GEOGRAPHY 352
advertisement

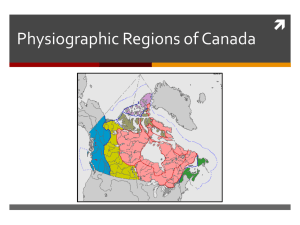
Geography 352 – World Regional Geography Exam 1 Study Guide The eventual test will be made up of as many as 100 Power Point identification, multiple choice, true/false, matching, and map questions. Not everything below will end up on the final version of the exam. “Nature” is a general term I use to mean qualities or attributes (including origins and locations). Power Point Identification Be able to match images on from lecture Power Point slides to the physiographic provinces of Europe that they represent. Be able to match the types of European natural vegetation portrayed on the lecture Power Point slides to their corresponding name. Be able to match images on the lecture Power Point slides to their corresponding type of European agriculture. Be able to match images on the lecture Power Point slides to the religions and branches of religions they represent. Multiple Choice, True/False, Matching, And Map Be able to match the four physiographic regions of Europe with their corresponding characteristics. What is the nature and origin of Loch Ness? What is the nature and location of fjords? Where are European volcanoes found? Be able to use a map similar to the one below to locate the physiographic regions of Europe. 1 What portion of the Central Uplands was used as an invasion route three times in the twentieth century? Why is Iceland where it is and what peculiar physical features does it possess? What are the nature of polders and the Delta Project? What are the climatic qualities of Ireland and why do they occur? What is the nature of Mediterranean climates? What is the nature of the puszta? What influence – if any – did Arabs have on Spain? What were the boundaries of the Roman Empire? Be able to tell the difference between Indo-European languages and languages from other language families. What are Europe’s Uralic languages? What is the nature of “Old Norse” and where is it still spoken? What is the tell-tale sign of Slavic settlement in Eastern Germany? What is the nature of the Basque language and how does it fit in with European nationalism? 2 What makes Switzerland so unusual in the context of European nationalism? What makes Belgium an interesting case study in the effects of language? Where do the huldufolk live and what do they say about the nature of religious belief in Europe? Who created the doctrines of Christianity and who established the institution of the Church in Rome? What was the role of the Roman Empire in the establishment of Christianity in Europe? Be able to match the religions (Islam) or branches of religions (Roman Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy) of Europe with the regions in the Balkans where they are dominant. What sects of Christianity influenced the divided Germany and what is the status of religion in the reunified Germany? Be able to match the religions and religious branches of Europe with their corresponding locations on a map similar to the one below. Be able to use the map below to identify some of the major forms of natural vegetation in Europe. 3 Be able to use the map below to identify the locations of European language families and languages. In which European country would you be most likely to find instances of glacial scouring and scoring (scratching) of exposed bedrock? In which physiographic province of Europe would you be most likely to find diamonds? What is the nature of glacially-carved valleys vs. those carved out by rivers? Where are the terms “glen” and “loch” used? 4 What are the origins of Arthur’s Seat and the Giant’s Causeway? What is the nature of the meseta? What is the nature of glacial deposition and where is the effect of glacial deposition most noticeable? What features make the Champagne Region distinctive? What is the nature of puys? What is the nature of the Rhine Graben? What is the nature of the Hercynian Hills? Be able to match Alpine System mountain ranges (Pyrenees, Apennines, Carpathians, and Dinaric Alps) with their corresponding characteristics. What is the nature and history of Mediterranean volcanoes? What are the characteristics of the various grasslands of Europe? What are the characteristics of orographic precipitation patterns in Europe? What does the suffix wald mean and what does it relate to? What is the nature of the boreal forest biome? What is the nature of tundra biomes? What is the nature of heaths or moors? What is the nature of Mediterranean agriculture? What are the peculiarities of European dairy production and consumption? What is the nature of European commercial mixed crop and livestock agriculture? What is the nature of grain farming in Europe? What is the nature of the transhumance livestock tradition in Europe? What is the nature of pastoral nomadism in Europe? 5 Be able to identify the characteristics and historical importance of the Celtic, Germanic and Slavic groups mentioned in lecture. Be able to match the Slavic language groups (East, West, and South) with their representative Slavic languages. Be able to match three Viking groups (Norse, Danes, and Swedes) with the areas they affected. What was the impact of the Islamic invasions on Europe? What were the periods in the development of English as a language and what were the primary influences during each period? What is the nature of languages and dialects in Spain? Be able to match the Indo-European language branches (Germanic, Romance, and Slavic) to their corresponding languages. What are the religious and linguistic significance of the Cyrillic alphabet? What was the nature of historic anti-Semitism in Europe? What are the characteristics of “pagan” religions in Europe? What are the characteristics of nationalism and nation-states in Europe? 6