Sample Formal Lab Write-up
advertisement

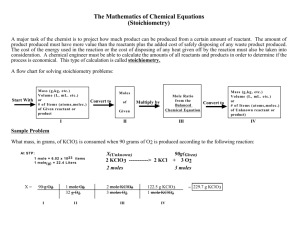
Sample Formal Lab Write-up Your name Title: Decomposition of potassium chlorate (KClO3) Purpose: This lab will demonstrate the decomposition (breakdown) of KClO3 into KCl solid and O2 gas when heated. The oxygen will be released into the atmosphere and the remaining KCl can be measured to determine the change in mass. Using the Law of Conservation of Mass we can determine the amount of oxygen released and calculate the percent of oxygen present in the original sample. Data: Mass of empty dish Mass of dish + KClO3 Mass of dish + KCl (after heating) 42.56 g 43.66 g 43.21 Calculations: 1. Mass of KClO3: 43.66 g -42.56 g = 1.10 g 2. Mass of KCl: 43.21 g -42.56 g = 0.69 g 3. Mass of O2: 1.10 g – 0.69 g = 0.41 g 4. Experimental % of oxygen using data: g of oxygen 0.41 g of KClO3 1.10 X 100 = 37 % 5. Actual % of oxygen using mass numbers: gfm of total oxygen gfm of KClO3 48 X 100 = 39 % 122.6 6. Calculate your % error using calculations #4 and #5 (39% - 37%)/39% * 100 = 5.1% error Analysis Questions: 1. What is the Law of Conservation of Mass? Conservation of mass means that matter cannot be created or destroyed. 2. How do we use the Law to determine the amount of oxygen? Since the oxygen was part of the original compound, it had mass. The change in mass had to come from the oxygen being released. The difference in the masses of the sample before and after being heated shows the amount of oxygen released. 3. What are possible sources of error in this lab? If the KClO3 was not heated enough, not all of the oxygen would have been removed. If there were other compounds in the dish, such as water, the loss of mass would have been greater than just oxygen. 4. Why does diatomic oxygen form when KClO3 is heated? Oxygen atoms are unstable because they have unpaired electrons in their valence shells and will form diatomic oxygen molecules which are more stable. Conclusion: Decomposition is a type of chemical reaction in which a single reactant breaks apart to form 2 or more new substances. When any chemical reaction occurs, the total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products. This is the Law of Conservation of Mass. We can use this to calculate mass that is either lost or gained during a chemical reaction. The oxygen is not destroyed, but rather is released as a gas to the air. Conservation of Mass can also be demonstrated by using a balanced equation. In a balanced equation, the number of atoms of an element has to be the same on both sides of the arrow. In this equation, for example 2 KClO3 2 KCl + 3 O2 show 2 K, 2 Cl and 6 O on each side of the arrow. In this experiment, our % oxygen was lower than the actual % oxygen in the formula. This means that we probably did not heat the dish long enough for all of the KClO3 to fully decompose and that there was some KClO3 left after we heated it. Next time we will makes sure to heat the sample for the full amount of time at the hottest part of the flame.