PETE 342 PETROLEUM RESERVOIR ENGINEERING I
advertisement

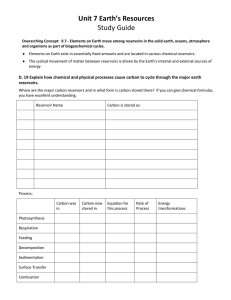
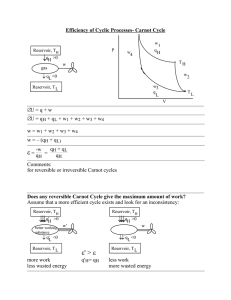
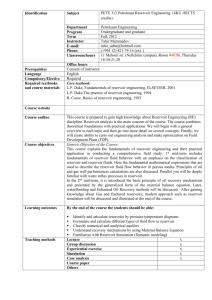
PETE 343 PETROLEUM RESERVOIR ENGINEERING I Fall 2008-2009 Dr. Parlaktuna COURSE DESCRIPTION Estimation of hydrocarbon pore volume and recovery factor. Classification of oil reservoirs. Reservoir performance prediction for solution gas drive, water drive, gas-cap drive, drainage and combination drive reservoirs using material balance approach. Water influx theory. Water and gas coning in oil producing formations. Characterization of fractured reservoirs. Decline Curve Analysis. COURSE OUTLINE 1. Introduction 2. Review of Fundamental Rock and Fluid Properties 3. Reservoir Drive Mechanisms, Reserve Estimates 3.1. Drive Mechanisms 3.2. Volumetric Calculations 3.3. Reserve Definitions 3.4. Probabilistic Approach for Reserve Estimates 4. Material Balance Equations 4.1. Introduction 4.2. General Material Balance Equation 4.3. Material Balance Equations for Different Drive Mechanisms 4.4. Material Balance Expressed as a Linear Equation 5. Fluid Flow through Porous Media 5.1 Single phase steady state and pseudo steady state model 5.2 Definition and derivation of volumetric average pressure equations 5.3 One well and multi well problems - Superposition 6. Water Influx 7. Predictive Methods for Reservoir Performance 6.1. Tarner Method 6.2. Schilthius Method 6.3 Havlena Odeh Method 8. Decline Curve Analysis 9. Coning (Reading Assignments) Books: Course Book: Dake, L.P., (1978) Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering, Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam Reference Book: Craft B.C., Hawkins, M.F., (1959) Applied Petroleum Reservoir Engineering, Prentice Hall Inc., New Jersey. Midterms: 1st Midterm: 2nd Midterm: November 8, 2008 December 27, 2008 Grading: Midterm I and II Final Homeworks (Saturday) (Saturday) 20 % each 30 % 30 %