Trifecta Anatomy Homework 1 (Ch1,2,4,5)
advertisement

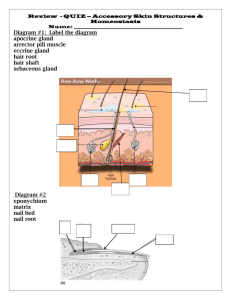
Chapter 1 Introduction to the Human Body Match column A with Column B. Column A 1. Female reproductive system___ 2. Male reproductive system___ 3. Digestive system___ 4. Respiratory system___ 5. Muscular system___ 6. Urinary system___ 7. Nervous system___ 8. Integumentary system___ 9. Skeletal system___ 10. Endocrine system___ 11. Lymphatic system___ 12. Cardiovascular system___ Column B A. bones and joints B. brain, spinal cord, nerves C. skeletal muscles D. larynx, trachea, lungs E. heart, blood vessels F. prostate gland, testis, ductus deferens G. thyroid gland, adrenal gland, pituitary H. esophagus, stomach, small intestine I. skin, hair, and nails J. ovary, uterus, uterine tube K. kidneys, ureters, urethra L. spleen, red bone marrow, lymph nodes Fill in the blank with directional terms. 13. The forearm is _______________________ to the left hand. 14. The thumb is _____________________ to the ring finger. 15. The ankle is __________________ to the thigh. 16. The sternum (breastbone) is ___________________ to the upper arm. 17. The occipital (back) of the head is ________________________ to the nose. 18. The thigh is ___________________ to the knee. 19. The nose is __________________ and _________________ to the left ear. 20. The right eye is ______________________ and _________________ to the nose. 21. Provide 2 organs that are found in epigastric region? 22. Provide 2 organs that are found in right lower quadrant? 23. What is the regional term for the lateral side of the leg? 24. Which plane is most useful in the studies of organs in the human body and why? 25. Describe the proper Standard Anatomical Position Chapter 2 Cells 1. Draw and label a typical cell with all its structure and organelles. 2. Define the composition and function of the plasma membrane 3. Describe the transcellular transport processes a. simple diffusion b. facilitated diffusion c. primary active transport d. secondary active transport e. endocytosis f. exocytosis 4. Describe the cell theory. Match column A with column B. Column A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. chromosomes uncoiled and uncondensed___ mitotic spindle forms___ chromosome are pulled apart___ cytokinesis occurs___ chromosomes lined up on equatorial plane___ nuclear membrane breaks down___ centrioles are no longer on opposite side___ Column B A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. Telophase Chapter 4 Tissues Use the key choice to identify the major tissue types described below. A. Connective Tissue B. Epithelium C. Muscle Tissue D. Nervous Tissue 1. lines body cavities and covers the body’s external surface ___ 2. pumps blood, flushes urine out of the body, allows one to swing a bat ___ 3. transmits electrochemical impulses ___ 4. anchors, packages, and supports body organs ___ 5. cells may absorb, secrete, and filter ___ 6. most involved in regulating and controlling body functions ___ 7. major functions is to contract ___ 8. synthesizes hormones ___ 9. the most durable tissue type ___ 10. abundant nonliving extracellular matrix ___ 11. most widespread tissue in the body ___ 12. forms nerves and the brain ___ 13. Describe and draw the different types of connective tissue NOT the four types of tissues. CT Drawing and labeling Areolar CT Adipose CT Reticular CT Dense regular CT Dense Irregular CT CT Cartilage Bones Blood Drawing and labeling Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Using the key choice, choose all responses that apply to the following descriptions. A. stratum basale D. stratum lucidum G. reticular layer B. stratum corneum E. stratum spinosum H. epidermis as a whole C. stratum granulosum F. papillary layer I. dermis as a whole 1. translucent cells in thick skin containg keratin fibrils ___ 2. dead cells ___ 3. dermal layer responsible for fingerprints ___ 4. vascular region ___ 5. major skin area that produces derivatives (nails and hair) ___ 6. epidermal region exhibiting the most rapid cell division ___ 7. scale-like dead cells, full of keratin, that constantly slough off ___ 8. mitotic cells filled with intermediate filaments ___ 9. has abundant elastic and collagenic fibers ___ 10. location of melanocytes and Merkel cells ___ 11. area where weblike prekeratin filaments first appear ___ 12. region of areolar connective tissue ___ Match the key choice with the appropriate descriptions. A. arrector pili D. hair follicle B. cutaneous receptors E. nail C. hair F. sebaceous glands G. apocrine sweat gland H. eccrine sweat gland 13. produces an accumulation of oily material that is known as a blackhead ___ 14. tiny muscles, attached to hair follicles, that pull the hair upright during fright ___ 15. perspiration glands with a role in temperature control ___ 16. sheath formed of both epithelial and connective tissues ___ 17. less numerous type of perspiration-producing gland __ 18. found everywhere on the body except the palms of hands and soles of feet ___ 19. primarily dead or keratinized cells 20. specialized nerve endings that respond to temperature, touch, etc. 21. its secretion is a lubricant for hair and skin ___ 22. “sports” a lunula and a cuticle ___ 23. found mainly in the pubic and axillary regions ___ 24. Why is the hypodermis not considered part of true skin?