Matter Notes
advertisement

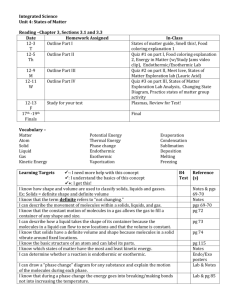
Matter Notes Chemistry = the study of matter and how it changes Properties of Matter Matter = anything that has mass and volume Property = characteristic Physical Properties Intensive – not affected by the amount of the substance e.g. - hardness - state: solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g) - color - malleability - density - temperature Extensive – affected by the amount of the substance - volume (area) - mass (weight) Physical vs. Chemical Properties Physical properties – can be observed and measured without changing the composition (chemical formula) of matter Physical properties are either intensive or extensive. Chemical properties – properties that can be observed only when substances interact with one another; changes the chemical formula (composition) All chemical properties are intensive. e.g. flammability, rust formation Evidence that a chemical reaction may have occurred Gas is produced Formation of a solid Heat or light is given off Change in color -1- Matter Notes (On whiteboard) States of Matter Shape Definite Indefinite Indefinite Solid Liquid Gas Volume Definite Definite Indefinite Density High High Very low 1000X lower than solids/liquids Compressible? No No Yes Mass Definite Definite Definite Note: States of matter are subject to changes in T and P. Solid liquid gas Vibrate slide past one another move freely and randomly Energy ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Energy Changes Related to Changes in States of Matter Endothermic, Sublimation Endothermic Melting, fusion Solid Exothermic freezing, Endothermic vaporization Liquid Exothermic condensation solidification Exothermic, Deposition -2- Gas Matter Notes Clarification of Terms (from whiteboard) Define: 1. a) hypothesis: If, then statements; a reasonable statement that can be tested (predicts) b) law: statement or mathematical expression of something that always happens; testable (describes) c) theory: broad generalization that is based on observation, experimentation, and reasoning; not testable; is modified as new information is discovered (explains) 2. a) malleable (capable of being hammered, rolled or pressed into various shapes without being broken) b) ductile (able to be drawn into a wire) 3. a) mass (amount of matter in an object, measured with a balance) b) weight (effect of gravity, therefore differs with location) 4. a) independent variable (experimenter manipulates; x axis) b) dependent variable (response to changes in independent variable; y axis) c) control (standard) 5. a) b) c) d) energy = ability to do work or produce energy law of conservation of energy (Energy cannot be created or destroyed) kinetic energy (energy of an object in motion) potential energy (energy of an object by its position and composition, i.e. energy that can be released) (Demo: penguin toy) 6. a) physical change (a change that does not alter the identity/composition of a substance, e.g. cutting something) b) chemical change (a change that alters the identity of a substance, e.g. combustion) (Demos: boiling water (endothermic, physical) burning candle (exothermic, chemical)) 7. Evidence that a chemical change may have taken place: a) production of a gas b) production of a solid (precipitate) c) change in color d) change in temperature -3-