Definition of Problem Broad Problem
advertisement
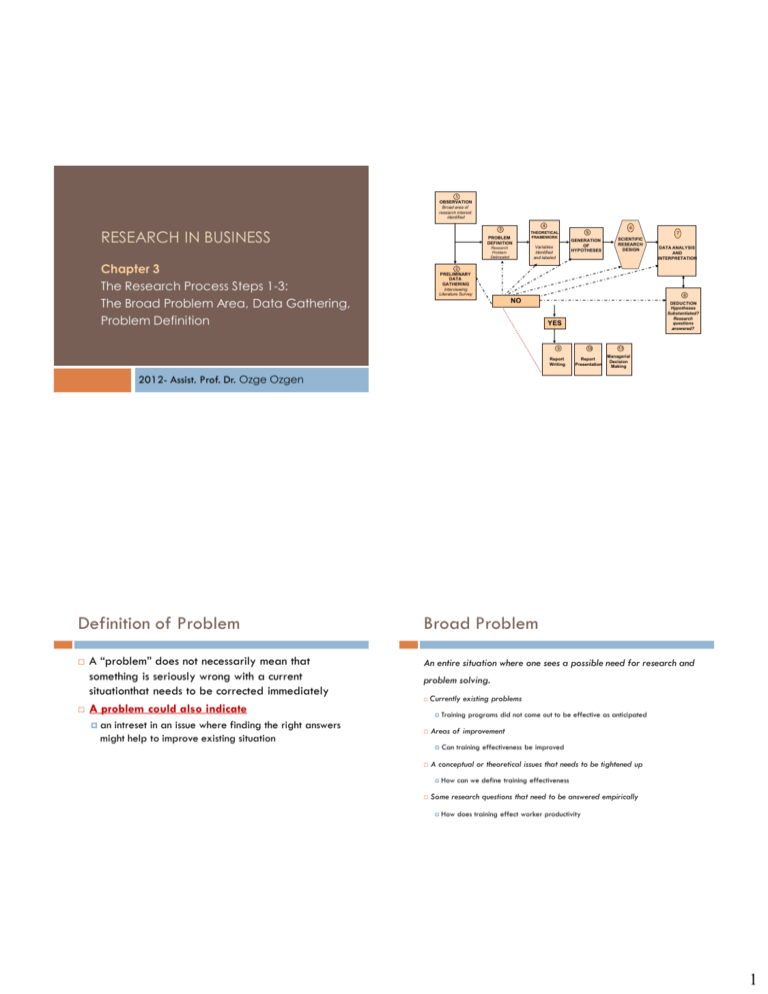
1 OBSERVATION Broad area of research interest identified RESEARCH IN BUSINESS 4 3 PROBLEM DEFINITION Variables identified and labeled Research Problem Delineated Chapter 3 The Research Process Steps 1-3: The Broad Problem Area, Data Gathering, Problem Definition 6 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK 5 GENERATION OF HYPOTHESES 7 SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH DESIGN 2 PRELIMINARY DATA GATHERING Interviewing Literature Survey DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION 8 NO DEDUCTION Hypotheses Substantiated? Research questions answered? YES 9 10 Report Writing Report Presentation 11 Managerial Decision Making 2012- Assist. Prof. Dr. Ozge Ozgen Definition of Problem A “problem” does not necessarily mean that something is seriously wrong with a current situationthat needs to be corrected immediately A problem could also indicate an intreset in an issue where finding the right answers might help to improve existing situation Broad Problem An entire situation where one sees a possible need for research and problem solving. Currently existing problems Areas of improvement A conceptual or theoretical issues that needs to be tightened up Some research questions that need to be answered empirically Training programs did not come out to be effective as anticipated Can training effectiveness be improved How can we define training effectiveness How does training effect worker productivity 1 Narrowing Down the Broad Problem Preliminary Data Collection Literature Survey Problem Definition A clear, precise(exact) and succinct(brief) statement of the question or issue that is to be investigated with the goal of finding a answer or solution. Examples for Broad Problem Areas The sales volume of a product is not picking up The newly installed information system is not being used by managers Inventory control is not effective Mistakes have increased in clerical jobs Flow of written communication is slow Preliminary Data Collection Background Information on The Organization The origin and history of the organization Size in terms of employees, assets, sales etc. Purpose and Ideology Location –regional, national etc. Resources (including human resources) Interdependent relations with other institutions Financial Position 2 Preliminary Data Collection Preliminary Data Collection Information on Structural Factors and Management Philosophy Perceptions, Attitudes and Behavioral Responses •Roles and positions •Nature of Work •Extent of specialization •Workflow interdependencies •Communication channels •Superiors in the organization •Control systems •Participation in decision making •Coordination and span of control •Client systems •Reward systems •Opportunities for advancement •Workflow systems •Organizational attitudes toward employees family responsibilities •Involment with community Secondary Data Advantages of Secondary Data Data gathered and recorded by someone else prior to and for a purpose other than the current project Is often: Historical Already assembled Inexpensive Obtained Rapidly 3 Disadvantages of Secondary Data Uncertain Accuracy Data Not Consistent with Needs Inappropriate Units of Measurement Time Period Inappropriate (Dated) Literature Review In order to eliminate the risk of “reinventing the wheel” Documentation of comprehensive review of published and unpublished work from secondary sources of data in the areas of specific, interest to researcher. Important variables that are likely to influence the situation are not left out A clearer idea emerges as to what variables would be most important to consider (parsimony) Literature Review A clear and logical presentation of relevant research work done to identify and highlight important variables and to document significant findings from earlier research which will serve as a foundation for the theoretical framework and hypothesis. All relevant information should be bring together in a cogent and logical manner instead of presenting all studies in a chronological order with bits of and pieces of un coordinated information A good literature review should lead to a logical good problem statement The problem statement can be made with precision and clarity Testability and replicability of current research is enhanced The problem investigated is perceived by scientific community Steps of Literature Review Identify relevant sources Textbooks, journals, theses, conference proceedings, reports, newspapers, Internet etc. Evaluate the quality of source!!! Extract the relevant information Writing up the literature review 4 APA Style Book by one author Book by two authors or more Internet Sources Rogers, B. (2008). Faster-than-light travel: What we've learned in the first twenty years. Retrieved August 24, 2008, from Mars University, Institute for Martian Studies Web site, http://www.eg.spacecentraltoday.mars/university/dept.html Rogers, B. (2008). Faster-than-light travel: What we've learned in the first twenty years. Retrieved August 24, 2008, from Mars University, Institute for Martian Studies Web site, http://www.eg.spacecentraltoday.mars/university/dept.html Mcdonalds, A. (1993). Practical methods for the apprehension and sustained containment of supernatural entities. In G. L. Yeager (Ed.), Paranormal and occult studies: Case studies in application (pp. 42–64). London: OtherWorld Books. Article Crackton, P. (1987). The Loonie: God's long-awaited gift to colourful pocket change? Canadian Change, 64(7), 34–37. Rottweiler, F. T., & Beauchemin, J. L. (1987). Detroit and Narnia: Two foes on the brink of destruction. Canadian/American Studies Journal, 54, 66-146. Article in a weekly magazine Article in a newspaper Smith, J., and Peter, Q. (1992). Hairball: An intensive peek behind the surface of an enigma. Hamilton, ON: McMaster University Press. Article in an edited book Sheril, R. D. (1956). The terrifying future: Contemplating color television. San Diego: Halstead. APA Style Henry, W. A., III. (1990, April 9). Making the grade in today's schools. Time, 135, 28–31. Wrong, M. (2005, August 17). "Never Gonna Give You Up" says Mayor. Toronto Sol, p. 4. Government document Revenue Canada. (2001). Advanced gouging: Manual for employees (MP 65–347/1124). Ottawa: Minister of Immigration and Revenue. Problem Discovery: The Iceberg Principle Organization Symptoms Problem Definition Based on Symptom True Problem Twenty-year-old Membership has been Neighborhood Demographic changes: neighborhood declining for years. residents prefer the Children in this 20- swimming New water park with expensive water year-old neighborhood association in a wave pool and water park and have have grown up. Older major city. slides moved into negative image of residents no longer town a few years ago. swimming pool. swim anywhere. 5 Well Defined Problem Statements THREE KEY FACTORS OF GOOD PROBLEM STATEMENT Relevant From a managerial perspective Problem exists in an organizational setting An area that a manager believes needs to be improved in the organization From academic perspective Nothing is know about topic Much is known about topic but the knowledge not integrated Much research are avaliable but the results are partly contradictory Established relationship do not hold in current situation Feasible Intresting IN-CLASS EXERCISES ON BROAD PROBLEM AREA AND PROBLEM DEFINITION MARKETING 1. The manager of Woodlands Restaurant is concerned about the low customer image of his restaurant. Well Defined Problem Statements How has the new product effected the sales of the product ? Has the advertising message resulted in enhanced recall? How does price and quality rate on consumers’ evaluation of products? What are the components of quality of life? IN-CLASS EXERCISES ON BROAD PROBLEM AREA AND PROBLEM DEFINITION 2. The Dreamland Advertising Agency is wondering why its strategy did not work. ACCOUNTING 3. Narayan Associates is interested in knowing the implications of high technology in factories, for accounting and auditing procedures and practices. 4. The Rosalin Auditing Company is perturbed about the different interpretations it is getting from the tax administrators and tax accountants. FINANCE 5. The board of directors of Jankrish Computers is worried about the stagnation of the market price of the Company's stock. 6. Saratoga Supers are perplexed about the low return on their capital investment. 1. To what extent do the customers of Woodlands Restaurant like the menu, the quality of food, the service, price, and ambiance of the restaurant? 2. Is the message in the most recent advertising of Dreamland Advertising Agency aimed at the right target group? 3. How should the currently standardized accounting procedures (such as depreciation, tax write-offs, etc) be changed, as factories resort to specialized technology? 4. What specific items in the balance sheet create misunderstandings and conflicts between those who assess the tax and those who prepare the tax returns and how can they be resolved? 5. To what extent do the following factors contribute to the stagnating market price of Jankrish's shares – the dividend policy, the growth rate, perceived managerial problems, and the capital market conditions? 6. Is the low return on the capital investment of Saratoga Supers, a function of low sales or high operating expenses? 6








