The House of Hannover (1714 – 1901)
advertisement

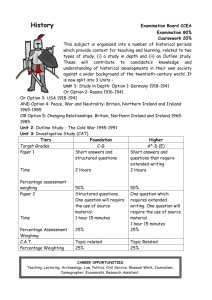
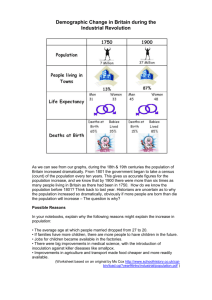
The House of Hannover (1714 – 1901) • • • • King George I George II, George III, George IV King William IV Queen Victoria George I (1714-1727) • The first Hanoverian king • James II’s son wanted to return as James III. He was Catholic. He tried to win the throne by force. The Old Pretender. • 1715 – first Jacobite rebellion • 1745 second Jacobite rebellion led by Bonnie Prince Charlie (=The Young Pretender, James II’s grandson, ). Defeated at Culloden in 1746. George I • Didn’t speak English • Didn’t get involved in British politics • Left most decisions to the Cabinet • Britain’s first PM: Robert Walpole • Walpole made sure that the power of the king would always be limited • Another influential PM: 1756-61, 1766-86 William Pitt the Elder, Earl of Chatham His focus was on trade The Seven Years’ War (1756-63) Britain gained control of Quebec & Montreal French trade interests destroyed in India - George III ended the war George III (1760-1820) • First Hanoverian king to be born in Britain • John Wilkes – champion of free speech • Loss of the American colonies American War of Independence (1775-83) ● Australia – Captain Cook 1770, the First Fleet arrived with convicts in 1788 Hulks – prison ships George III (1760-1820) • 1800 – Act of Union with Ireland • New Country after 1 Jan 1801: United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland This union lasted for 120 years. • 1707 – Act of Union with Scotland • 1603 – Union of the Crowns • 1536 – Act of Union of England and Wales The Industrial Revolution (about 1750s - late 1800s) • 1750 – Britain was an agricultural society • 1850 – Britain was an industrial nation Several influences came together at the same time to revolutionise British industry. - iron - cotton, wool (1764 spinning machine, 1785 a power machine for weaving) - improved transport John Wesley (1703-1791) • An Anglican cleric • Travelled around the country preaching in small groups to the lower classes • Had a very personal and emotional style of preaching • The Methodist Church -first part of the Church of England -later became a separate church The French Revolution 1789 • Divided Britain • 1793 – Britain went to war after France had invaded the Low Countries • 1805 – Trafalgar, Lord Nelson as commander of Br fleet -Trafalgar Square, London - Nelson’s Column The French Revolution • 1815 – Waterloo • British general: Wellington • Napoleonic Wars – brought economic prosperity. • Peace came in 1815 – everything changed • General misery. Petty crimes – severe punishments • Workhouses – Charles Dickens • Growth of towns and cities 1832 – The Reform Bill • It gave the vote to a large circle of middleclass men • 1833 – reformed parliament: • 1833 – The Emancipation Act - abolition of slavery in the British Empire William Wilberforce • 1833 – the first effective Factory Act • 1834 – Tolpuddle in Dorset 1838 - The People’s Charter • Equal representation, universal suffrage and vote by ballot • = the Chartists • 1839 – riots in Newport, Wales • 1840 – the movement was defeated 1840s: ‘We must make this country a cheap country for living.’ • 1842 – abolishment of many import duties • 1846 – abolishment of the Corn Laws that kept the price of corn higher than necessary • Free trade instead of protectionism • PM: Sir Robert Peel Queen Victoria (1837 – 1901) • Crowned at the age of 18 • Got married in 1840. Her husband was a German prince, Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg • Prince Albert died in 1861. • Had 9 children • Her rule was the longest of any British monarch 1851 – The Great Exhibition, Crystal Palace, London • The world’s first international trade The railway system • By 1840 – about 4000 kms of track • 1851 – passenger trains • People moved to suburbs • The rise of the middle class Florence Nightingale (1820-1910) • 1854-56 – the Crimean War • The ‘lady of the Lamp’ • Improved the conditions of military hospitals Second Reform Bill - 1867 • • • • 1 million working-class men got the vote 1872 – the Ballot Act made voting secret Trade unions were given a legal status Education Act of 1870 – established primary schools where there were no Church schools 1860s-1870s • The modern state as we know it was built • Number of voters in 1884: 60% of men in towns and 70% of men in the country • Civil service • The value of monarchy was questioned • 1868: Our life in the Highlands • Balmoral Castle Victorian values • Associated with middle class people • loyalty, Protestant work ethic • Franz Winterhalter: Queen Victoria and her family Prime Ministers • Lord Palmerston (1855-58, 1859-65) • Benjamin Disraeli (1868, 1874-1880) • William Gladstone (1868-74, 1880-85, 1886, 1892-94) Foreign policy • 1815-65 – Britain was the undisputed mistress of the world • 1854 – the Crimean War • 1839-42 – the war in Afghanistan • 1839 – the Opium War • 1857 – the Indian Mutiny • 1877 – Empress of India Ireland • 1845-47 – the Irish Potato Famine • About 1 million people died, 1 million people emigrated to the US and Britain • Population of Ireland: 5 million in early 19th c 8 million in mid-19th c now: about 6 million • Struggle for self-government (Home Rule) • Wales • By 1870s: Wales became an industrial society • Coal and steel industry in the south • Population: 0,5 million (1800s) – 2 million (1900s) • Scotland • Industrial area: Glasgow and Edinburgh • Highland Clearances The British Empire • 1497 – John Cabot claimed the ‘New Found Land’ for Henry VII • Elizabeth I (1588-1603) • Sir Francis Drake – 1580 • Buccaneers • Chartered companies: 1600 – English East India Company • Virginia North America • • • • 1585 – Sir Walter Raleigh 1607 – Jamestown 1620 – Pilgrim Fathers Religious refugees: 1639 Connecticut, 1634 Maryland – haven for Roman Catholics • 1664 – New Amsterdam • 1756-63 – Seven Years’ War The Caribbean • 1623 – Saint Christopher • 1655 – Jamaica • 1672 – the Royal Africa Company was set up to import black slaves • Reasons so far: trade • religious persecution • penal settlement • 1718 – Transportation Act • 1782 – loss of the 13 American colonies Asia • • • • • • • • The Indian subcontinent 1700s – 3 trading posts Company Rule 1857- 8 – Indian Mutiny Under the direct control of the Br govt 1877 – Victoria= Empress of India Burma Afghanistan Australia • 1770 – Capt Cook • 1788 – First Fleet • Convicts • Gibraltar - 1714 • New Zealand • 1805 – Trafalgar • Br= master of the seas Africa • Dutch settlement in the south • Napoleonic Wars (1799-1815) • 1806 Britain purchased the Cape Colony from the Dutch • 1910 Union of South Africa – dominion • ‘Scramble for Africa’ • Egypt – the Suez Canal The Middle East • 1919 – the British Empire at its height • The Treaty of Versailles gave Britain most of the German Empire in Africa • Collapse of the Ottoman Empire – british acquisition of Palestine and Iraq in 1918 • Dissolution of Empire • Commonwealth of Nations • • • • 1887 – Golden Jubilee 1901 – Victoria died Edward VII (1901-10) Liberal reforms – beginnings of the welfare state • Lloyd George PM and his budget • George V (1910-36) • The House of Windsor • • • • • • 1911 Parliament Act House of Lords – limited power 1914 – WWI Central Powers – Allies End: 11 Nov 1918 Votes to women: 1918, 1928 • Suffragettes • Emmeline Pankhurst • Rise of the Labour Party • • • • The Irish problem 1914 – Home Rule 1916 – Easter Rising 1921: the Irish Free State and Northern Ireland • 1926 – General Strike • The Great Depression 1929 – • Edward VIII abdicated because of Mrs Simpson • George VI 1936-1952 • WWII • The Blitz Loss of Empire • United Nations Charter in 1945 called for progress towards self-government • The Partition of India – 1947 • 1931 – British Commonwealth of Nations • Loss of power and status on the world stage • The old imperial spirit revived in 1982 – Falklands War • Elizabeth II (1952 – • Born in 1926 • Immigration • Social Darwinism • Britain and the EU • Margaret Thatcher (1925 – 2013) • PM 1979-90 • Thatcherism • Northern Ireland • 1921, Ulster, 1972, The Troubles • Devolution: Northern Ireland Assembly