Notes # _____ - The Animal Cell
advertisement

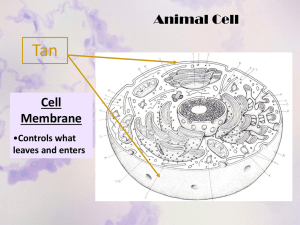
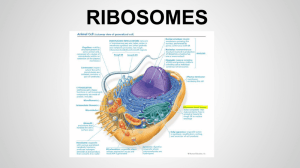
Notes # _____ - Cell Organelles This sheet accompanies the “Animal Cell Diagram” and “Plant Cell Diagram” Reviewing Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3. All cells are produced from other cells. The Organelles of the Animal Cell 1. Lysosome – digest food, break down old cell parts, viruses, and using enzymes. 2. Mitochondria – the “power plants” of the cell, they generate the energy a cell needs. 3. Nucleus – usually located near the center of the cell, home to your DNA and the nucleolus (#15). Serves as the control center for the cell and directs all cell activity. 4. (Rough) Endoplasmic reticulum – where proteins are produced by ribosomes and are shipped within the cell like “interoffice mail.” 5. Vacuole – store water and nutrients, “refrigerators.” 6. Membrane – controls what enters and exits the cell like a “bouncer” or “gatekeeper.” 7. Golgi bodies – receive products from the endoplasmic reticulum and package them for shipment outside of the cell like the “post office.” 8. Cytoplasm – “jelly-like” fluid that takes up most of the cell, this is where chemical reactions take place. 9. Ribosomes – “factories” of the cell, they “read” the directions given by the nucleus and produce proteins or replace damaged cell parts. 10. Nucleolus – where ribosomes are produced, inside the nucleus. The Organelles of the Plant Cell 1. Lysosome – digest food, break down old cell parts, viruses, and using enzymes. 2. Mitochondria – the “power plants” of the cell, they generate the energy a cell needs. 3. Nucleus – usually located near the center of the cell, home to your DNA and the nucleolus (#15). Serves as the control center for the cell and directs all cell activity. 4. (Rough) Endoplasmic reticulum – where proteins are produced by ribosomes and are shipped within the cell like “interoffice mail.” 5. Vacuole – store water and nutrients, “refrigerators.” 6. Membrane – controls what enters and exits the cell like a “bouncer” or “gatekeeper.” 7. Golgi bodies – receive products from the endoplasmic reticulum and package them for shipment outside of the cell like the “post office.” 8. Cytoplasm – “jelly-like” fluid that takes up most of the cell, this is where chemical reactions take place. 9. Ribosomes – “factories” of the cell, they “read” the directions given by the nucleus and produce proteins or replace damaged cell parts. 10. Nucleolus – where ribosomes are produced, inside the nucleus. 11. Cell Wall – provides extra support for the cell and gives it its shape. Mostly made of cellulose, the main component of wood and paper. 12. Chloroplasts – Food making structures that contain chlorophyll, which uses CO2, sunlight, and water to make sugars (photosynthesis).