YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY COURSE SYLLABUS
advertisement
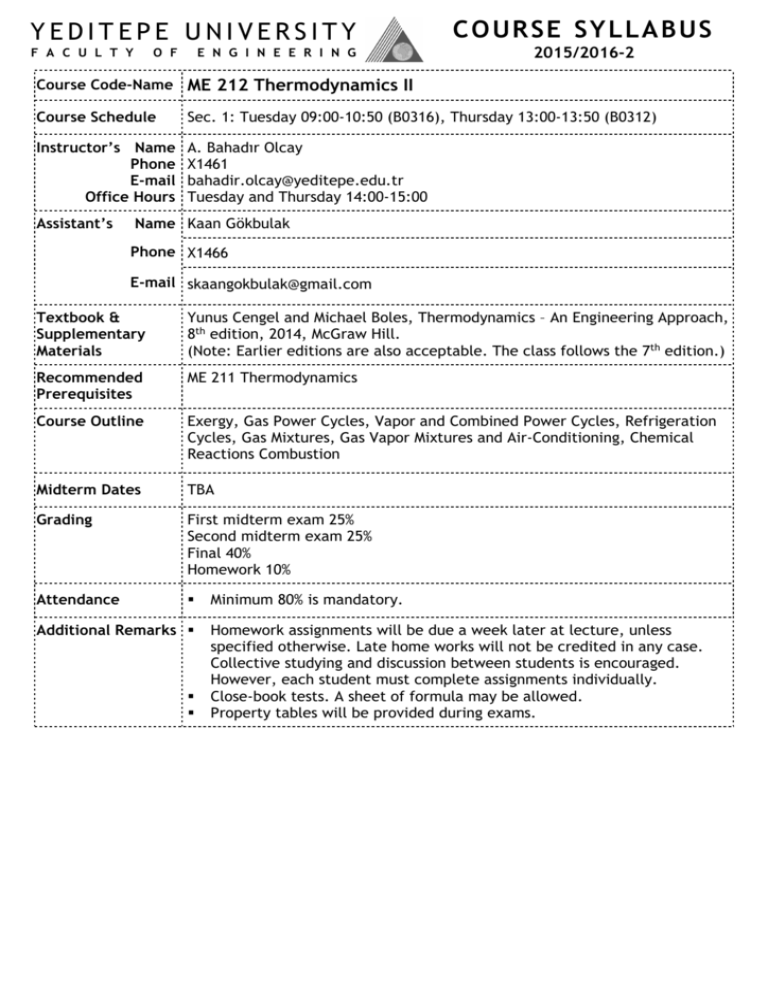
YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY F A C U L T Y O F E N G I N E E R I N G C OU R SE S YL L A BU S 2015/2016-2 Course Code-Name ME 212 Thermodynamics II Course Schedule Sec. 1: Tuesday 09:00-10:50 (B0316), Thursday 13:00-13:50 (B0312) Instructor’s Name Phone E-mail Office Hours A. Bahadır Olcay X1461 bahadir.olcay@yeditepe.edu.tr Tuesday and Thursday 14:00-15:00 Assistant’s Name Kaan Gökbulak Phone X1466 E-mail skaangokbulak@gmail.com Textbook & Supplementary Materials Yunus Cengel and Michael Boles, Thermodynamics – An Engineering Approach, 8th edition, 2014, McGraw Hill. (Note: Earlier editions are also acceptable. The class follows the 7th edition.) Recommended Prerequisites ME 211 Thermodynamics Course Outline Exergy, Gas Power Cycles, Vapor and Combined Power Cycles, Refrigeration Cycles, Gas Mixtures, Gas Vapor Mixtures and Air-Conditioning, Chemical Reactions Combustion Midterm Dates TBA Grading First midterm exam 25% Second midterm exam 25% Final 40% Homework 10% Attendance Minimum 80% is mandatory. Additional Remarks Homework assignments will be due a week later at lecture, unless specified otherwise. Late home works will not be credited in any case. Collective studying and discussion between students is encouraged. However, each student must complete assignments individually. Close-book tests. A sheet of formula may be allowed. Property tables will be provided during exams. YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY F A C U L T Y O F E N G I N E E R I N G C OU R SE S YL L A BU S 2015/2016-2 Course Code-Name ME 212 Thermodynamics II Course Objectives 1.To describe the fundamentals of the power and refrigeration systems, mixtures and chemical reactions 2.To give students the background required to pursue further studies in thermal science 3.To provide students the necessary tools to achieve the knowledge of thermal systems Course Outcomes i. Adequate knowledge in mathematics, science and engineering subjects pertaining to the relevant discipline; ability to use theoretical and applied information in these areas to model and solve engineering problems. (Matematik, fen bilimleri ve kendi dalları ile ilgili mühendislik konularında yeterli bilgi birikimi; bu alanlardaki kuramsal ve uygulamalı bilgileri mühendislik problemlerini modelleme ve çözme için uygulayabilme becerisi.) ii. Ability to identify, formulate, and solve complex engineering problems; ability to select and apply proper analysis and modeling methods for this purpose. (Karmaşık mühendislik problemlerini saptama, tanımlama, formüle etme ve çözme becerisi; bu amaçla uygun analiz ve modelleme yöntemlerini seçme ve uygulama becerisi.) xii. Tasarım dahil olmak üzere ısıl sistemler alanında çalışabilme becerisi