Thinking Reading Strategies chart (Autosaved).
advertisement
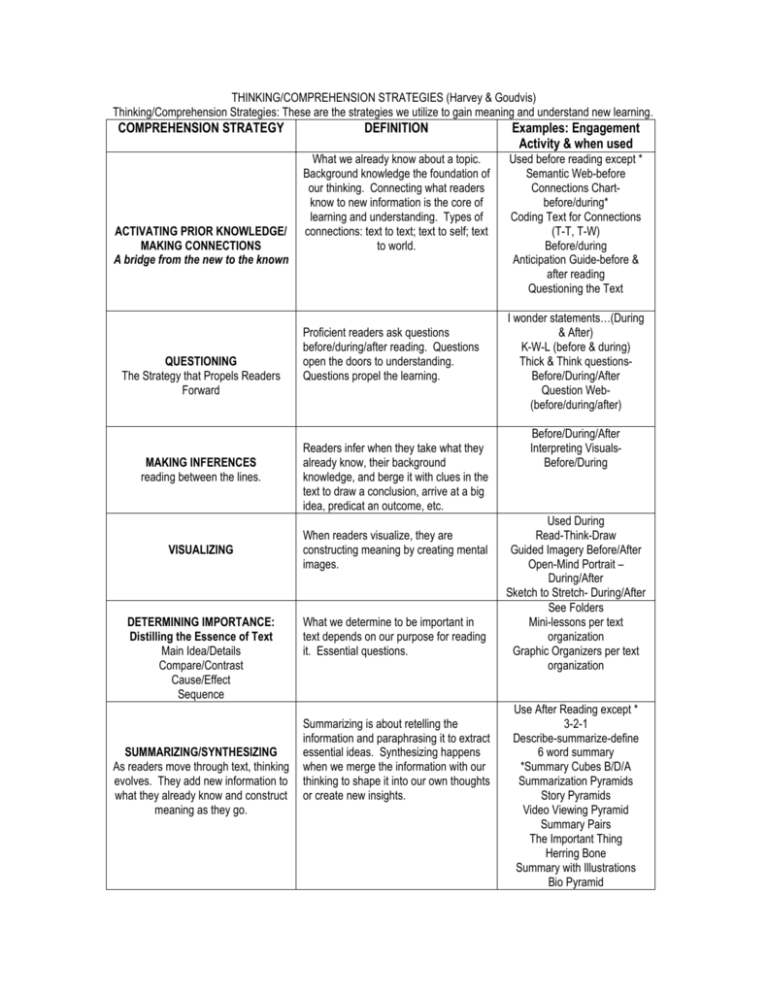
THINKING/COMPREHENSION STRATEGIES (Harvey & Goudvis) Thinking/Comprehension Strategies: These are the strategies we utilize to gain meaning and understand new learning. COMPREHENSION STRATEGY ACTIVATING PRIOR KNOWLEDGE/ MAKING CONNECTIONS A bridge from the new to the known QUESTIONING The Strategy that Propels Readers Forward MAKING INFERENCES reading between the lines. VISUALIZING DETERMINING IMPORTANCE: Distilling the Essence of Text Main Idea/Details Compare/Contrast Cause/Effect Sequence SUMMARIZING/SYNTHESIZING As readers move through text, thinking evolves. They add new information to what they already know and construct meaning as they go. DEFINITION What we already know about a topic. Background knowledge the foundation of our thinking. Connecting what readers know to new information is the core of learning and understanding. Types of connections: text to text; text to self; text to world. Proficient readers ask questions before/during/after reading. Questions open the doors to understanding. Questions propel the learning. Readers infer when they take what they already know, their background knowledge, and berge it with clues in the text to draw a conclusion, arrive at a big idea, predicat an outcome, etc. When readers visualize, they are constructing meaning by creating mental images. What we determine to be important in text depends on our purpose for reading it. Essential questions. Summarizing is about retelling the information and paraphrasing it to extract essential ideas. Synthesizing happens when we merge the information with our thinking to shape it into our own thoughts or create new insights. Examples: Engagement Activity & when used Used before reading except * Semantic Web-before Connections Chartbefore/during* Coding Text for Connections (T-T, T-W) Before/during Anticipation Guide-before & after reading Questioning the Text I wonder statements…(During & After) K-W-L (before & during) Thick & Think questionsBefore/During/After Question Web(before/during/after) Before/During/After Interpreting VisualsBefore/During Used During Read-Think-Draw Guided Imagery Before/After Open-Mind Portrait – During/After Sketch to Stretch- During/After See Folders Mini-lessons per text organization Graphic Organizers per text organization Use After Reading except * 3-2-1 Describe-summarize-define 6 word summary *Summary Cubes B/D/A Summarization Pyramids Story Pyramids Video Viewing Pyramid Summary Pairs The Important Thing Herring Bone Summary with Illustrations Bio Pyramid TEACHING STUDENTS HOW TO : • monitor their understanding and keep track of meaning • listen to the voice in their head to make sense of text • They notice when they stray from thinking about text, notice when meaning breaks down • understand how a variety of strategies can help them repair meaning when it breaks down • know when, why, and how to apply specific strategies to maintain further understanding MONITORING When readers monitor, they become aware of their thinking as they read. (SEE DEFINITION FOR WHAT THIS MEANS- THIS IS DIFFERENT THAN TEACHER MONITOR for PROGRESS) Used During Read/Think/Draw Margin notes Coding text Say Something Process For Planning: 1. 2Think about what learning/comprehension strategy students will need in order to gain meaning from the content-to get the specific learning. Think about the specific learning of the lesson. What about the content do you want them to learn? 3. 4. WALT: We are Learning to… Teacher will write the learning intention for the day on the board 5. Use the I Do, We Do, You Do Process: Once the above planning has been decided the teacher MUST model learning intention and expectation by doing a mini-lesson . Teacher would then refer to chart and related folder to locate mini-lesson to model strategy and engagement activity for lesson 6. I Do: (teacher modeling using a think aloud to expose process- model using minilesson/engagement activity to show thinking) We Do: have student attempt together, with teacher guidance,share thinking through random reporting, T/P/S, or white boards You Do: have students attempt a question individually to assess if ready to continue on in the learning independently. Then have students apply the same process modeled by teacher to a new situation. (specific learning previously stated) 7. Assess the learning: How do you know that they know?