FASTRACK Advantage
Assessments (v2)
for PLATO Web Learning Network users
Corporate Headquarters
PLATO Learning, Inc.
10801 Nesbitt Avenue S.
Bloomington, MN 55437
800.869.2000
952.832.1200 (FAX)
PLATO Support Services
Website: http://support.plato.com
Email: http://support.plato.com/email
Voice: 800.869.2200
International Offices
PLATO Learning (Canada), Inc.
200-1311 Howe Street
Vancouver, British Columbia V6Z 2P3
Toll free: 866.567.5286
Phone: 604.691.1792
Fax: 604.691.1763
PLATO Learning (UK) Ltd.
Statesman House,
Stafferton Way,
Maidenhead,
Berkshire,
SL6 1AD
Main: 44 1628 588 300
Fax: 44 1628 588 333
Sales: 44 1628 588 359
Tech Support: 44 1628 588 345
Tech Support Fax: 44 1628 588 340
World Wide Website
http://www.plato.com
Copyright © 2005 by PLATO Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. PLATO® is a registered trademark of PLATO
Learning, Inc. PLATO Learning is a trademark of PLATO Learning, Inc. All company names and products are
trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Contents
GENERAL INFORMATION ...................................................................................................... 1
READING COMPREHENSION AND SKILLS & STRATEGIES ASSESSMENT ............. 4
OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................... 4
ASSESSING LEARNERS ................................................................................................................. 5
SELECTING A SKILL LEVEL .......................................................................................................... 6
PASSING PERCENTAGES ............................................................................................................... 8
COMPLETING THE ASSESSMENT ................................................................................................... 9
DETERMINING INDIVIDUAL LEARNING PATHS ........................................................................... 10
LANGUAGE ARTS ASSESSMENT ........................................................................................ 13
OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................. 13
ASSESSING LEARNERS ............................................................................................................... 14
SELECTING A SKILL LEVEL ........................................................................................................ 15
PASSING PERCENTAGES ............................................................................................................. 16
COMPLETING THE ASSESSMENT ................................................................................................. 17
DETERMINING INDIVIDUAL LEARNING PATHS ........................................................................... 18
MATH ASSESSMENT............................................................................................................... 21
OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................. 21
ASSESSING LEARNERS ............................................................................................................... 22
SELECTING A SKILL LEVEL ........................................................................................................ 23
PASSING PERCENTAGES ............................................................................................................. 24
COMPLETING THE ASSESSMENT ................................................................................................. 25
DETERMINING INDIVIDUAL LEARNING PATHS ........................................................................... 26
REPORTS.................................................................................................................................... 29
SCOPE AND SEQUENCE ........................................................................................................ 31
READING COMPREHENSION ....................................................................................................... 32
READING SKILLS AND STRATEGIES ............................................................................................ 33
LANGUAGE ARTS ....................................................................................................................... 36
MATH ........................................................................................................................................ 39
i
General Information
Introduction
FASTRACK Advantage Assessments are instructional systems that combine
skills assessment and skills development. With these assessments, you can
conveniently establish and monitor the beginning, progression, and
completion status of learners in your program.
Purpose
FASTRACK Advantage Assessments serve the following purposes:
• Determines a grade level for a specific learner.
• Places learners in the appropriate activities while exempting them from
others.
• Indicates student progress (except in Reading Comprehension)
Benefits
The FASTRACK Advantage Assessments benefit you and your learners in
the following ways:
• Accessed from PLATO Web Learning Network.
• Addresses skill levels from grade 2 to grade 14, depending on the
curriculum.
• Adjusts the test duration depending on a learner’s skill level.
• Reports a grade level.
• Allows instructors to suggest (learners then enter it) a starting grade level to
decrease test time.
• Allows learners to stop a test and resume it later.
Continued on next page
1
General Information, Continued
FASTRACK
Advantage
Assessments
and Tests
Placement tests have relatively low stakes. You can use the FASTRACK
Advantage Assessments to place learners in the courseware they need and are
ready for. The assessments are short and quick to administer, so the learner
can start the appropriate courseware as quickly as possible. Because the tests
are so short, they are the least reliable of the various tests shown. Since they
are low-stakes tests, we believe this trade-off of reliability for speed is
acceptable.
After placement, students move into the PLATO instructional activities. Each
PLATO tutorial includes quizzes and interactions that determine
understanding. Each module includes a test that shows the learner has
mastered the objective of the module. These assessments are longer and are
drawn from a larger pool of questions. Since each mastery test covers a single
objective, mastery tests tend to be more reliable than placement tests.
Mastery of a course may also be a prerequisite for standardized tests, like a
statewide assessment. These tests are moderate in length. They are carefully
prepared to have high reliability, because the stakes may be very high:
graduation, acceptance into a program, and so forth.
Continued on next page
2
General Information, Continued
FASTRACK Advantage Assessments and Tests (continued)
This diagram shows how various assessments fit into an overall view of
assessment and instruction
Process
overview
The table below identifies the eduTest FASTRACK Assessment process.
Stage
1
2
3
Description
Learners begin FASTRACK Advantage Assessments by taking
one or more assessment tests to determine their skill level.
Upon completion of the test, the system generates an individual
learning path based on the learner’s test performance.
Learners then complete the PLATO courseware in their individual
learning path to increase their skill level.
Note Reading Comprehension is the only assessment that does
not indicate an increase in grade level as learners progress
through the curriculum.
3
Reading Comprehension and
Skills & Strategies Assessment
Overview
Description
The Reading Comprehension assessment provides prescriptions in the
following curricula:
• Vocabulary and Reading Comprehension
• Advanced Reading Strategies
The Skills and Strategies assessment provides prescriptions in the following
curricula:
•
•
•
•
Recommendation
Essential Reading Skills
Fundamental Reading Skills
Intermediate Reading Skills
Advanced Reading Skills
You do not need the Vocabulary and Reading Comprehension courseware
to use the FASTRACK Advantage Reading Comprehension Assessment,
but you will need it in order to make assignments for vocabulary and
reading comprehension practice.
Scope and
Sequence
Refer to the Scope and Sequence section at the end of this document on page
31.
In this section
This section includes the following topics.
Topic
Assessing Learners
Selecting a Skill Level
Passing Percentages
Completing the Assessment
Determining Individual Learning Paths
4
See Page
5
6
8
9
10
Assessing Learners
Introduction
When learners select a FASTRACK Advantage Assessment curriculum, they
begin with the assessment test.
Test description
The assessment test can take from 30 minutes to a few hours, depending on
learner speed and skill level. The test is adaptive and the more questions a
learner answers correctly, the longer the test will take. Therefore, estimate a
learner’s starting skill level as accurately as possible. If a learner does not
select a starting skill level, the assessment starting level defaults to Level D
(grade 5) or Level E (grade 6), depending on the subject.
Note A learner does not need to complete the test in one sitting. Learners
can exit the test and resume where they left off at another session.
5
Selecting a Skill Level
Description
When learners start the assessment test, the system asks them to enter a
starting skill level assigned by an instructor. Learners decrease the amount of
time they need to complete the assessment test by selecting the correct
starting level.
Not selecting a
skill level
If you do not select a skill level, the learner begins the FASTRACK
Advantage Reading Comprehension Assessment at test level E. The default
starting level for FASTRACK Advantage Reading Skills and Strategies
Assessment is Level D.
If you already know the learner’s reading skill level, you may skip the
FASTRACK Advantage Reading Comprehension Assessment and have the
learner start at a level you choose in the FASTRACK Advantage Reading
Skills and Strategies Assessment.
However, if the student has completed FASTRACK Advantage Reading
Comprehension Assessment before starting FASTRACK Advantage Reading
Skills and Strategies test, the level achieved in the Reading Comprehension
assessment is the best level to assign for FASTRACK Advantage Reading
Skills and Strategies.
Confidentiality
Only instructors and administrators have access to a learner’s starting grade
level from PLATO Web Learning Network. Learners will know their starting
level identified by letter, not the associated grade level or levels.
Continued on next page
6
Selecting a Skill Level, Continued
Using Reading
Comprehension
and Skills and
Strategies
together
You can use FASTRACK Advantage Reading Comprehension assessment
and FASTRACK Advantage Reading Skills and Strategies assessments
together to determine a learner’s starting skill level.
Use the Reading Comprehension assessment to determine a learner’s overall
reading level when it is not known. Since Comprehension has 12 levels and
Skills and Strategies has only five levels, use the following table to determine
a learner’s starting skill level in Skills and Strategies based on their Reading
Comprehension grade.
Reading Comprehension Grade
3.00
4.00
5.00
6.00
7.00
8.00
9.00
10.00 and higher
Skills and Strategies Starting Level
B
C
D
D
F
F
F
I
Testing strategy FASTRACK Advantage uses an adaptive testing strategy to minimize the
amount of time spent on each of the assessment tests.
Stage
Description
1
Learners begin tests at a level assigned by their instructor or as
determined by the level the learner achieved in the Reading
Comprehension assessment.
Learners progress through the questions in the assigned level until
they demonstrate mastery or non-mastery of the material and skill
level.
Learners continue to progress through the skill levels until they
reach a level they are unable to master.
The test ends and PLATO Web Learning Network assigns the
learner the non-mastered skill level as the initial level for the
instruction.
2
3
4
7
Passing Percentages
Introduction
FASTRACK Advantage assessments require that the learner master all
modules or courses in each level before continuing on to the next level.
Description
The table below identifies for each curriculum what percentage of the
questions for a module or course a learner must answer correctly to go on to
the next higher level.
Curriculum
Vocabulary and Reading
Comprehension
Module or course
passing percentage
80
Essential Reading Skills
67
Fundamental Reading Skills
67
Intermediate Reading Skills
67
Advanced Reading Skills
67
Mastery
Must answer 8 of 10
questions correctly to
master level
Must master all
modules to master
level
Must master all
courses to master
level
Must master all
courses to master
level
Must master all
modules to master
level
Example
Suppose a learner begins at Level B of Reading Skills and Strategies and
masters Level B through D and half the modules in Level E. The initial level
is E.
8
Completing the Assessment
Introduction
FASTRACK Advantage continues testing learners until they reach the highest
level they can master.
Process
overview
The table below identifies how a learner completes the assessment.
Stage
1
2
3
Description
Once the learner reaches the highest level they can master, the test
will end.
PLATO Web Learning Network automatically generates a grade
level and creates an individual Reading Skills and Strategies
assignment for the learner.
The learner exits the system following the online instructions.
Note Learners can manually exit the test and force it to be
scored. However, the score reported will not be accurate
and the student will not be able to retake the test without
instructor intervention.
Scoring
PLATO Web Learning Network assesses learner skill level only on the
portion of the test they completed.
Resume testing
Since the assessment test might take a few hours, learners may take the test in
several sessions. They can exit the test and not score it by following the onscreen instructions, then resume the test at a later time.
9
Determining Individual Learning Paths
Introduction
Upon completion of the assessment test, learners receive an individual
assignment in the FASTRACK Advantage Reading Skills and Strategies
curriculum. At any time, they may review courseware levels and objectives
already mastered.
PLATO Web Learning Network assessment test feature allows each learner to
have a learning path unique to his or her individual needs.
PLATO Web
Learning
Network
activities to
assign
Reading Comprehension activities are assigned through PLATO Web
Learning Network. Use the table below to determine what to assign based on
the grade level reported for Reading Comprehension.
FASTRACK
Advantage Reading
Comprehension grade
level
3
•
•
4
•
•
5
•
•
6
•
•
7
•
•
8
•
•
9
•
•
•
•
•
•
Activities to Assign in
PLATO Web Learning Network
Vocabulary and Reading Stories, Level 3
Vocabulary and Reading Information, Level 3
Vocabulary and Reading Stories, Level 4
Vocabulary and Reading Information, Level 4
Vocabulary and Reading Stories, Level 5
Vocabulary and Reading Information, Level 5
Vocabulary and Reading Stories, Level 6
Vocabulary and Reading Information, Level 6
Vocabulary and Reading Literature, Level 7
Vocabulary and Reading Expository Test, Level 7
Vocabulary and Reading Literature, Level 8
Vocabulary and Reading Expository Test, Level 8
Vocabulary and Reading Literature, Level 9
Vocabulary and Reading Expository Test, Level 9
Reading Social Sciences, Practice Level 9
Reading Literature, Practice Level 9
Reading History, Practice Level 9
Reading Science, Practice Level 9
Continued on next page
10
Determining Individual Learning Paths, Continued
PLATO Web Learning Network activities to assign (continued)
FASTRACK Advantage
Reading Comprehension
grade level
10
11
12
13
14
Activities to Assign in PLATO Web Learning
Network
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Reading Social Sciences, Practice Level 10
Reading Literature, Practice Level 10
Reading History, Practice Level 10
Reading Science, Practice Level 10
Reading Social Sciences, Practice Level 11
Reading Literature, Practice Level 11
Reading History, Practice Level 11
Reading Science, Practice Level 11
Reading Social Sciences, Practice Level 12
Reading Literature, Practice Level 12
Reading History, Practice Level 12
Reading Science, Practice Level 12
Reading Social Sciences, Practice Level 13
Reading Literature, Practice Level 13
Reading History, Practice Level 13
Reading Science, Practice Level 13
Reading Social Sciences, Practice Level 14
Reading Literature, Practice Level 14
Reading History, Practice Level 14
Reading Science, Practice Level 14
Continued on next page
11
Determining Individual Learning Paths, Continued
Examples
The following examples illustrate a learner’s exemption from and completion
of activities after taking the assessment and mastery tests for the Reading
Skills and Strategies curricula.
In this example, the learner was exempted from seven modules after taking
the assessment. The learner went through each module from which they were
not exempted and mastered them; therefore, showing mastery and completion
on those modules.
12
Language Arts Assessment
Overview
Description
The Language Arts assessment provides prescriptions in the following
curriculum:
• Writing Series
Scope and
Sequence
Refer to the Scope and Sequence section at the end of this document on page
31.
In this section
This section includes the following topics.
Topic
Assessing Learners
Selecting a Skill Level
Passing Percentages
Completing the Assessment
Determining Individual Learning Paths
See Page
14
15
16
17
10
13
Assessing Learners
Introduction
When learners select a FASTRACK Advantage curriculum, they begin with
the assessment test. The remainder of the curriculum is unavailable until after
they complete the assessment test and the system scores the test.
Test description
The assessment test can take from 30 minutes to a few hours, depending on
learner speed and skill level. The test is adaptive and the more questions a
learner answers correctly, the longer the test will take. Therefore, estimate a
learner’s starting skill level as accurately as possible. If you do not select a
skill level, the assessment starting level defaults to Level E.
Note A learner does not need to complete the test in one sitting. Learners
can exit the test and resume where they left off at another session.
14
Selecting a Skill Level
Introduction
You should match the skills in the level to each learner’s capability when
assigning an initial level.
Description
When learners start the assessment test, the system asks them to enter a
starting skill level assigned by an instructor. Starting learners at the correct
level decreases the amount of time they need to complete the assessment test.
Not selecting a
skill level
If a skill level is not selected, the learner begins the tests at Level E.
Testing strategy FASTRACK Advantage uses an adaptive testing strategy to minimize the
amount of time spent on each of the assessment tests.
Stage
1
2
3
4
Description
Learners begin tests at a level assigned by their instructor.
The learner progresses through the questions in the assigned level
until he or she demonstrates mastery or non-mastery of the
material and skill level.
The learner continues to progress through the skill levels until he
or she reaches a level he or she is unable to master.
The test ends and the Pathways system assigns the learner the nonmastered skill level as the initial level for the assessment.
15
Passing Percentages
Introduction
Each FASTRACK Advantage curriculum requires that the learner master
80% of the modules in a level before continuing onto the next level.
Adjustments
As soon as a learner fails 20% of the objectives in a level, level mastery is not
possible. FASTRACK Advantage decreases testing one or two levels and
allows the learner to proceed. When decreasing levels, FASTRACK
Advantage considers performance in the failed level to determine whether to
drop back one or two levels.
Example
A learner may begin but not master Level D. If the learner’s performance in
Level D was poor, the assessment test decreases to Level B. If the learner still
does not master that level, the test decreases to Level A (the curriculum
beginning). If the learner masters Level B, he or she progresses to Level C.
16
Completing the Assessment
Introduction
FASTRACK Advantage continues testing learners until they reach the highest
level they can master.
Process
overview
The table below identifies how a learner completes the assessment.
Stage
1
2
3
Description
Once the learner reaches the highest level they can master, the test
will end.
PLATO Web Learning Network automatically generates a grade
level and creates an individual assignment for the learner.
The learner exits the system.
Note Learners can manually exit the test and force it to be
scored. However, the score reported will not be accurate
and the student will not be able to retake the test without
instructor intervention.
Scoring
PLATO Web Learning Network assesses learner skill level only on the
portion of the test they completed.
Resume testing
Since the assessment test might take a few hours, learners may take the test in
several sessions. They can exit the test and not score it by following the onscreen instructions, then resume the test at a later time.
17
Determining Individual Learning Paths
Introduction
Upon completion of the assessment test, learners receive an individual
assignment in the FASTRACK Advantage curriculum. At any time, they may
review courseware levels and objectives already mastered.
PLATO Web Learning Network assessment test feature allows each learner to
have a learning path unique to his or her individual needs.
Examples
The following examples illustrate a variety of learner assessment test results.
Exemption example
This example shows a learner in the Advantage Language Arts curriculum.
The learner entered the assessment at Level E and was exempted in Levels A
through E. The learner was unable to pass all activities in Level F and
therefore begins the curriculum assignment on Level F.
Continued on next page
18
Determining Individual Learning Paths, Continued
Examples (continued)
Partial exemption example
This example shows the partial exemptions in Level E of the Language Arts
curriculum. The learner was exempted from four objectives and was having
difficulty with and unable to pass the remaining objectives. The learner does
not advance to the next level.
Continued on next page
19
Determining Individual Learning Paths, Continued
Examples (continued)
Mastery and completion example
This example shows mastery and completion within the courseware after the
learner completes the assessment test. The learner completes the activities and
receives mastery of the activity within the curricula and outside the
assessment..
20
Math Assessment
Overview
Description
The Math assessment provides prescriptions in the following curricula:
•
•
•
•
Math Fundamentals
Geometry and Measurement 1
PLATO Algebra 1
PLATO Algebra 2
Scope and
Sequence
Refer to the Scope and Sequence section at the end of this document on page
31.
In this section
This section includes the following topics.
Topic
Assessing Learners
Selecting a Skill Level
Passing Percentages
Completing the Assessment
Determining Individual Learning Paths
See Page
22
23
24
25
26
21
Assessing Learners
Introduction
When learners select a FASTRACK Advantage curriculum, they begin with
the assessment test. The remainder of the curriculum is unavailable until after
they complete the assessment test and the system scores the test.
Test description
The assessment test can take from 30 minutes to a few hours, depending on
learner speed and skill level. The test is adaptive and the more questions a
learner answers correctly, the longer the test will take. Therefore, estimate a
learner’s starting skill level as accurately as possible. If you do not select a
skill level, the assessment starting level defaults to Level E.
Note A learner does not need to complete the test in one sitting. Learners
can exit the test and resume where they left off at another session.
22
Selecting a Skill Level
Introduction
You should match the skills in the level to each learner’s capability when
assigning an initial level.
Description
When learners start the assessment test, the system asks them to enter a
starting skill level assigned by an instructor. Starting learners at the correct
level decreases the amount of time they need to complete the assessment test.
Not selecting a
skill level
If a skill level is not selected, the learner begins the tests at Level E.
Testing strategy FASTRACK Advantage uses an adaptive testing strategy to minimize the
amount of time spent on each of the assessment tests.
Stage
1
2
3
4
Description
Learners begin tests at a level assigned by their instructor.
The learner progresses through the questions in the assigned level
until he or she demonstrates mastery or non-mastery of the
material and skill level.
The learner continues to progress through the skill levels until he
or she reaches a level he or she is unable to master.
The test ends and the Pathways system assigns the learner the nonmastered skill level as the initial level for the assessment.
23
Passing Percentages
Introduction
Each FASTRACK Advantage curriculum requires that the learner master
80% of the modules in a level before continuing onto the next level.
Adjustments
As soon as a learner fails 20% of the objectives in a level, level mastery is not
possible. FASTRACK Advantage decreases testing one or two levels and
allows the learner to proceed. When decreasing levels, FASTRACK
Advantage considers performance in the failed level to determine whether to
drop back one or two levels.
Example
A learner may begin but not master Level D. If the learner’s performance in
Level D was poor, the assessment test decreases to Level B. If the learner still
does not master that level, the test decreases to Level A (the curriculum
beginning). If the learner masters Level B, he or she progresses to Level C.
24
Completing the Assessment
Introduction
FASTRACK Advantage continues testing learners until they reach the highest
level they can master.
Process
overview
The table below identifies how a learner completes the assessment.
Stage
1
2
3
Description
Once the learner reaches the highest level they can master, the test
will end.
PLATO Web Learning Network automatically generates a grade
level and creates an individual assignment for the learner.
The learner exits the system.
Note Learners can manually exit the test and force it to be
scored. However, the score reported will not be accurate
and the student will not be able to retake the test without
instructor intervention.
Scoring
PLATO Web Learning Network assesses learner skill level only on the
portion of the test they completed.
Resume testing
Since the assessment test might take a few hours, learners may take the test in
several sessions. They can exit the test and not score it by following the onscreen instructions, then resume the test at a later time.
25
Determining Individual Learning Paths
Introduction
Upon completion of the assessment test, learners receive an individual
assignment in the FASTRACK Advantage curriculum. At any time, they may
review courseware levels and objectives already mastered.
PLATO Web Learning Network assessment test feature allows each learner to
have a learning path unique to his or her individual needs.
Examples
The following examples illustrate a variety of learner assessment test results.
Exemption example
This example shows a learner in the Advantage Math curriculum. The learner
entered the assessment at Level E and was exempted in Levels A through E.
The learner was unable to pass all activities in Level F and therefore begins
the curriculum assignment on Level F.
Continued on next page
26
Determining Individual Learning Paths, Continued
Examples (continued)
Partial exemption example
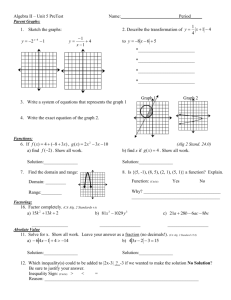
This example shows the partial exemptions in Level E of the Math
curriculum. The learner was exempted from four objectives and was having
difficulty with and unable to pass the remaining objectives. The learner does
not advance to the next level.
math_partial_exempt.bmp
Continued on next page
27
Determining Individual Learning Paths, Continued
Examples (continued)
Mastery and completion example
This example shows mastery and completion within the courseware after the
learner completes the assessment test. The learner completes the activities and
receives mastery of the activity within the curricula and outside the
assessment.
28
Reports
Introduction
PLATO Web Learning Network provides FASTRACK Advantage
fAssessment reports that show initial skill level, current grade level, and
grade level gain. Instructors can use these reports to track learner progress.
Caution
FASTRACK reports are for placement only. Grade levels reported are
competency-based. Do not use FASTRACK reports in lieu of standardized
test grade levels.
Report
description
PLATO Web Learning Network provides the FASTRACK Summary Report.
This report displays the following information by Group or Class, depending
on your selection:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Learner Name
Initial Grade
Date for Initial Grade
Current Grade
Date of Current Grade
Grade Gain
Time on Task
Continued on next page
29
Reports, Continued
Field
descriptions
The table below identifies various items that display on the FASTRACK
Summary report.
Note Different schools and areas of the country may teach different topics
or skills in different grades, so these numbers may be approximate for
your learners. They are most useful as a measure of skill gain by
learners, how much they have accomplished since taking the initial
assessment test.
Item
Initial grade
Current grade
Grade gain
Description
Displays the grade determined by the assessment test
prior to fulfilling assignments.
Displays the current learner skill level. This grade
increases as a learner masters more objectives in the
curriculum.
Displays the difference between the learner’s initial
grade and the current grade. This number represents the
amount of progress a learner has made in the curriculum.
Note Grade gain does not report for Reading
Comprehension. Reading Comprehension
activities allow students to practice certain skills,
not master skills.
Report sample
30
The following is an example of the FASTRACK Summary for an individual
learner in one study area.
Scope and Sequence
Introduction
Each curriculum is divided into skill levels; each level addresses a number of
objectives. The curriculum begins with the basics and the difficulty increases
with each skill level.
In the section
This section contains scope and sequence information for the following.
Topics
Reading Comprehension
Reading Skills and Strategies
Language Arts
Math
See Page
32
33
36
39
31
Reading Comprehension
Description
32
The table below shows the curriculum covered by the FASTRACK
Advantage Reading Comprehension Assessment. The Reading
Comprehension courseware is assigned through PLATO Web Learning
Network because it is not mastery-based. Therefore, courseware is not
automatically exempted or assigned by FASTRACK.
Skill Level
B
Reading Level
3
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Objectives
Literal and inferential comprehension of
narrative and expository Language Arts
applicable to the grade level.
Same
Same
Same
Same
Same
Same
Same
Same
Same
Same
Same
Reading Skills and Strategies
Description
Skill Level
B
Grade
Level
3
C
4
Modules or Courses in Level
Pronouns
Possessive Pronouns
Contractions with Is and Am
Contractions with Will
Contractions with Are
Contractions with Not
Contractions with Would
Tenses of Regular Verbs
Tenses of Irregular Verbs
Comparisons
Compound Words
Abbreviations
Cause and Effect Words
Negative Prefixes
Prefixes
Prefixes of Number
Homonyms
Homophones
Idioms
Similes
Synonyms
Antonyms
Being a Word Detective
Finding Main Ideas 1
Finding Main Ideas 2
What Happens Next?
Finding What You Need
Drawing Conclusions
Working with Order
Finding Causes and Effects
Finding What’s Similar and What’s Different
Finding Facts and Opinions
Continued on next page
33
Reading Skills and Strategies, Continued
Description Description (continued)
Skill Level Grade Level
Modules or Courses in Level
D
5-6
Expanding Your Vocabulary
Using What You Know
Separating Facts from Opinions
Asking and Answering Questions
Reading Between the Lines
Finding What’s Important
Summarizing What You Read
Using Pictures to Help You Understand,
Picturing What You Read
Tracking Your Understanding
F
7-9
Enriching Your Vocabulary
Using Prior Knowledge When You Read
Discovering Facts and Opinions
Using Question/Answer Strategy
Making Inferences
Locating What’s Important
Summarizing What’s Important
Using Graphics to Help You Understand
Visualizing When You Read
Monitoring Your Comprehension
Continued on next page
34
Reading Skills and Strategies, Continued
DescriptionDescription (continued)
Skill Level Grade Level
Modules or Courses in Level
I
10
Finding the Resources
Asking Questions
Finding Answers
Preparing for Review
Putting It Together
Building Your Vocabulary
Reading to Remember
Doing Your Best on Reading Tests
Building Your Social Sciences Vocabulary
Understanding Social Sciences
A Strategy for Reading Social Sciences
Building Your Literature Vocabulary
Understanding Literature
A Strategy for Reading Literature
Building Your History Vocabulary
Understanding History
A Strategy for Reading History
Building Your Sciences Vocabulary
Understanding Sciences
A Strategy for Reading Sciences
35
Language Arts
Description
Skill Level
A
B
C
D
Modules in Level
What is a Plural?
Plurals with s and es
Capital Letters
Proper Nouns and Capitals
The Basics of Punctuation
What Is a verb?
Two Kinds of Verbs
Unusual Plurals
How To Form Possessives
Using Possessives
Possessive Pronouns and Adjectives
Titles and Capital Letters
Commas 1
Colons and Semicolons
Parts of a Verb
Some Strange Verbs
Verbs and Tenses
What Is a Noun?
Two Kinds of Nouns
More Kinds of Nouns
Nouns and Verbs and Number
What Are Negative Words?
Quotation Marks
What Is a Pronoun?
Personal Pronouns
Personal Pronouns with Ownership
Other Pronouns
Recognizing Adjectives
More About Adjectives
Identifying Adjectives
More About Adverbs
What Is a Sentence?
Parts of a Sentence
More About Sentences
Three Kinds of Sentences
Confusing Verbs 1
Continued on next page
36
Language Arts, Continued
Description (continued)
Skill Level
E
F
Modules in Level
Nouns, Pronouns, and Gender
Pronouns and Number
Making Nouns and Pronouns Agree in Sentences
A Subject and Its Verb Must Agree
Subjects and Irregular Verbs
Making Verbs and Unusual Nouns Agree
Starting a Sentence with THERE or HERE
What Is a Sentence Fragment?
Run-on Sentences 1
Synonyms and Antonyms
Homophones: Words That Sound Alike
Writing Personal Business Letters
Addresses and Return Addresses
Spelling Rules
More Spelling Rules
Forming Plurals and Possessives
Commonly Misspelled Words
Punctuation – End Marks
Commas 2
Using :,;,--,-,""
Recognizing Verbs
Identifying Subjects
Types of Nouns
How Nouns are Used
The Pronoun: Replacement for a Noun
How Pronouns Are Used
Regular Verbs
Irregular Verbs
Subject and Verb Agreement
Pronoun and Antecedent Agreement
Correct Pronoun Use
Correct Use of Adjectives and Adverbs – Comparatives
Continued on next page
37
Language Arts, Continued
Description (continued)
Skill Level
G
H
I
38
Modules in Level
Learning About Prepositions
Using Articles
Identifying Phrases
What Is a Clause?
More About Phrases
Different Kinds of Clauses
One Way to Link Ideas
Letter of Application
Filling Out an Application
Modifiers of Meaning
Verbal Phrases
Prepositional Phrases
Confusing Verbs 2
Confusing Words
Sentence Fragments
Dependent and Independent Clauses
Run-on Sentences
The Topic Sentence
Unnecessary Sentences
Order of Sentences in Paragraphs
Transitional Devices
Improving Structure in Paragraphs
Paragraph Development and Organization
Inappropriate Language
Word Choice Errors
Using Figures of Speech in Writing
Effective Writing
Misplaced Modifiers
Parallel Structure within Sentences
Awkward Sentence Structure
Math
Description
Skill Level
A
B
Modules in Level
Whole Numbers 0-9
Counting Numbers
Meaning of Addition
Whole Numbers 10-99
Whole Numbers 100-999
Addition Facts 1
Addition Facts 2
Addition Properties
Addition Skills 1
Addition Skills 2
Meaning of Subtraction
Subtraction Facts
Subtraction Skills 1
Hundreds and Thousands
Addition Skills 3
Addition Skills 4
Subtraction Skills 2
Subtraction Skills 3
Subtraction Skills 4
Problem Solving 1
Millions/Billions and Trillions
Meaning of Multiplication
Multiplication Facts 1
Multiplication Skills 1
Multiplication Properties 1
Multiplication Facts 2
Multiplication Skills 2
Meaning of Division
Division Facts
Division Skills 1
Plane Figures 1
Continued on next page
39
Math, Continued
Description (continued)
Skill Level
C
D
Modules in Level
Multiplication Properties 2
Multiplication Skills 3
Multiplication Skills 4
Division Skills 2
Multiplication Skills 5
Division Skills 3
Multiplication Skills 6
Multiplication Skills 7
Problem Solving 2
Division Skills 4
Meaning of Fractions
Division Skills 5
Division Skills 6
Division Skills 7
Division Skills 8
Problem Solving 3
Common 3-Dimensional Figures
Equivalent Fractions
Multiples and Common Denominators
Comparing Fractions
Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Adding and Subtracting Fractions 1
Adding and Subtracting Fractions 2
Plane Figures 2
Figure Comparison
Continued on next page
40
Math, Continued
Description (continued)
Skill Level
E
F
Modules in Level
Adding Mixed Numbers
Subtracting Mixed Numbers 1
Subtracting Mixed Numbers 2
Linear Measurement
Area Measurement
Volume and Capacity Measurement
Multiplying Fractions
Dividing Fractions 1
Dividing Fractions 2
Multiplying and Dividing Mixed Numbers 1
Multiplying and Dividing Mixed Numbers 2
Problem Solving 4
Ratio Concepts
Decimal Fractions 1
Decimal Fractions 2
Proportion Concepts
Adding and Subtracting Decimals
Multiplying Decimals
Problem Solving 5
Percent Concepts 1
Percent Concepts 2
Problem Solving 6
Metric Measurement
Area, Part 1
Area, Part 2
Volume
Using Measurement
Visualizing Percents Less than 1 % (Alg 1.1)
Converting Percents Less than 1% to Decimals (Alg 1.1)
Converting a Decimal to a Fraction of a Percent (Alg 1.1)
Finding the Amount with Percents Less than 1% (Alg 1.1)
Visualizing Percents Greater than 100% (Alg 1.1)
Converting Percents Greater than 100% to Decimals (Alg 1.1)
Converting a Number Greater than 1 go a Percent (Alg 1.1)
Mean, Median, and Mode (Alg 1.1)
Continued on next page
41
Math, Continued
Description (continued)
Skill Level
G
Modules in Level
Problem Solving 7
Odd and Even Numbers (Alg 1.1)
Prime and Composite Numbers (Alg 1.1)
Exponents: Exponential Form (Alg 1.1)
Exponents: Expanded Form (Alg 1.1)
Exponents: Product Rule (Alg 1.1)
Exponents: Power Rule (Alg 1.1)
The Additive Inverse of Integers (Alg 1.1)
Adding Integers (Alg 1.1)
Subtracting Integers (Alg 1.1)
Multiplying Integers (Alg 1.1)
Dividing Integers (Alg 1.1)
Expressions in 1 Variable (Alg 1.1)
Expressions in 2 or more Variables (Alg 1.1)
Determining the Truth Value of a Statement (Alg 1.1)
Order of Operations (Alg 1.1)
Adding Monomials (Alg 1.1)
Subtracting Monomials (Alg 1.1)
Multiplying Monomials (Alg 1.1)
Dividing Monomials (Alg 1.1)
Adding Binomials and Monomials (Alg 1.1)
Subtracting Binomials and Monomials (Alg 1.1)
Multiplying Binomials and Monomials (Alg 1.1)
Dividing Binomials by Monomials (Alg 1.1)
Probability and Possible Outcomes (Alg 1.1)
Probability of an Event (Alg 1.1)
Solving Problems with Probability (Alg 1.1)
Solving Problems with Percents (Alg 1.1)
Solving Problems with Mean, Median, and Mode (Alg 1.1)
Estimation Basics (Alg 1.1)
Estimation by Clustering (Alg 1.1)
Scaling and Proportion, Part 1 (Alg 1.1)
Scaling and Proportion, Part 2 (Alg 1.1)
Continued on next page
42
Math, Continued
Description (continued)
Skill Level
H
Modules in Level
Square Roots of Perfect Squares (Alg 1.1)
Square Roots of Imperfect Squares (Alg 1.1)
Multiplying Common Fractions (Alg 1.1)
Adding and Subtracting Fractions (Alg 1.1)
Adding and Subtracting Mixed Numbers (Alg 1.1)
Dividing Fractions (Alg 1.1)
Multiplying and Dividing Mixed Numbers (Alg 1.1)
Mental Math with Whole Numbers and Decimals (Alg 1.1)
Mental Math with Fractions and Percents (Alg 1.1)
Linear Equations in 1 Variable: Solving by Inspection (Alg 1.1)
Linear Equations in 1 Variable: Isolating the Variable (Alg 1.1)
Linear Inequalities in 1 Variable, Part 1 (Alg 1.1)
Linear Inequalities in 1 Variable, Part 1 (Alg 1.1)
More Difficult Linear Inequalities in 1 Variable (Alg 1.1)
Special Angles, Part 1
Special Angles, Part 2
Circles/Arcs/Circumferences
The Pythagorean Theorem – Geometry and Measurement 1
Using Geometry
Using Basic Number Ideas (Alg 1.1)
Special Quadratic Equations, Part 1 (Alg 1.1)
Special Quadratic Equation, Part 2 (Alg 1.1)
Using Linear Equations to Solve Problems (Alg 1.1)
Using Quadratic Equations to Solve Problems (Alg 1.1)
Coordinate Plan (Alg 1.1)
Identifying Points on a Coordinate Plane (Alg 1.1)
Ordered Pairs as Solutions of Linear Equations (Alg 1.1)
Graphing Linear Equations in 2 Variables (Alg 1.1)
Literal Equations (Alg 1.1)
Adapting and Using Formulas (Alg 1.1)
Patterns and Sequences (Alg 1.1)
Functions (Alg 1.1)
Describing Functions with Equations, Tables, and Graphs (Alg 1.1)
Linear Patters (Alg 1.1)
Graphs, Slopes, and y-Intercepts (Alg 1.1)
Interpreting Graphs to Solve Problems (Alg 1.1)
Continued on next page
43
Math, Continued
Description (continued)
Skill Level
I
Modules in Level
Solving and Graphing Systems of Equations (Alg 1.1)
Solving Problems with Systems of Linear Equations (Alg 1.1)
Additive Inverse of an Integer (Alg 1.2)
Integer Sum (Alg 1.2)
Integer Difference (Alg 1.2)
Integer Product (Alg 1.2)
Integer Quotient (Alg 1.2)
Adding Fractions (Alg 1.2)
Subtracting Fractions (Alg 1.2)
Multiplicative Inverse of a Fraction (Alg 1.2)
Product of Fractions (Alg 1.2)
Quotient of Fractions (Alg 1.2)
Basic Set Concepts: Elements in a Set (Alg 1.2)
Basic Set Concepts: Finite or Infinite (Alg 1.2)
Basic Set Concepts: Subsets (Alg 1.2)
Basic Set Concepts: Roster and Set-builder Forms (Alg 1.2)
Union of Sets (Alg 1.2)
Intersection of Sets (Alg 1.2)
Positive and Negative Exponents (Alg 1.2)
Integer Exponents and the Product Rule (Alg 1.2)
Integer Exponents and the Quotient Rule (Alg 1.2)
Integer Exponents and the Power Rule, Part 1 (Alg 1.2)
Integer Exponents and the Power Rule, Part 2 (Alg 1.2)
Square Roots of Integers (Alg 1.2)
Multiplication Rule for Radicals (Alg 1.2)
Division Rule for Radicals (Alg 1.2)
Simplifying Radicals, Part 1 (Alg 1.2)
Simplifying Radicals, Part 2 (Alg 1.2)
Continued on next page
44
Math, Continued
Description (continued)
Skill Level
J
Modules in Level
Classifying Polynomials (Alg 1.2)
Additive Inverse of a Monomial (Alg 1.2)
Monomial Sum (Alg 1.2)
Monomial Difference (Alg 1.2)
Monomial Product (Alg 1.2)
Monomial Quotient (Alg 1.2)
Binomial Sum (Alg 1.2)
Additive Inverse of a Binomial (Alg 1.2)
Binomial Difference (Alg 1.2)
Value of a Polynomial (Alg 1.2)
Polynomial Sum (Alg 1.2)
Polynomial Difference (Alg 1.2)
Product of a Monomial and Polynomial (Alg 1.2)
Simplifying Polynomial Expressions (Alg 1.2)
Product of Polynomials (Alg 1.2)
Quotient of a Monomial and Polynomial (Alg 1.2)
Quotient of a Binomial and Polynomial (Alg 1.2)
Greatest Common Factors of Monomials (Alg 1.2)
Monomial Factors of Polynomials (Alg 1.2)
Binomial Factors of Polynomials, Part 1 (Alg 1.2)
Binomial Factors of Polynomials, Part 1 (Alg 1.2)
Factoring the Difference of 2 Squares (Alg 1.2)
Factoring Perfect Square Trinomials (Alg 1.2)
Factoring Trinomials, Part 1 (Alg 1.2)
Factoring Trinomials, Part 2 (Alg 1.2)
Simple Equations in 1 Variable: Using Inspection (Alg 1.2)
Simple Equations in 1 Variable: Isolating the Variable (Alg 1.2)
More Difficult Linear Equations in 1 Variable (Alg 1.2)
Absolute Value of a Number (Alg 1.2)
Equations with Absolute Values (Alg 1.2)
Graphing a Solution Set on a Number Line (Alg 1.2)
Solving and Graphing Equations in 1 Variable (Alg 1.2)
Solving Problems With Linear Equations in 1 Variable (Alg 1.2)
Linear Inequalities in 1 Variable, Part 1 (Alg 1.2)
Linear Inequalities in 1 Variable, Part 2 (Alg 1.2)
Linear Inequalities in 1 Variable, Part 3 (Alg 1.3)
Continued on next page
45
Math, Continued
Description (continued)
Skill Level
K
Modules in Level
Solving Simple Quadratic Equations (Alg 1.2)
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring, Part 1 (Alg 1.2)
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring, Part 2 (Alg 1.2)
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring, Part 3 (Alg 1.2)
Quadratic Formula (Alg 1.2)
Solving Problems With Quadratic Equations (Alg 1.2)
Evaluating Rational Expressions (Alg 2.1)
Restrictions on Rational Expressions (Alg 2.1)
Equivalent Forms of Rational Expressions (Alg 2.1)
Simplifying Rational Expressions (Alg 2.1)
Sum of Rational Expressions, Part 1 (Alg 2.1)
Difference of Rational Expressions, Part 1 (Alg 2.1)
Product of Rational Expressions (Alg 2.1)
Quotient of Rational Expressions (Alg 2.1)
Common Denominators of Rational Expressions (Alg 2.1)
Sum of Rational Expressions, Part 2 (Alg 2.1)
Difference of Rational Expressions, Part 2 (Alg 2.1)
The Coordinate Plane (Alg 2.1)
Graphing Ordered Pairs (Alg 2.1)
Solutions of Linear Equations as Ordered Pairs (Alg 2.1)
Graphing a Linear Equation in 2 Variables (Alg 2.1)
Graphing a Linear Inequality in 2 Variables (Alg 2.1)
Slope of a Line from 2 Points (Alg 2.1)
The y-Intercept of a Line (Alg 2.1)
Using the Slope and y-Intercept to Graph a Line (Alg 2.1)
Finding the Slope and y-Intercept from an Equation (Alg 2.1)
Writing Equations in Slope-Intercept Form (Alg 2.1)
Identifying Graphs from Their Equations (Alg 2.1)
Parallel Lines and Their Slopes (Alg 2.1)
Perpendicular Lines and Their Slopes (Alg 2.1)
Equations of Parallel or Perpendicular Lines (Alg 2.1)
Solving Linear Systems of Equations: Graphs (Alg 2.1)
Classifying Linear Systems (Alg 2.1)
Continued on next page
46
Math, Continued
Description (continued)
Skill Level
K, contin.
L
Modules in Level
Solving Linear Systems of Inequalities: Graphs (Alg 2.1)
Solving Linear Systems of Equations: Substitution (Alg 2.1)
Solving Linear Systems of Equations: Addition (Alg 2.1)
Solving Linear Systems of Equations: Matrices 1 (Alg 2.1)
Solving Linear Systems of Equations: Matrices 2 (Alg 2.1)
Solving Problems with Linear Systems (Alg 2.1)
Change Experiments and Probability (Alg 2.1)
Determining the Probability of an Event (Alg 2.1)
Multiplication Principle of Counting (Alg 2.1)
Introduction to Vectors (Alg 2.1)
Vector Addition (Alg 2.1)
Rules for Exponents and Radicals (Alg 2.2)
Rationalizing the Denominator in Rational Expressions (Alg 2.2)
Applying Rules for Exponents and Radicals (Alg 2.2)
Scientific Notation (Alg 2.2)
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions (Alg 2.2)
Multiplying Algebraic Expressions (Alg 2.2)
Factoring Algebraic Expressions (Alg 2.2)
Factoring Sums and Differences of Perfect Cubes (Alg 2.2)
Factoring or Using the Quadratic Formula (Alg 2.2)
Rational Expressions: Simplify (Alg 2.2)
Rational Expressions: Add and Subtract (Alg 2.2)
Rational Expressions: Multiply and Divide (Alg 2.2)
Evaluating Expressions with Absolute Value (Alg 2.2)
Absolute Value, Inequalities, and Interval Notation (Alg 2.2)
Graphing Linear Inequalities in 1 Variable (Alg 2.2)
Graphing with Restrictions on the Variable (Alg 2.2)
Graphing Solution Sets of Associated Inequalities (Alg 2.2)
Calculating the Slope of a Line (Alg 2.2)
Point-Slope and Slope-Intercept Forms of Equations (Alg 2.2)
Equation of a Line Given a Point and Parallel Line (Alg 2.2)
Equation of a Line Given a Point and Perpendicular Line (Alg 2.2)
Perpendicular Bisector of a Line Segment (Alg 2.2)
Continued on next page
47
Math, Continued
Description (continued)
Skill Level
L, contin.
48
Modules in Level
Distance between 2 Points (Alg 2.2)
Distance between a Point and a Line (Alg 2.2)
Distance and Circles (Alg 2.2)
Parabola and Its Intercepts (Alg 2.2)
Parabola and Its Vertex (Alg 2.2)
Ellipse (Alg 2.2)
Hyperbola (Alg 2.2)
Equations of Ellipses and Hyperbolas (Alg 2.2)
Defining a Functions with Its Rule (Alg 2.2)
Finding Values of a Function Using Its Rule (Alg 2.2)
Equations and Graphs of Functions, Part 1 (Alg 2.2)
Equations and Graphs of Functions, Part 2 (Alg 2.2)
Translations and Transformations (Alg 2.2)
Functional Values (Alg 2.2)
Composite Functions (Alg 2.2)
Domain Values of Composite Functions (Alg 2.2)
Inverse of a Function (Alg 2.2)
Determining if a Function Has an Inverse (Alg 2.2)
Solving Problems with Linear Functions (Alg 2.2)
Solving Problems with Quadratic Functions (Alg 2.2)
Properties of Exponential Functions (Alg 2.2)
Properties of Logarithmic Functions (Alg 2.2)
Recognizing Graphs of Types of Functions (Alg 2.2)
Solving Problems: Exponential and Logarithmic (Alg 2.2)
Exponential Growth (Alg 2.2)
Exponential Decay (Alg 2.2)
Copyright © 2005 by PLATO Learning, Inc.All rights reserved. PLATO® is a registered trademark of PLATO Learning, Inc. PLATO
Learning is a trademark of PLATO Learning, Inc. All company names and products are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective holders.
FASTRACK Advantage Assessments (v2) for PLATO Web Learning Network users