Name
Date
CHAPTER
7
CHAPTER TEST
Form C
Balancing Nationalism
and Sectionalism
Part 1: Main Ideas
Write the letter of the best answer. (4 points each)
______ 1. The Monroe Doctrine was largely a response to
a. the debate over admitting slave states to the Union.
b. the interest of European nations in creating colonies in North and South America.
c. the need to strengthen the national economy despite sectional differences.
d. fighting between western settlers and Native Americans.
______ 2. The 1828 “Tariff of Abominations” was given that name by those who
thought the tariff hurt the South while helping
a. British importers.
b. small farmers.
c. Northern manufacturers.
d. frontier settlers in the West.
______ 4. Andrew Jackson used the power of the presidency to
a. influence Supreme Court decisions in which he was interested.
b. fire many federal officials and appoint loyal followers in their places.
c. raise tariffs to fill the government treasury with funds.
d. recognize the land claims of the Cherokee Nation.
______ 5. The factory system was dependent on all of the following except
a. craftsmen.
b. inexpensive labor.
c. interchangeable parts.
d. power-driven machinery.
______ 6. Some Native American peoples in the Southeast were called “the five
civilized tribes” because
a. they joined together in an alliance.
b. they welcomed white settlers on their lands.
c. they had adopted aspects of European culture.
d. their traditional cultures had written languages.
132 Unit 2, Chapter 7
© McDougal Littell Inc. All rights reserved.
______ 3. The American System helped bring the nation together by
a. maintaining the balance between slave states and free states.
b. withdrawing funds from the unpopular Bank of the United States.
c. giving common people across the nation a voice in the national government.
d. creating a better transportation network to facilitate the exchange of goods.
Name
Test Form C continued
______ 7. Nullification promotes the idea of
a. nationalism.
b. states’ rights.
c. judicial review.
d. territorial expansion.
______ 8. The Whig Party, formed in 1834, supported
a. protective tariffs and a federal banking system.
b. pet banks and a national currency.
c. states’ rights and nullification.
d. expanded voting rights and Indian removal.
______ 9. The concept of states’ rights was enthusiastically supported by
a. John Marshall.
b. Daniel Webster.
c. Andrew Jackson.
d. John C. Calhoun.
______ 10. Andrew Jackson’s “pet banks” contributed to the Panic of 1837 by
a. lending money to members of Congress at lower rates than they did to others.
b. printing paper money that was not backed up by gold and silver.
c. making risky loans to factory owners in New England.
d. calling in loans made to state governments.
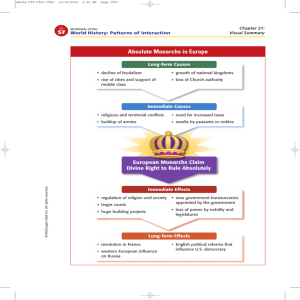
Part 2: Map Skills
Use the map to answer questions 11–15 on page 134. Answer each question on the line
provided. (4 points each)
Warsaw Pact countries
United States
Boundary Settlements, 1818–1819
NATO members
45°
Ceded by U.S.
to Britain, 1818
Occupied by
U.S. and Britain,
1818–1846
NH
Ceded by Britain
to U.S., 1818
VT
(1791)
MA
NY
CT
40°
N
RI
PA
IL
(1818)
NJ
OH
(1803)
IN
(1816)
DE
MD
VA
AdamsOnís Tre
aty
35°
AT L A N T I C
OCEAN
KY
(1792)
Line 1 819
© McDougal Littell Inc. All rights reserved.
Claimed by U.S.
and Britain until 1842
NC
TN
(1796)
SC
Rivers
30°
0
0
PAC I F I C
OCEAN
AL
(1819)
MS
(1817)
GA
Current state
boundaries
Spanish
Territory
400 Miles
70°
Ceded by Spain
to U.S., 1819,
by Adams-Onís Treaty
800 Kilometers
75°
80°
85°
120°
90°
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism 133
Name
Test Form C continued
11. Name a function performed by many of the rivers on the map.
12. What was the status of West Virginia in 1819?
13. Why does the map provide no date for New York’s becoming a state?
14. What line of latitude defines the northern border of the Adams-Onís Treaty Line?
15. If the United States had not followed the idea of manifest destiny, would its
national security have been compromised? Explain your answer.
Part 3: Interpreting Charts
Use the chart to answer the following questions in complete sentences. (4 points each)
State
Louisiana
Massachusetts
215,529
Total Free
White Persons
89,231
Total
Enslaved Persons
Total Free
Black Persons
109,588
16,710
610,408
603,359
1
7,048
1,918,608
1,868,061
75
44,870
South Carolina
581,185
257,863
315,401
7,921
Vermont
280,652
279,771
0
881
1,211,405
694,300
469,757
47,348
New York
Virginia
16. In which states did the enslaved population outnumber the free white
population?
17. Which states on the chart were most likely considered Northern states? Use
your knowledge from the chapter and statistics from the chart to help you
explain your answer.
134 Unit 2, Chapter 7
© McDougal Littell Inc. All rights reserved.
1830 Census Statistics
Total
Population
Name
Test Form C continued
18. Which states on the chart were most likely considered Southern states? Use
your knowledge from the chapter and statistics from the chart to help you
explain your answer.
19. Describe Louisiana’s population in 1830 in relation to the other states listed.
20. Which statistic(s) on the chart did you find the most surprising? Why?
Part 4: Extended Response
© McDougal Littell Inc. All rights reserved.
Answer each of the following questions in a short essay on the back of this paper or on a
separate sheet. (10 points each)
21. Describe two factors that contributed to feelings of nationalism in the early
1800s and two factors that contributed to feelings of sectionalism. Explain
your answers. Think About:
• the American System
• economic differences between regions
• the Missouri Compromise
• the tariffs of 1828 and 1832
• states’ rights and the idea of nullification
• the War of 1812 and America’s status as a nation
22. In what ways did Andrew Jackson’s presidency mark a new era in national
politics? Think About:
• the expansion of voting rights
• Jackson’s political experience
• Jackson’s style as president
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism 135