Geometry Test –Chapter 5-Version 1 Name__________________
advertisement
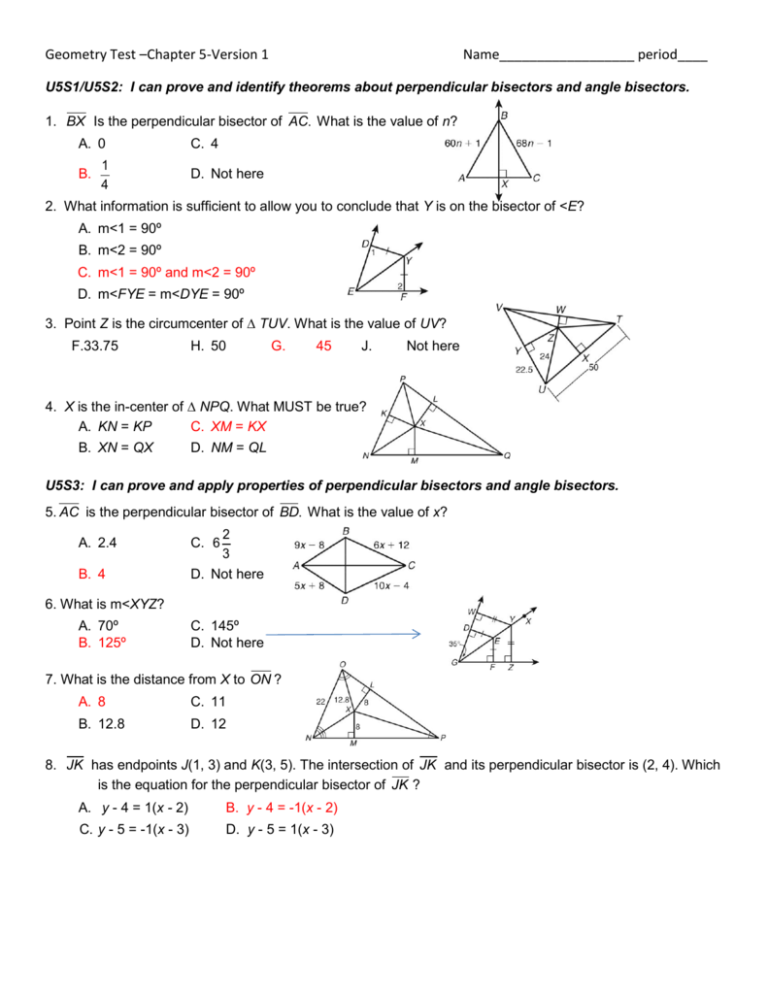
Geometry Test –Chapter 5-Version 1 Name__________________ period____ U5S1/U5S2: I can prove and identify theorems about perpendicular bisectors and angle bisectors. 1. BX Is the perpendicular bisector of AC. What is the value of n? A. 0 B. 1 4 C. 4 D. Not here 2. What information is sufficient to allow you to conclude that Y is on the bisector of <E? A. m<1 = 90º B. m<2 = 90º C. m<1 = 90º and m<2 = 90º D. m<FYE = m<DYE = 90º 3. Point Z is the circumcenter of ∆ TUV. What is the value of UV? F.33.75 H. 50 G. 45 J. Not here 4. X is the in-center of ∆ NPQ. What MUST be true? A. KN = KP C. XM = KX B. XN = QX D. NM = QL U5S3: I can prove and apply properties of perpendicular bisectors and angle bisectors. 5. AC is the perpendicular bisector of BD. What is the value of x? 2 3 A. 2.4 C. 6 B. 4 D. Not here 6. What is m<XYZ? A. 70º B. 125º C. 145º D. Not here 7. What is the distance from X to ON ? A. 8 C. 11 B. 12.8 D. 12 8. JK has endpoints J(1, 3) and K(3, 5). The intersection of JK and its perpendicular bisector is (2, 4). Which is the equation for the perpendicular bisector of JK ? A. y - 4 = 1(x - 2) B. y - 4 = -1(x - 2) C. y - 5 = -1(x - 3) D. y - 5 = 1(x - 3) U5S4: I can apply properties of medians and altitudes Use the figure for Exercises 13-15. GB 12 2 and CD 10. 3 Find each length. 13. FG ____6 1/3_____________ 14. BF ____19_____________ 15. GD ________3 1/3_________ 16. Find the coordinates of the orthocenter of the triangle. A. (-2, 5) C. (1, 5) B. (-3.5, 5) D. (0, 4) U5S5: I can prove and use properties of triangle mid-segments. 9. ∆ TUV is the mid-segment triangle of ∆ ABC. Which angle does NOT necessarily measure 40°? A. <VTU B.<CTV C.<TUA D.<VBU 10. SQ is a mid-segment of ∆ NOP. What is the length of OP ? F. 5 H. 23 G. 14 J. 46 11. CA is a mid-segment of ∆ VTU. What is the measure of <BCA? A. 40° B. 50° 12. PQ is the mid-segment of ∆ GHK, and GH is the mid-segment of ∆ KLM. What is the length of PK? A. 4 C. 14 B. 7 D. 28 U5S6a: I can write indirect proofs. 17. What would you do to start this indirect proof? Prove: State that 18. Which statement is used in an indirect proof to show that an equiangular triangle cannot have a right angle? F. An equilateral triangle has 60 degree angles G. An equilateral triangle has a right angle H. Isosceles and Scalene triangles cannot have right angles J. An equilateral triangle has congruent sides U5S6b: I can apply inequalities in one triangle. 19. If the expressions 10x - 7, 7x + 6, and 3x2 represent the sides of a triangle, which value for x is acceptable? A. 1 B. 3 C. 6 D. 7 20. Which shows the angles of ∆ FED in order from smallest to largest? A. <D, <E, <F C. <E, <F, <D B.<F, <D, <E D. <D, <F, <E 21. Which inequality best describes the possible lengths of the third side of a triangle with two sides of lengths 11 and 9? A. 9 < s < 11 C. -2 < s < 20 B. 11 < s < 9 D. 2 < s < 20 22. If a triangle has the angle measures 20 degrees, 55 degrees and 95 degrees. Across from which angle will be the longest side? A. 20° B. 55° C. 95° D. Cannot be determined U5S7: I can apply inequalities in two triangles (Hinge theorem and converse) 23. Which best describes the range of values for x? A. 2< x < 7 C. x < 15 B. 0 <x < 15 D 6<x<7 24. If m<ADB > m<BDC, which best describes the range of values for x? A. 0 < x < 22 C. 4 < x < 22 B. x < 22 D. x > 22 25. Which statement about r must be true? Bonus – Real answer is 3 F. r 3 7 H r3 3 G. r or r 3 7 3 J r or r 3 7 26. Make a comparison between the two sides. A. AB>DE B. AB<DE C. AB=DE D. cannot be determined U5S8a: I can use the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve problems. 27. What is the value of x in simplest radical form? F. 3 12 H. 72 G. 6 2 J. 89 28. Which numbers form a Pythagorean triple? A. 3, 4, 6 B. 7, 6 2, 11 C. 9, 12, 15 D. 8, 15, 18 29. What is the value of x? A. 13 C. 119 B. 17 D. 169 30. Which number forms a Pythagorean triple with 8 and 10? A. 6 B.15 C. 2 D. 18 U5S8b: I can use Pythagorean inequalities and equality to classify triangles. 31. The sides of a triangle measure 7, 8, and12. Which type of triangle is it? A. acute B. obtuse C. equilateral D. right 32. The sides of a triangle measure 16, 30, and 34. Which type of triangle is it? F. acute G. obtuse H. equilateral J. right 33. The lengths of two sides of an obtuse triangle are 12 and 16. Which could be the length of the third side? F. 9 H. 20 G. 10 J. 25 34. Are the sides 5,12,and 13, sides of a right triangle and if so are they a Pythagorean triple A. yes, no B. no, yes C. no, no D. yes, yes U5S9: I can apply properties of special right triangles. 35. What is the perimeter of a 45°-45 -90° triangle with hypotenuse length of 6? A. 12 B. 12 2 C. 9 3 D. 6 6 2 36. What is the area of a 30°-60°-90° triangle with hypotenuse length of 16? F. 16 G. 32 H. 32 3 J. 64 3 37.What is the value of x in simplest radical form? A 2.5 B 5 2 C 5 2 2 D 5 2 38. Which is a correct set of values? F x = 27, y 9 3, z 18 3 G x = 27, y 18 3, z 9 3 H x 9 3, y = 27, z 18 3 J x 18 3, y 9 3, z = 27