AP Stats Chapter 13.notebook
advertisement

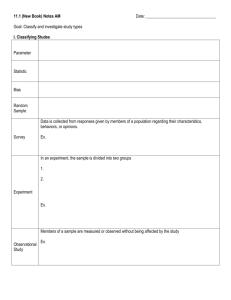
AP Stats Chapter 13.notebook November 21, 2014 Chapter 13!!! Other ways of collecting data, other than surveys Observational Study : Researches don't assign choices, they simply observe them. Nothing is done to change behavior....results are simply observed. Retrospective Study: An observational study where subjects are identified and then past data is collected. Prospective Study: An observational study where subjects are identified and then data is collected as it happens. NOTE!!!! Observational studies do not demonstrate causation. Observed 50 band students grades. They averaged better GPA's than non­band students. Does being in band cause you to get better grades? AP Stats Chapter 13.notebook November 21, 2014 Experiments: In an experiment something is done to effect a change in the individuals in order to look for a change in the variable and data. Terms, parts, information about experiments: An experiment requires, random assignment, most experiments need two groups (one where something is introduced to change behavior and one where it is not introduced.) These groups have to be assigned randomly. This is to avoid lurking variables or bias. An experiment will look at the relationship between at least two variables. One variable is the explanatory variable or the factor. The experiment checks to see if changes in this variable have an effect on another variable, the response variable. Note, we've seen these terms before during regression. The difference here is that in an experiment the experimenter actively and deliberately manipulates the factor to control details of the possible treatments and assigns the subjects randomly. AP Stats Chapter 13.notebook November 21, 2014 The "Who" that gets experimented on can be refered to many different ways. When humans are the "who" they are called subjects or participants. When the individuals are not humans (rats, school districts, petri dishes of bactria) they are called experimental units. Specific values that the experimenter uses for a factor are called levels. For example some subjects are allowed to sleep 4 hours per night, some 6, some 8. These are the levels. The combination of specific levels from all the factors that an experimental unit recieves is called the treatment. Basically, its everything that is done to change or look for a change between subjects. AP Stats Chapter 13.notebook November 21, 2014 The four priciples of experimental design 1.) Control: We control sources of variation other than the factors we are using by making conditions as similar as possible for all treatment groups. This includes some treatment groups who are not introduced to any of the treatments (these individuals are called the control group). 2.) Randomize: Avoid bias. We don't want a group that is receiving a given level of treatment to have some other lurking variable causing differences. The best way to avoid this is to randomly assign groups. 3.) Replicate: You must be able to repeat the experiment with the same results. Replication of an entire experiment with the controlled sources of variation at different levels is an essential step in science. 4.) Block: Sometimes attributes of the experimental units that we are not studying and that we can't control may still have an affect on the outcomes of the experiment. If we group randomly assign these units to all treatment groups we can remove the variability caused by these attributes. These groups of similar units are called blocks. INSERT Soccer example here.