: opportunity cost of a xylophone is 3 yarns; thus, opportunity cost of a yarn is 1/3 xylophone. Gale: opportunity cost of a xylophone is 6 yarns; thus, opportunity cost of a yarn is 1/6 xylophone. 2. Abby: either 6 xylophones or 18 yarns, Gale: either 2 xylophones or 12 yarns Absolute advantage Xylophone: Abby Yarn: Abby Comparative advantage Xylophone: Abby Yarn: Gale 3. Joint PPF is two line segments given by y = 30 – 3x when 0 ≤ x ≤ 6 y = 48 – 6x when 6 ≤ x ≤ 8. 4. See part 3. 5. Price of a xylophone: between 3 and 6 yarns Price of a yarn: between 1/6 and 1/3 xylophone 2