Heart Study Sheet Answers - TangHua2012-2013
advertisement

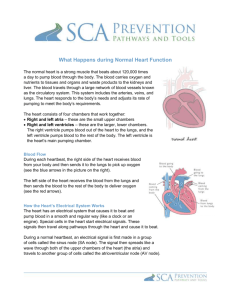
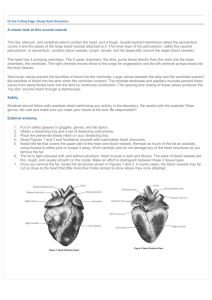
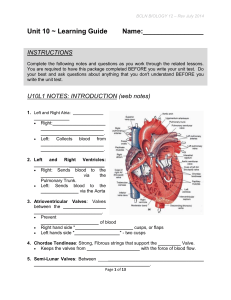
Key L.O. K – 1 Heart Identification and Functions 1. The heart on your left in diagrams is called the right side because the diagram is set up to indicate a person facing you. 2. Myocardium refers to the muscular wall of the hear. 3 The function of the Septum is to separate the left and right side of the hear. 4. Atrioventricular valves are found between the atria and the ventricles. 5. The different between the valves is the right side has 3 cusps and left side has 2 cusps. 6. The chordae tendineae is a strong fibrous string that supports the valves of the heart. 7. At the junction of the ventricle and the aorta or the ventricle and Pulmonary Trunk is another valve called the semi-lunar valve. 8. The Pulmonary Trunk is one large vessel that branches into two left and right Pulmonary Artery which take blood to the left and right lung to be oxygenated. 9. The walls of the Left Ventricle thicker than those of the Right Ventricle because it has the harder job of sending blood to the entire body. 10. The function of the atria is to send blood to the ventricles. 11. If the Chordae Tendinae that attached to the atrioventricular valves pulled loose the pressure caused by the contraction of the ventricle could force the cusps to invert causing a backflow of blood in the heart. L.O. K – 2 SA Node, AV Node, and Pukinje Fibres 1. The phrase “the heartbeat is intrinsic” means that it originates in the heart itself 2. Systole is another word for the contraction of the heart muscle is. 3. Diastole is another word for the relaxation of the heart muscle is. 4. The phases of the cardiac cycle and the length of time required by each phase is 1) 0.15 sec atrial systole/ventricular diastole 2) 0.03 sec - atrial diastole/ventricular systole 3)0.4 sec – atria diastole/ventricular diastole. 5. The lubb-Dupp sound of a heart beat is caused by the closing of the valves. 6. The two names for the tissue found in the upper wall of the right atrium is nodal tissue or the sinoatrial node 7. At the bottom of the right atrium is another type of tissue called the atrioventricular node. 8. The function of the sinoatrial node is to initiate the heartbeat by automatically sending out excitation impulses which cause the atria to contract.(pacemaker) 9. If the sinoatrial node is damaged the heart will continue to beat but at a slower pace. 10. The function of the Atrioventricular node is to stimulate the ventricles to contract 11. Perkinje fibers carry the message from the AV Node to the ventricle muscle tissue. 12. Be able to identify the different stages of a normal EKG. Pretty quick response system though L.O. K – 3 Autonomic Regulation of the Heart 1. Within the brain is a rate control center called the medulla oblongata. 2. The medulla oblongata can alter the rate of the heart beat by way of part of the nervous system called the autonomic nervous system. 3. The nerve that sends electrical information from the medulla oblongata to the SA Node is the vagus nerve. 4. The autonomic nervous system has two parts to it parasympathetic and sympathetic. 5. The part the speeds up the heart is called the sympathetic. 6. The part that slows down the heart is called the parasympathetic. L.O. K – 4 Blood Pressure: Hypertension and Hypotension 1. The name for the device that takes blood pressure readings is a sphygmomanometer 2. Normal blood pressure for a young adult is 120/80. 3. The first number in a blood pressure reading stands for the systolic reading as ventricles contract. 4. The second number in a blood pressure reading stands for the diastolic readings as the heart relaxes. 5. A pulse is initiated by the left ventricle. 6. The elastic recoil ability of the arteries make a pulse possible. 7. The artery help maintain blood pressure by expansion – lower blood pressure and contraction – raises blood pressure. 8. Hypertension – high blood pressure 9. Hypotension – low blood pressure 10. Be able to list at least 5 very important factors that are responsible for high blood pressure. Smoking, stimulants, lack of exercise, diet, stress, plaque, high salt intake, working too hard, age/sex/race 11. Explain how the veins, arteries, and capillaries can regulate blood pressure. Dialation or constriction of the blood vessels regulates blood pressure. 12. Explain how the spleen can regulate blood pressure. Can hold up to 20 – 30% of red blood cells – store or release depending on the need of the body L.O. K – 5 Systolic Pressure vs Diastolic Preesure 1. The highest arterial pressure is called systolic. 2. The lowest arterial pressure is called diastolic. 3. Diastolic pressure occurs while the heart ventricles are relaxed. 4. Systolic pressure occurs while the heart is ejecting blood. 5. Arteries have the highest blood pressure. 6. What blood vessel has the lowest blood pressure are the capillaries 7. Can you have a blood pressure of 120/140? Explain. No, blood pressure will never be higher when the heart is at rest than when it is not. The bottom number is related to the heart being at rest therefore it will never be higher than the top number.