CCNA 2
advertisement

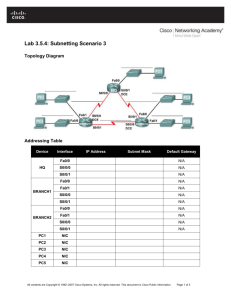
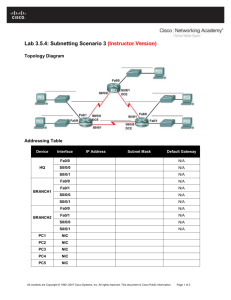
Tecnologies de Xarxes D’Ordinadors (CCNA) CCNA 2: ROUTING PROTOCOLS AND CONCEPTS V4.0 CASE STUDY CCNA 2: Routing Protocols and Concepts v4.0 Case Study Overview and Objectives This case study allows students to complete a network design, implementation, and troubleshooting project using the skills gained in CCNA 2. Students will use the skills that have already been developed to use, make and connect the proper cabling to the appropriate devices. It is crucial to read and understand the scenarios to make sure that all requirements are fulfilled. Each scenario guides the student through the proper steps to ensure that the project is completed properly. This case study requires the student to accomplish the following tasks: Set up the physical layout of the network using the diagram and accompanying narrative Correctly configure the routers with a basic router configuration Correctly configure the routing features that the design requirements describe Troubleshoot and test the connectivity between all devices Provide detailed documentation in a prescribed form, as listed in the deliverables section 2 CCNA 2: Routing Protocols and Concepts v4.0 Case Study Scenario and Phase 1: Project Description ISP Lo2 Lo1 HQ LAN_B Lo0 HQ LAN_A HQ EIGRP AS 10 S0/1 S0/0 OSPF PID 20 Branch1 LAN_A S0/1 S0/0 PC 1 Fa0/0 S0/1 Branch1 S0/0 SW Branch2 LAN Fa0/0 PC 2 Branch2 Lo0 Branch1 LAN_B A company has several people responsible for maintaining various sections of the internetwork infrastructure. Many technicians have done an excellent job with the small portion for which they are responsible. One of the other network associates who was responsible for a larger portion of the infrastructure suddenly left the company. This left redesign and implementation on this portion of the internetwork unfinished. A technician is given the task to complete the design and implementation of the unfinished network. After taking home the documentation to study over the weekend, it is apparent to the technician why the network associate left suddenly. The few documents that existed were poorly written. So during the weekend the technician reconstructs the diagram above from an existing diagram that was found. It represents the new internetwork design. It shows the planned devices at each site. After returning to work Monday morning, the technician presents the new diagram to the Network Infrastructure Team Leader that assigned the project. After discussion, it is determined that new documentation must be developed for the project. Use the following information to implement the network. Network address: 193.100.50.0/24 Required number of subnets: 7 3 CCNA 2: Routing Protocols and Concepts v4.0 Case Study Phase 2: IP Addressing Now that the basic plan is in place, the team leader assigns the technician to develop a prototype for the new internetwork. Use the network address assigned along with the subnetting requirements, to subnet the network. From the IP addressing scheme, assign IP addresses to the appropriate interfaces on all routers and computers in the internetwork. Obtain approval of this phase of development from the team leader (Instructor) before proceeding to Phase 3. IP Addressing Requirements: The waste of IP addresses have to be the minimum per network assigned Branch1 LAN_A will require 60 host IP addresses Branch1 LAN_B will require 10 host IP addresses HQ LAN_A will require 10 host IP addresses HQ LAN_B will require 10 host IP addresses Branch2 LAN will require 60 host IP addresses The link between HQ and Branch1 will require an IP address for each end of the link The link between HQ and Branch2 will require an IP address for each end of the link The IP addressing allocated has to allow summarize each routing domain separately Fill in the chart below to document the final addressing scheme: Assign the last IP address available to end devices Assign the first IP address available to routers ISP is represented as a loopback in this prototype of the final network The link between Branch1 and Branch2 has a 194.0.0.0/30 assigned Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 N/A Lo0 N/A S0/0 N/A Branch1 S0/1 194.0.0.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch2 HQ S0/0 N/A N/A 194.0.0.2 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/1 N/A S0/0 N/A S0/1 N/A Lo0 N/A Lo1 N/A Lo2 200.200.200.1 255.255.255.252 ISP 4 CCNA 2: Routing Protocols and Concepts v4.0 PC 1 N/A PC 2 N/A Case Study Phase 3: Basic Router and Workstation Configuration The technician is assigned to create a basic configuration on routers and workstations. The requirements are as follows: 1. Configure router name, passwords, and banner display. Console Password: cisco Vty password: cisco Enable secret password: class Banner MOTD: 2. 3. *************************** Welcome to <router_name> CLI. *************************** Configure interfaces. Configure the IP address and subnet mask Configure descriptions in point-to-point interfaces: Link <router1_name> - <router2_name> Configure descriptions in LAN interfaces: LAN <LAN_name> Configure end devices. Configure the IP address and subnet mask Configure the Default Gateway Phase 4: Routing Configuration The technician is assigned to configure the routing of the topology. The requirements are as follows: OSPF with the Process ID 20. Serial0/0 and Loopback1 of HQ are inside the OSPF process. EIGRP with Autonomous System 10. Branch2 propagates OSPF routing information about all its directly connected networks. Branch2 sends and receives OSPF routing updates only through serial0/1 interface between HQ and Branch2. HQ sends and receives OSPF routing updates only through serial0/0 interface between HQ and Branch2. EIGRP activated only for the specific subnets in the domain. Branch1 propagates EIGRP routing information about all its directly connected networks. 5 CCNA 2: Routing Protocols and Concepts v4.0 Branch1 sends and receives EIGRP routing updates only through serial0/0 interface. The HQ’s default gateway is ISP. Case Study EIGRP does not include any summarized network to NULL0 interfaces in any routing table. Serial0/1 and Loopback0 of HQ are inside the EIGRP process. HQ sends and receives routing updates only through serial0/1 interface. Connection between domains: o The connection between Branch1 and the networks inside OSPF domain requires only one command. You have to reach Branch2 LAN, the serial link HQ-B2 and the HQ’s Loopback1 from any host in Branch1 LANs. The packets will pass through B1-B2 Link. A default static route is not valid. o The connection between Branch2 and the networks inside EIGRP domain requires only one command. You have to reach Branch1 LANs, the serial link HQ-B1 and the HQ’s Loopback0 from any host in Branch2 LAN. The packets will pass through B1-B2 Link. A default static route is not valid. Branch1 and Branch2 forwards packets to HQ when they not find a match between the destination IP address in the packet header and their routing tables (NOTE: You can only modify the HQ’s configuration to achieve this requirement). Phase 5: Verifying the Network The technician has to verify if there is full connectivity in the network. Phase 6: Documenting the Network In order to support the network properly, documentation is required. Create documentation that is logically organized to make troubleshooting simpler: show cdp neighbors show ip interface brief show ip route show ip protocol show interface <type_slot_port> show version show startup-config 6 CCNA 2: Routing Protocols and Concepts v4.0 Case Study Case Study Deliverables The key lesson of this case study is the importance of thorough and clear documentation. There should be two types of documentation completed. General Documentation: A complete narrative of the project should be typed using word processing software. Since the scenarios break up the entire task into pieces, take care to address each scenario task so that any layperson could understand that particular task. Microsoft Excel or another spreadsheet program could be used to simply list the equipment and serial numbers. Microsoft Visio or any paint program could be used to draw the network. Provide documentation that specifies how the connectivity was tested. Technical Documentation: The technical documentation should include details of the network topology. Visio or any paint program could be used to draw the network. The technical documentation has to include a table or tables with the following details: IP addressing of all interfaces DCE/DTE information Router passwords Banner MOTD Interface descriptions IP addressing and gateway assignments for all PCs Router output from the following commands should be captured and placed into this documentation (for each router): show cdp neighbors show ip interface brief show ip route show ip protocol show interface <type_slot_port> show version show startup-config 7