BI SC 004
advertisement

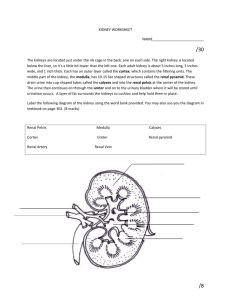
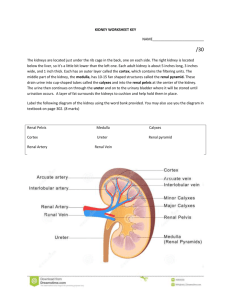
BI SC 004 Human Body: Form and Function STUDY GUIDE The Urinary System Dr. Martha Aynardi aynardi@psu.edu Chapter Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to: ◦ Recall the major functions of the kidneys. ◦ Identify the following structures of the urinary system and recall their functions: kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra. ◦ Identify the following structures of the kidney: renal cortex, renal medulla, and renal pelvis. ◦ Recall the function of the nephron. ◦ Differentiate between the 2 main parts of the nephron: the renal corpuscle and the renal tubule. ◦ Identify which structures are a part of the renal corpuscle. Define glomerulus and describe its function. ◦ Recall the functions of the afferent and efferent arterioles. ◦ Recall the function of Bowman’s capsule. ◦ Define filtrate. ◦ Differentiate between blood, plasma, and filtrate. ◦ Identify the following regions of the renal tubule and their main functions: proximal convoluted tubule, the loop of Henle, the distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct. ◦ Recall the function of the 3 kidney processes: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. ◦ Summarize kidney function and the process of urine formation. ◦ Describe and give cause to the following diseases and conditions of the urinary system: cystitis, glomerulonephritis, renal failure, and UTI. Recall the major functions of the kidneys (pg. 579-580). ◦ The kidneys filter wastes from the blood and excrete them in the urine. Identify the following structures of the urinary system and recall their functions: kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra (pg. 580). Identify the following structures of the kidney: renal cortex, renal medulla, and renal pelvis (pg. 581). Recall the function of the nephron (pg. 583). ◦ The nephron, the basic functional unit in the kidney, includes the renal corpuscle and a renal tubule, which empties into the collecting system through a collecting duct. ◦ The nephron is responsible for: The production of filtrate. The reabsorption of nutrients, water, and ions. The secretion of ions, acids, drugs, and toxins. Differentiate between the 2 main parts of the nephron: the renal corpuscle and the renal tubule. ◦ Renal corpuscle is a round structure consisting of a capillary network called the glomerulus which arises from the afferent arteriole and a cup-shaped chamber called Bowman’s capsule. ◦ Filtrate leaves the renal corpuscle and enters the renal tubule. The renal tubule is responsible for reabsorbing all of the useful organic molecules from the filtrate; reabsorbing over 90% of the water in the filtrate, and secreting into the tubular fluid any waste products that were missed by the filtration process. Identify which structures are a part of the renal corpuscle. Define glomerulus and describe its function (pg. 583). ◦ The renal corpuscle consists of a cup-shaped chamber called Bowman’s capsule and a capillary network called the glomerulus. ◦ The glomerulus is a knot of capillaries that projects into the enlarged, proximal end of a nephron known as Bowman’s capsule; is the site of filtration - the first step in the production of urine. Recall the functions of the afferent and efferent arterioles. Recall the function of Bowman’s capsule (pg. 583). ◦ Afferent arterioles carry blood TO a glomerulus of the kidney. ◦ Efferent arterioles carry blood AWAY FROM a glomerulus of the kidney. ◦ Bowman’s capsule is a cup-shaped structure at the end of the renal tubule that encapsulates the glomerulus and receives filtrate from it Define filtrate (pg. 583). When does filtrate become urine? ◦ Filtrate is a protein-free solution produced by filtration. As this filtrate travels along the renal tubule, its composition changes and the result is urine. Differentiate between blood, plasma, and filtrate (pg. 583). ◦ The circulating fluid of the body is called blood. It is a specialized connective tissue that contains cells suspended in a fluid matrix. ◦ Plasma is the fluid ground substance of blood; it is what remains after the cells have been removed from a sample of whole blood. ◦ Filtrate is the fluid produced by filtration at a glomerulus in the kidney. It is essentially blood plasma minus the plasma proteins. Identify the following regions of the renal tubule and their main functions: proximal convoluted tubule, the loop of Henle, the distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct (pg. 584). Recall the function of the 3 kidney processes: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion (pg. 587). ◦ In filtration, blood pressure forces plasma minus plasma proteins across the wall of the glomerulus into Bowman’s capsule. ◦ Reabsorption is the removal of water and solute molecules from the filtrate and their re-entry into the circulation at the peritubular capillaries surrounding the renal tubule. ◦ Secretion is the transport of solutes out of the peritubular capillaries, across the tubular epithelium, and into the filtrate of the renal tubules. Summarize kidney function and the process of urine formation (pg. 590). Describe and give cause to the following diseases and conditions of the urinary system: cystitis, glomerulonephritis, renal failure, and UTI. ◦ Cystitis is the inflammation of the lining of the urinary bladder – often due to a bacterial infection. ◦ Glomerulonephritis is the inflammation of the glomeruli (the filtration units of the nephron). ◦ Renal failure is an inability of the kidneys to excrete wastes in sufficient quantities to maintain homeostasis. ◦ UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) is an infection of the urinary tract by bacteria or fungi (yeast). Key Terms ◦ Kidney ◦ Ureter ◦ Urinary bladder ◦ Urethra ◦ Renal cortex ◦ Renal medulla ◦ Renal pelvis ◦ Nephron ◦ Renal corpuscle ◦ Renal tubule ◦ Glomerulus ◦ Afferent arterioles ◦ Efferent arterioles ◦ Bowman’s capsule Chapter Review Questions Can you answer the following questions? ◦ What are the major functions of the kidneys? ◦ Can you identify the following structures of the urinary system and recall their functions? Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder, Urethra ◦ Can you identify the following structures of the kidney? Renal cortex, Renal medulla, Renal pelvis ◦ What is the function of the nephron? ◦ Can you differentiate between the 2 main parts of the nephron (the renal corpuscle and the renal tubule)? ◦ Can you identify which structures are a part of the renal corpuscle? What is the glomerulus and can you describe its function? ◦ What are the functions of the afferent and efferent arterioles? What is the function of Bowman’s capsule? ◦ What is filtrate? And when does filtrate become urine? ◦ Can you differentiate between blood, plasma, and filtrate? ◦ Can you identify the following regions of the renal tubule and their main functions? Proximal convoluted tubule, the loop of Henle, the distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct ◦ What is the function of the 3 kidney processes: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion? ◦ Can you summarize kidney function and the process of urine formation? ◦ Can you describe and give cause to the following diseases and conditions of the urinary system: cystitis, glomerulonephritis, renal failure, and UTI? Questions to consider when studying for the exam ◦ How does structure relate to function? ◦ Are you able to recognize examples and apply knowledge? ◦ Do you know the sequential steps of any mechanisms discussed?