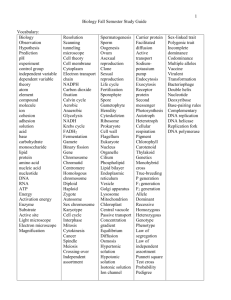
Biology Standards assessment #4 study guide

Biology Standards Assessment #4 Guide with answers.
1.
What does Lugol’s test for and what is the color change?
Starch. Turns black
2.
What does Benedict’s test for and what is the color change? Simple sugars, turns to a brown then orange.
3.
What does Sudan III test for and how do you know that it is a positive test? Lipids. Red oily layer separates.
4.
Biuret’s is an indicator for which molecule and what color change do you look for?
Proetins, turns violet
5.
How does an enzyme affect chemical reactions? Speeds up a chemical reaction
6.
What are the types of carbon-based molecules that were talked about in class?
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids
7.
What do you look for to identify a carbohydrate molecule? 1:2:1 ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
8.
If you look at the structure of a molecule and you see an NH
2, an R-group, and COOH, what type of molecule is it? Amino acid
9.
What is the difference in exothermic and endothermic reactions?
Exothermic releases energy and endothermic absorbs energy from the surroundings.
10.
What is pH? The amount of hydrogen ions that is present in a solution. The more hydrogen ions present, the lower the pH.
11.
What is a theory? Proposed explanation for a wide range of observations.
12.
What is an ion? An atom that has lost or gained electrons
13.
What is biodiversity? Variety of life
14.
What is Biology? Study of life
15.
What is an ecosystem? Physical environment with different species that interact
16.
How does an organism maintain homeostasis? Using negative feedback
17.
What is a carbohydrate molecules that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen – sugars and starches
18.
What is the difference in a monomer and a polymer? Monoer are subunits. Polymers is a large molecule of monomers.
19.
How do you know a molecule is a protein? Proteins are made of more than one amino acid
20.
How do you identify a nucleic acid?
NH
2, an R-group, and COOH
21.
How do you identify a lipid? Greater ratio of carbon and hydrogens
22.
What is cohesion? The attraction among molecules that are the same
23.
What is adhesion?
Attraction of molecules that are different.
24.
What is the difference in reactants and products? Reactants are the things that undergo a chemical reaction while the products are a result of an equation.
25.
If given a chemical equation, be able to tell the products and reactants. (look at page 50 for an example)
26.
What is activation energy? The amount of energy that is needed to start a chemical reaction.
27.
What is a cell? Basic unit of life
28.
What is the difference in a eukaryotic cell and a prokaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles while prokaryotic cells do not.
29.
I may have a picture of a cell on the test and have you identify an organelle from it. See page 74 in your book
30.
You will need to know each cell organelle and their functions. Use the chart you copied in your notes or the book.
31.
What is the function of the nucleolus? Makes ribosomes
32.
Why is the mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell? Supplies energy to the cell.
33.
Describe the cell membrane.
Forms a boundary between the inside and outside of a cell and only allows certain things to enter and exit.
34.
What does selective permeability mean? Allows some, but not all, materials to cross
35.
What is diffusion and osmosis? Diffusion is the movement of particles other than water from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. Osmosis is the diffusion of water.
36.
What is the difference in passive and active transport? Passive transport does not require energy and active transport does.
37.
Describe each of the following: a.
Isotonic has the same concentration on both sides of the cell b.
Hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of particles than a cell c.
Hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of particles than a cell.
38.
Explain why facilitated diffusion does not require energy from a cell. Facilitated diffusion allows molecules to pass through a transport protein from high to low.
39.
What are the two types of active transport and describe each one?
Endocytosis – engulfs particles and brings them into the cell.
Exocytosis – particles are in a vesicle and are released outside of the cell.
40.
Describe mitosis. Is the division of the cell nucleus and the contents -
41.
What are the 4 stages of mitosis? Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
42.
Tell what happens to the chromosomes in each stage of mitosis. 1 st they condense,2 nd line up in the center, 3 rd split in half and move to the sides, 4 th uncoil in two new cells. Look at page 141
43.
Be able to tell which stage of mitosis a cell is in from a picture. (look at page141 for help)
44.
What is apoptosis? Programmed cell death.
45.
How does a cell know that it needs to grow? Growth factor tells the cells to start dividing.
46.
What is uncontrolled cell division? Cancer
47.
What is asexual reproduction? Offspring are produced from a single parent.
48.
What is photosynthesis and the formula? – capturing sunlight to make sugar for plants a.
6H2O + 6CO2 = C6H12O6 +6O2
49.
What is cellular respiration and the formula? Releases chemical energy from sugar to make ATP when oxygen is present. C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6H2O+6CO2+ATP
50.
How do cellular respiration and photosynthesis relate?
The products of one are the reactants of the other
51.
Describe ATP and ADP. ATP is the high energy molecule that transfers energy. ADP is the low energy miles that is converted back to ATP
52.
What is the light dependent and light independent reaction of photosynthesis? Lightdependent captures sunlight and the light-independent uses energy from the lightdependent to make sugars.
53.
What is the difference in aerobic and anaerobic? Aerobic reactions require oxygen and anaerobic do not.
54.
What is fermentation? Anaerobic process by which ATP is produced by glycolysis
55.
What are sex chromosomes and autosomes? Sex chromosomes directly control the development of sexual characteristics – make you male or female.
Autosomes contains genes for characteristics not directly related to the sex of the organism.
56.
What are somatic cells and gametes? Somatic cells are your body cells while gametes are you sex cells (sperm and egg)
57.
What is meiosis? Form of nuclear division that divides a diploid cell into haploid cells
58.
Know the steps of meiosis and be able to pick the stages out.
Look at page 174-175 in book
59.
What is the difference in haploid and diploid?
Haploid means that the cell only has one copy of each chromosome. Diploid means a cell has two copies of each chromosome.
60.
What are traits? Characteristics that are inherited
61.
What is a phenotype? The physical appearance of a trait
62.
What is a genotype? The genetic makeup of an organism.
63.
Describe the difference in heterozygous and homozygous. Heterozygous has two different alleles for a trait. Homozygous has two of the same alleles for the trait.
64.
What is an allele? The different forms of a trait
65.
What is the difference in a dominant and recessive trait? Dominant is the allele that is expressed when two different alleles or two different alleles are present. Recessive is the the allele that is only expressed when two copies are present.
66.
What do we use to represent the different alleles? Letters, Capital for dominant and lowercase for recessive.