Colter_4275_Taxonomy
advertisement

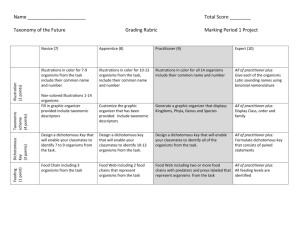
Unit: Biological Evolution: Unity and Diversity th Teacher’s Name: Colter Huhn Grade Level: 7 Date: Friday Lesson Topic/Title: Taxonomic Keys Expected Duration of Lesson: 18 minutes (cut down activity based on time.) Lesson Objectives: SWBAT…: o Create a classification system and dichotomous taxonomic key that leads to identification of a single organism through paired statements o Understand how taxonomic keys are a tool used with a classification system to identify organisms Academic Language Objective: • Taxonomic Key, Dichotomous Key Standards/Benchmarks Addressed: SC8.1.4: Diversity of Organisms: Students investigate the interconnectedness of organisms, identifying similarity and diversity of organisms through a classification system of hierarchical relationships and structural homologies. • SC8.2.3: Students clearly and accurately communicate the result of their own work, as well as information obtained from other sources. • EU: Organism share many similarities, yet are very diverse. Materials and Equipment Needed: • Smartboard, Interactive Science: The Diversity of Life text/workbook, PowerPoint, Notebooks, 6-­‐ Ziploc bags containing 20 pre-­‐cut cards with alien pictures on them (numbered 1-­‐20), Creepy Critters Chart (one per table), Creepy Critters Project Outline (two per table) Classroom Management and Organizational Considerations: Discuss working quietly so as not to disturb others. Dismiss tables at a time to get computers so not a large group of people. Must walk around constantly to keep students on task and answer questions about problems. Step by Step Procedures: Include the following elements – • • • • Hook: Dichotomous key of students in our classroom on the board with all the students names listed. (2 min.) Pretest: “What is classification and why is it important? What is a tool that scientists use to identify organisms based paired statements?” Have projected on screen and read them out loud. o Answer on half sheet of paper pass forward (1 min.) Objectives: “Create a dichotomous taxonomic key that leads to identification of single organisms by distinguishing characteristics. Understand how taxonomic keys are a tool used with a classification system to identify organisms.” Post on the projection screen and read out loud. Review: Have different students answer the 7 levels of taxa in classification, what the three domains are, what the four main kingdoms of Eukaryotes are (3 min.). o Transition: How are the characteristics of classification useful? Lecture: Relate classification to many examples the students know, and those from other fields of science. “Classification is important in everyday life,” (10 min). o Have students get out their cell phones and open their contacts. Ask if they wanted to call their mom, and they forgot her number, how they would find it in their contacts list. (Alphabetical) You explain that makes your contacts classified. o Talk about going to the grocery store, and if you were looking for butter, where would you go? (Dairy section). Then ask what if I wanted milk too, where would I go? (Same). “What about yogurt?” (Same thing.) Tell them that this is classification, grouping objects with similar characteristics. It makes it easier to find one specific item, by its grouping with similar items. o Then say different genres and artists in your iPod, or books in a library by author and the Dewey decimal system. o Then tell them it is used in other sciences § In Chemistry, elements on the Periodic Table (Noble Gases, Halogens, Alkali Metals, Transition Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals). § In Geology, rocks are classified into their different types (igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic). o Why Do Biologists Classify Organisms?: Imagine walking into a rainforest and trying to find information about an organism you see. You have a huge book of animals listed by their names from A-­‐Z. How are you going to identify this animal? § This is why scientists have split them into their groups using the Hierarchy of Life (K, P, C, O, F, G, S.) acronym ask them what they mean (review). o Explain organisms can’t always be identified, but taxonomic keys are very useful in doing so. (4 min.) o Define taxonomic key o Explain what paired statements are o Explain there are steps to follow • Activity/Assessment: Creep Critters Project pass out Ziploc bags to each table containing 20 numbered alien drawings and Project description, two per table. (22 min.) o Break tables up further into two groups of two Classification Team and Dichotomous Key Team. o Explain that the teams should collaborate constantly o Have classification team start right away, and have dichotomous key team look at page 20-­‐21 in their textbook. o Tell dichotomous key team to start as soon as they can on their key and explain what they are doing to the Classification team. • Assessment: “What is classification and why is it important? What is a tool that scientists use to identify organisms based paired statements?” Have projected on screen and read them out loud. o Answer on half sheet of paper pass forward (1 min.) • Review: Briefly review what a taxonomical key is and how they are used with classification to identify organisms. (1 min.) Differentiation/Special Consideration Models: • When dividing teams of two at tables pair higher level students with lower level students. The higher level students will understand the concepts more by teaching them to the lower level student, and the lower level student will gain more hearing the information by someone of their own age with a more similar “voice” than I. Diversity/Cultural Considerations: Classification team uses a lot of visuals, I could purposefully put students with language barriers or learn better visually in this team. Names:_____________________ Date:______________________ Creepy Critters! Imagine it's the year 2525. A planet similar to Earth has recently been found in a newly identified solar system in another galaxy. We have sent a space probe with a molecular transport beam to this planet to beam back a variety of different living creatures. Scientists examine the structure of each of these creatures and realize that they need to create a dichotomous key and classification system to help them compare the alien life forms to each other and discover how they might be related. The lead scientist sends your team illustrations of the organisms and asks you to help develop this classification system. Your teams’ role is to study the illustrations and come up with a possible classification scheme and dichotomous key based on the information provided about each organism. You'll be asked to explain to the scientific team how and why you organized the creatures this way. Procedures: Split your table into two teams of two. Two of you are responsible for classifying the aliens two of you are responsible for making a dichotomous key. Classification Team: 1. Study cards labeled (1-­‐20). Note similarities and differences among the creatures. You might have groups based on bristles, antennae, eyes, body shape etc. 2. Choose one general characteristic to categorize your aliens into two large groups. Ex: has ‘abc’ and does not have ‘abc’. 3. Groups do not have to have the same number of aliens in each. 4. After you have completed your two groups, split each group into two new groups. 5. Choose one characteristic to separate the first group. 6. Choose one characteristic to separate the second group. 7. You should have 4 groups when completed. 8. Continue splitting each group until you can no longer split them into new categories anymore. 9. Fill in the chart based on characteristics you’ve identified that separate the aliens. Dichotomous Key Team: 1. Use Page 20 in your book to help you. 2. Start with the most inclusive characteristics work your way down to the most specific. 3. You will need to use your Classification teams’ chart. Both: 1. Classification needs to happen first the dichotomous key team, should assist the classification team in organizing the aliens so they can be separated into a key. 2. The classification team should also assist with the making of the key by helping come up with the paired statements. 1 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 19 18 20 12/5/12 Identifying Organisms • Our Classroom 1a: Students Male (Mike, Dusty, David, Sonny)…………………………Go to 2 1b: Students Female (Mariel, Melissa, Paige, Dr. Burrows).……………Go to 2 2a: With other than brown eyes (LIST ALL NAMES)……………………......Go to 3 2b: With eye color other than brown (List All Names)………………....... 3a: With Blonde hair…………………………………………………………..John Doe (only student with non-brown eyes and blonde hair) 3b: With hair other than blonde………………………………………….Not Brown Eyed Students Taxonomic Keys h7p://www.qldscienceteachers.com/junior-­‐‑science/ biology/classification-­‐‑of-­‐‑organisms h7p://davidmoskowiG.net/publications/ wildlife-­‐‑of-­‐‑the-­‐‑pacific-­‐‑northwest/ h7p://ecx.images-­‐‑amazon.com/images/I/ 51PA3RDG3PL._SL500_AA300_.jpg Introduction • • • • • Classification is an important part of everyday life. Grocery Store Library (Dewey Decimal System) Your Music on an iPod or Computer In Chemistry: Elements on the Periodic Table o o o o o Noble Gases Halogens Alkali Metals Transition Metals Alkaline Earth Metals • In Geology: Rocks are classified into their different types o Igneous o Sedimentary o Metamorphic Review • We know that organisms are classified into 7 levels, what are they? • The 3 Domains are? • The 4 main Kingdoms are? • We know characteristics of each of these groups, but how is that useful? h7p://www.squidoo.com/the-­‐‑unique-­‐‑characteristics-­‐‑of-­‐‑ birds? utm_source=google&utm_medium=imgres&utm_campaign =framebuster Why Do Biologists Classify Organisms? • Imagine how difficult it would be to find information about one particular organism if you had no idea even where to begin. • Organizing living things into groups is what biologists have done. • Classification: process of grouping things based on their similarities h7p://usiweb.usi.edu/students/2005/s_t_u/schaefert/ rainforestanimals.jpg Lesson Objectives • Create a dichotomous taxonomic key that leads to identification of single organisms by distinguishing characteristics • Understand how taxonomic keys are a tool used with a classification system to identify organisms 1 12/5/12 How can we tell these aliens apart? Taxonomic Key • It’s not always possible to know the identity of an organism. • Taxonomic Key: consists of a series of paired statements that describe the various physical characteristics of different organisms. h7p://www.webquest.hawaii.edu/kahihi/sciencedictionary/images/ taxonomicKey.gif We can classify the aliens by their characteristics. • • • • • • • Creepy Cri7ers Project • Work together • Classification team start immediately filling in chart • Dichotomous Key Team: reference Page 20-21 and begin writing outline of key (fill in once classification team has finished) Head Shape Body Shape # of Eyes Hair Antennae Spot on Body Etc. h7ps://twimg0-­‐‑a.akamaihd.net/profile_images/ 188302352/nasalogo_twi7er.jpg Assessment Review h7p://youoffendmeyouoffendmyfamily.com/wordpress/wp-­‐‑ content/uploads/2010/07/the-­‐‑comic-­‐‑book-­‐‑guy-­‐‑pondering1.gif h7p://deepintoscripture.com/2012/02/02/in-­‐‑which-­‐‑im-­‐‑all-­‐‑ focussed-­‐‑then-­‐‑oooooh-­‐‑shiny/ • What is classification and why is it important? • What is a tool that scientists use to identify organisms based on paired statements? • Taxonomic Key: consists of a series of paired statements that describe the various physical characteristics of different organisms • Classification is used to identify organisms using a dichotomous or taxonomic key. 2