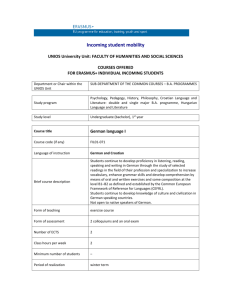
GER2140 German Cinema - The Chinese University of Hong Kong
advertisement
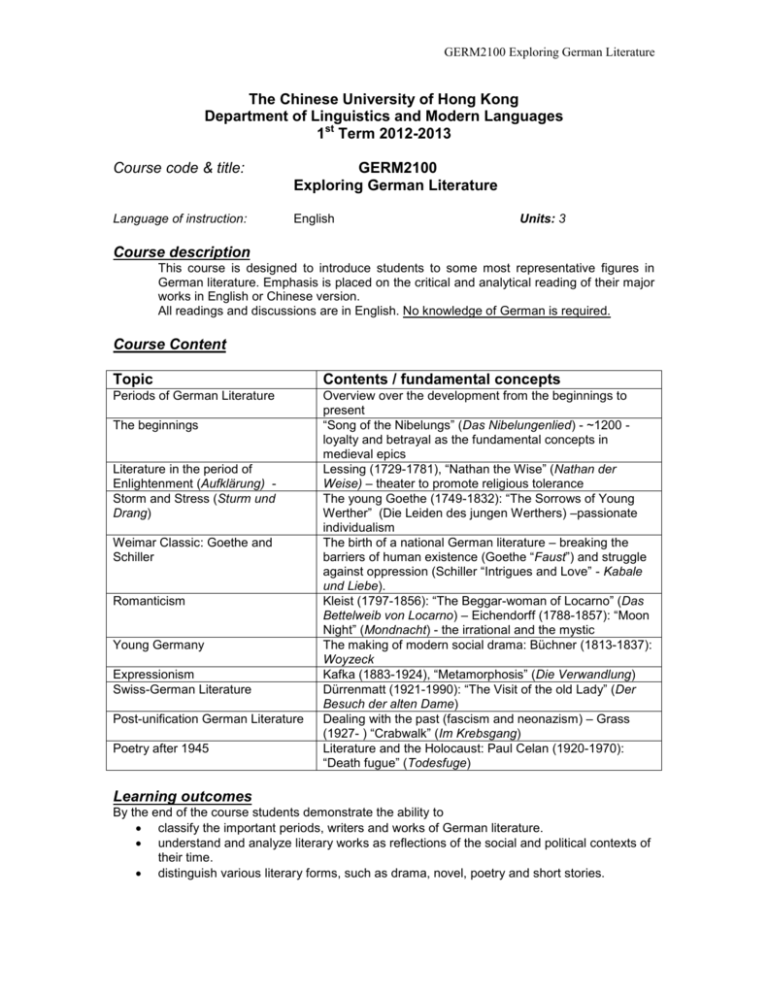
GERM2100 Exploring German Literature The Chinese University of Hong Kong Department of Linguistics and Modern Languages 1st Term 2012-2013 Course code & title: GERM2100 Exploring German Literature Language of instruction: English Units: 3 Course description This course is designed to introduce students to some most representative figures in German literature. Emphasis is placed on the critical and analytical reading of their major works in English or Chinese version. All readings and discussions are in English. No knowledge of German is required. Course Content Topic Contents / fundamental concepts Periods of German Literature Overview over the development from the beginnings to present “Song of the Nibelungs” (Das Nibelungenlied) - ~1200 loyalty and betrayal as the fundamental concepts in medieval epics Lessing (1729-1781), “Nathan the Wise” (Nathan der Weise) – theater to promote religious tolerance The young Goethe (1749-1832): “The Sorrows of Young Werther” (Die Leiden des jungen Werthers) –passionate individualism The birth of a national German literature – breaking the barriers of human existence (Goethe “Faust”) and struggle against oppression (Schiller “Intrigues and Love” - Kabale und Liebe). Kleist (1797-1856): “The Beggar-woman of Locarno” (Das Bettelweib von Locarno) – Eichendorff (1788-1857): “Moon Night” (Mondnacht) - the irrational and the mystic The making of modern social drama: Büchner (1813-1837): Woyzeck Kafka (1883-1924), “Metamorphosis” (Die Verwandlung) Dürrenmatt (1921-1990): “The Visit of the old Lady” (Der Besuch der alten Dame) Dealing with the past (fascism and neonazism) – Grass (1927- ) “Crabwalk” (Im Krebsgang) Literature and the Holocaust: Paul Celan (1920-1970): “Death fugue” (Todesfuge) The beginnings Literature in the period of Enlightenment (Aufklärung) Storm and Stress (Sturm und Drang) Weimar Classic: Goethe and Schiller Romanticism Young Germany Expressionism Swiss-German Literature Post-unification German Literature Poetry after 1945 Learning outcomes By the end of the course students demonstrate the ability to classify the important periods, writers and works of German literature. understand and analyze literary works as reflections of the social and political contexts of their time. distinguish various literary forms, such as drama, novel, poetry and short stories. GERM2100 Exploring German Literature discuss and compare the portrayal of basic human issues (love, hate, friendship, loyalty, betrayal, family, coming of age, struggle for freedom, the supernatural) in important works of German literature in different periods. approach literature from a creative perspective through hands-on practice on drama and poetry. Learning activities Lecture (hr) in/out class 2 -- Interactive tutorial (hr) Projects (Presentation) (hr) in/out class 1 -- in/out class -- 2 Web-based teaching (hr) Homework / Selfstudy (hr) in/out class in/out class -- 0.5 3 All listed activities are mandatory (M). Assessment scheme Task nature Participation in class Presentation Assignments Test Description Weight active participation in class, including class preparation and knowledge of assigned texts introducing a German author and his works (in groups of 2-3 students) 2 assignments on 2 works discussed in class (each 15%) quiz and questions 10% 30% 30% 30% Learning resources for students Excerpts of the selected works are put online on moodle Handouts Recommended reading: Watanabe-O’Kelly, Helen (ed) (1997) The Cambridge history of German literature. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Kim, Vivian (1992) A concise history of German literature to 1900. Columbia: Camden House. Stoehr, Ingo Roland (2001) German literature of the twentieth century: from aestheticism to postmodernism. Rochester, N.Y.: Camden House. All books are put on reserve in the University Library. Feedback for evaluation Our programme highly values students’ feedback and comments and is happy to use them for reflection on our teaching and improvement. Students are very welcome to provide comments and feedback on the course any time to their course teacher or the course level coordinator through email or in personal conversation. In addition, students’ feedbacks will be collected in the middle of the term through an open-end questionnaire and the teacher will discuss the feedbacks in class and make improvements if necessary. The course will also follow the university’s course evaluation exercise at the end of the term, and students’ feedbacks will be used for future course planning and teaching. GERM2100 Exploring German Literature Course schedule Remarks Week 1 Sep 10 - 15 Content Introduction to the course Overview of German Literature The medieval Epic Week 2 Sep 17 - 22 Enlightenment Week 3 Sep 24 - 29 Storm and Stress / Weimar Classic Week 4 Oct 1 - 6 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Oct 8 - 13 Oct 15 - 20 Oct 22 - 27 Week 8 Oct 29 – Nov 3 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Nov 5 - 10 Nov 12 - 17 Nov 19 - 24 Week 12 Nov 26 – Dec 1 Poetry after 1945 Week 13 Dec 3 - 8 Final discussion Test No class Oct 1: Public holiday Weimar Classic (continued) Romanticism Young Germany Assignment 1 (due 22 Oct.) Expressionism Swiss-German literature Post-Unification literature continued Assignment 2 (due 17 Dec.) Subject to changes Class sections and teacher’s contact details: Time Mo14:30-16:15 We13:30-14:15 Room UCA102 UCA111 Teacher Dr Ulrich WANNAGAT E-mail/Tel.: uwannagat@cuhk.edu.hk Tel.: 39437699 Office Leung Kau Kui Building G/F Rm 23 For further information and inquiries you are welcome to contact the teacher! Office hours: Tu10:00-12:00 & Th14:00-15:00 or gladly by appointment Attention is drawn to University policy and regulations on honesty in academic work, and to the disciplinary guidelines and procedures applicable to breaches of such policy and regulations. Details may be found at h t t p : / / w w w. c u h k . e d u . h k / p o l i c y / a c a d e m i c h o n e s t y / . With each assignment, students will be required to submit a statement that they are aware of these policies, regulations, guidelines and procedures.