Exercise 15-31 The Platter Valley factory of Bybee Industries
advertisement

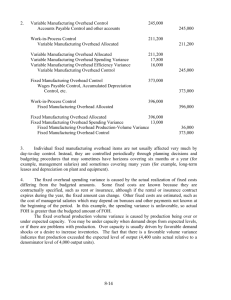
Exercise 15-31 The Platter Valley factory of Bybee Industries manufactures field boots. The cost of each boot includes direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead. The firm traces all direct costs to products and assigns overhead based on direct labor hours. The firm budgeted $15,000 variable factory overhead and 2,500 direct labor hours to manufacture 5,000 pairs of boots in March 2010. The factory spent 2,700 direct labor hours in March 2010 to manufacture 4,800 pairs of boots and spent $15,600 on variable factory overhead during the month. Budgeted variable factory overhead Budgeted direct labor hours Budgeted production in pairs of boots Actual variable factory overhead Actual direct labor hours Actual production in pairs of boots $15,000 2,500 5,000 $15,600 2,700 4,800 Required 1. Compute the flexible-budget variance, the spending variance, and the efficiency variance for variable overhead for March. Exercise 15-32 (Continuation of Exercise 15-31.) For March 2010, the Platter Valley factory of Bybee Industries budgeted $90,000 fixed factory overhead. Its practical capacity is 2,500 direct labor hours per month (to manufacture 5,000 pairs of boots). The factory spent 2,700 direct labor hours in March 2010 to manufacture 4,800 pairs of boots. The actual fixed overhead incurred for the month was $92,000. Budgeted fixed factory overhead Budgeted direct labor hours Budgeted production in pairs of boots Actual fixed factory overhead Actual direct labor hours Actual production in pairs of boots $90,000 2,500 5,000 $92,000 2,700 4,800 Required 1. 2. Compute the spending (budget) variance and the production-volume variance for fixed overhead. Compute fixed overhead flexible budget variance. Exercise 15-39 The following information is available from Swinnery Company for its operations in December: Data Factory overhead incurred $40,000 Variable overhead expenses, incurred $24,150 Fixed overhead expenses, budgeted $18,000 Direct labor hours (DLH) worked 4,200 Standard direct labor hours allowed for the units manufactured 4,000 Denominator level of activity, in DLHs 4,500 (a modification of the problem – I always use denominator level rather than practical capacity) Actual variable OVH rate/DLH worked $5.75 Standard variable overhead rate per DLH $5.00 Swinnery uses direct labor hours (DLHs) to apply factory overhead cost. Required Compute the four overhead variances. 15-31 Variable Factory Overhead Variances (30 minutes) 1. Standard variable overhead rate per direct labor hour (DLH): BudgetedTotal VariableFactoryOverhead BudgetedTotalDirect Labor Hours = $15,000/2,500 hours = $6.00 per direct labor hour (DLH) Standard direct-labor hours (DLHs) per unit: BudgetedTotalDirectLabor Hours BudgetedTotalUnits = 2,500 DLHs/5,000 units = 0.50 DLHs/unit Variable Overhead Variance Analysis Actual Cost (AQ x AP) 2,700 hrs. x $5.7777/hr. $6.00/hr. = $15,600 FB Based on Inputs (AQ x SP) 2,700 x $6.00/hr. FB Based on Output (SQ x SP) (4,800 x 0.5) x = $16,200 = $14,400 Spending variance Efficiency variance = $600 F = $1,800 U or, = AQ x (AP – SP) or, = (AH – SH) x SR = 2,700 x ($5.7777 - $6.00) = (2,700 – 2,400) x $6.00/hr. = $600F = $1,800U Flexible Budget Actual Cost Output $15,600 Based on $14,400 Flexible-budget variance = $15,600 – $14,400 = $1,200U 2. To Record Favorable Variable Overhead Spending Variance: Dr. Factory Overhead (or, Variable Factory Overhead) $ 600 Cr. Variable Overhead Spending Variance $ 600 To Record Unfavorable Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance: Dr. Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance $1,800 Cr. Factory Overhead (or, Variable Factory Overhead) $1,800 3. The factory had a favorable variable overhead spending variance. This could be a result of conscientious efforts of workers and the manager of the factory in conserving uses of variable factory items. Alternatively, it could have been due, at least in part, to the use of an inappropriate activity measure (direct labor-hours) for assigning variable factory overhead costs. The $1,800 unfavorable variable overhead efficiency variance is a result of using more direct labor hours (DLHs) to manufacture the output of the period (2,700 hours to make 4,800 units of output) than the standard DLHs allowed (2,400 hours) for this level of output. As long as DLHs worked is related to variable overhead costs incurred, then the efficiency variance indicates the cost to the company (in terms of variable overhead) of using 300 extra DLHs this period. The $1,200 unfavorable flexible-budget variance indicates that the firm did not exercise good overall control regarding variable factory overhead costs. Again, this is a valid conclusion provided that DLHs is a reasonably good activity measure for the consumption of variable factory overhead cost. 15-32 Fixed Overhead Variances (30 minutes) 1. Standard fixed factory overhead application rate per direct labor hour (DLH): = BudgetedFixedFactoryOverhead TotalDirectLaborHours, PracticalCapacity = $90,000/2,500 DLHs = $36.00 per DLH Standard direct-labor hours (DLH) per unit: Budgeted Total Direct Labor Hours = Practical Capacity Units = 2,500 hours/5,000 units = 0.5 DLHs per unit Fixed Overhead Variance Analysis Actual Cost Applied (SQ x SP) 4,800 units x 0.5 hrs. x Budget $36/hr. $92,000 $90,000 = $86,400 Spending variance Production-volume variance = $92,000 – $90,000 = $90,000 – $86,400 = $2,000U = $3,600U or, = SP x (Denominator Volume – SQ) = $36/hr. (2,500 hrs. – 2,400 hrs.) = $36/hr. x 100 hrs. = $3,600U 2. Fixed factory overhead (FOH) flexible-budget variance = FOH spending variance = $2,000U 3. To Record Unfavorable Fixed Overhead Spending Variance: Dr. Fixed Overhead Spending Variance Cr. Factory Overhead (or, Fixed Factory Overhead) $ 2,000 $2,000 To Record Unfavorable Production-Volume Variance: Dr. Production Volume Variance Cr. Factory Overhead (or, Fixed Factory Overhead) $ 3,600 $ 3,600 4. The $2,000 unfavorable fixed factory overhead spending variance could be a result of unexpected fluctuations, overspending, or budgeting errors in one or more fixed overhead items. However, since the amount is small (2.22% of the budget amount), it is unlikely that the management needs to spend any time or resources to investigate this variance. The $3,600 unfavorable production volume variance is a result of the lower output for the period (4,800 units) as compared to the volume of output (5,000 units) assumed when the fixed overhead allocation rate was determined. The production manager is responsible for the unfavorable variance if the reason for the lower output is a result of activities or events in the factory such as equipment failure, inefficient workers, or high defective rates. However, the factory is doing its job if the lower production is a result of the decreased demand for its product. As indicated in the text, this variance generally has shared responsibility (with marketing, purchasing, etc.). Note that when the denominator activity level is set at practical capacity, then resulting production volume variances can be interpreted as the cost of unused capacity. The disclosure of this information over time can help managers make better decisions regarding capacity-related spending. Exercise 15-39 Fixed overhead application rate: $18,000 ÷ 4,500 = $4.00/DLH Actual fixed overhead: $40,000 – $24,150 = $15,850; Actual variable OH rate/DLH = $24,150/4,200DLHs = $5.75/DLH Standard Cost Flexible Budget Flexible Budget Based on Inputs Based on Outputs (AQ x SP) (SQ x SP) Applied to Actual Production (AQ x AP) (SQ x SP) Variable (4,200 x $5.75) (4,200 x $5.00) (4,000 x $5.00) $5.00) Overhead = $24,150 = $21,000 = $20,000 Spending Efficiency Variance = $3,150U Variance = $1,000U Fixed Overhead Actual Lump-sum Amount $15,850 $18,000 Spending Variance = $2,150F (4,000 x = $20,000 N/A Lump-Sum Amount N/A Applied (SQ x SP) (4,000 x $4.00) $18,000 = $16,000 Production-Volume Variance = $2,000U (4,000 x $9.00) $36,000 $40,000 Total Overhead Total Overhead Variance = $4,000U (from a product-costing standpoint this is referred to as total underapplied overhead of $4,000) Four-Variance Decomposition of Total Overhead Variance for December: (1) Variable Overhead Spending Variance = $3,150U (2) Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance = $1,000U (3) Fixed Overhead Spending Variance = $2,150F (4) Production Volume Variance = $2,000U = $4,000U Total Overhead Variance