Chapter 9 Study Guide
advertisement

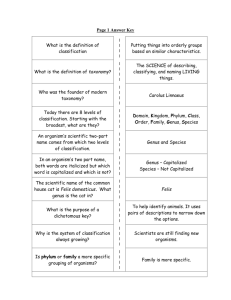
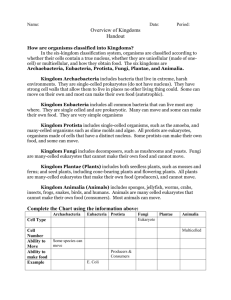
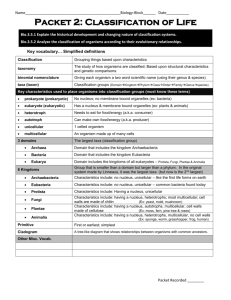
Chapter 9 Study Guide 1. Classification – the division of organisms into groups or classes based on characteristics. a. The more characteristics organisms share, the more closely related they are. 2. Taxonomy – The science of classifying, describing and naming living things. 3. Carolus Linneaus – The founder of modern taxonomy. 4. The seven levels of classification – Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species. - used to identify organisms; Series of Paired Statements 5. Dichotomous Key a. You should be able to read a dichotomous key Shows the similarities and differences between organisms. 6. Branching Diagram – a. If given a diagram, you should be able to answer questions on it. 7.Scientific Names – Humans – Homo sapien a. First part of the scientific name is the genus – Always capitalize b. Second part of the scientific name is the species – Always lower case c. Both parts should be underlined or italicized 8. The six kingdoms: Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Archaebacteria, Eubacteria 9. Example of an organism in each kingdom: a. b. c. d. e. Animalia – Sponge Plantae – Pine Tree Fungi – Mold or Mushroom Protista – Euglena Eubacteria – E. coli 10. The Six Kingdoms and characteristics of each: f. Animalia – Complex, multicellular organisms that can often move and have specialized sense organs, which allow them to respond to their environment. g. Plantae – Complex, Multicellular organisms that have a cell wall, do not move and make their own food through the process of photosynthesis. h. Fungi – Complex, multicellular organisms that are not green, do not eat or make their own food, but absorb nutrients that were broken down in their surroundings. i. Protista – single-celled or simple multicellular organisms that do not fit into any other kingdom. j. Eubacteria – single-celled prokaryotes that live in soil, water and on and in the human body k.Archaebacteria – single-celled prokaryotes that live in extreme environments.










![Classisifaction[1].](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009242731_1-b3ac9cc742de7cd8bc604e238c88928e-300x300.png)






