3rd Grade - IC Language
advertisement
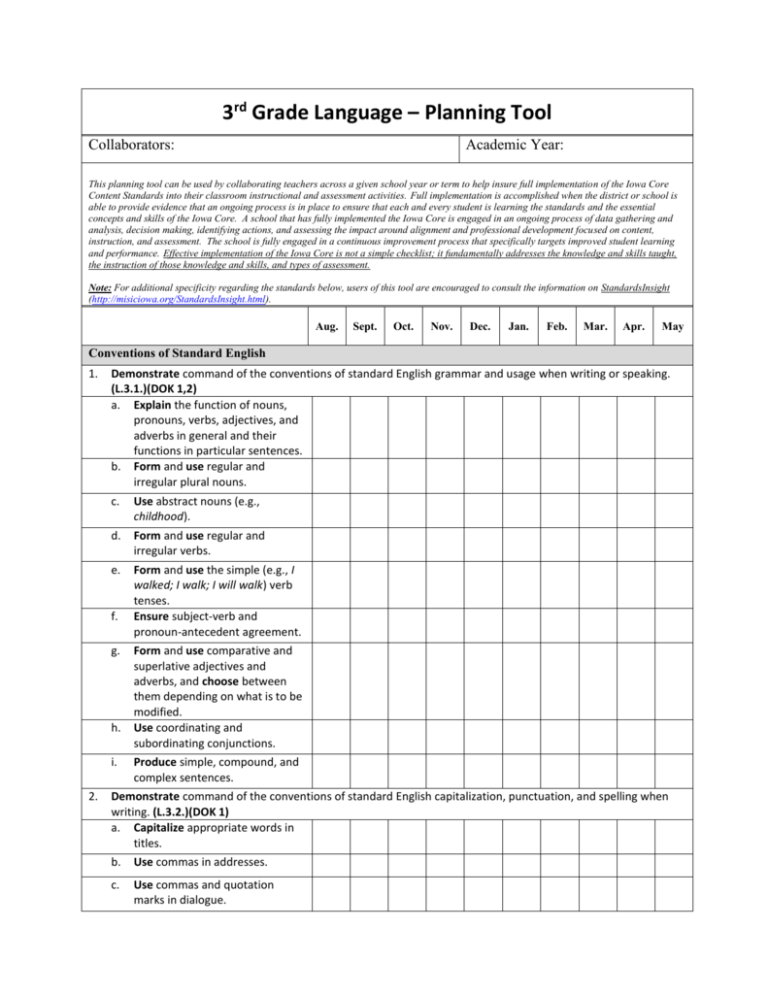
3rd Grade Language – Planning Tool Collaborators: Academic Year: This planning tool can be used by collaborating teachers across a given school year or term to help insure full implementation of the Iowa Core Content Standards into their classroom instructional and assessment activities. Full implementation is accomplished when the district or school is able to provide evidence that an ongoing process is in place to ensure that each and every student is learning the standards and the essential concepts and skills of the Iowa Core. A school that has fully implemented the Iowa Core is engaged in an ongoing process of data gathering and analysis, decision making, identifying actions, and assessing the impact around alignment and professional development focused on content, instruction, and assessment. The school is fully engaged in a continuous improvement process that specifically targets improved student learning and performance. Effective implementation of the Iowa Core is not a simple checklist; it fundamentally addresses the knowledge and skills taught, the instruction of those knowledge and skills, and types of assessment. Note: For additional specificity regarding the standards below, users of this tool are encouraged to consult the information on StandardsInsight (http://misiciowa.org/StandardsInsight.html). Aug. Sept. Oct. Nov. Dec. Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. May Conventions of Standard English 1. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. (L.3.1.)(DOK 1,2) a. Explain the function of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in general and their functions in particular sentences. b. Form and use regular and irregular plural nouns. c. Use abstract nouns (e.g., childhood). d. Form and use regular and irregular verbs. e. Form and use the simple (e.g., I walked; I walk; I will walk) verb tenses. Ensure subject-verb and pronoun-antecedent agreement. f. g. h. i. 2. Form and use comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs, and choose between them depending on what is to be modified. Use coordinating and subordinating conjunctions. Produce simple, compound, and complex sentences. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. (L.3.2.)(DOK 1) a. Capitalize appropriate words in titles. b. Use commas in addresses. c. Use commas and quotation marks in dialogue. Aug. d. Sept. Oct. Nov. Dec. Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. May Form and use possessives. e. Use conventional spelling for high-frequency and other studied words and for adding suffixes to base words (e.g., sitting, smiled, cries, happiness). f. Use spelling patterns and generalizations (e.g., word families, position-based spellings, syllable patterns, ending rules, meaningful word parts) in writing words. g. Consult reference materials, including beginning dictionaries, as needed to check and correct spellings. Knowledge of Language 3. Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening. (L.3.3.)(DOK 2) a. Choose words and phrases for effect. b. Recognize and observe differences between the conventions of spoken and written standard English. Vocabulary Acquisition and Use 4. Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning word and phrases based on grade 3 reading and content, choosing flexibly from a range of strategies.(L.3.4.)(DOK 1,2,3) a. 5. Use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. b. Determine the meaning of the new word formed when a known affix is added to a known word (e.g., agreeable/disagreeable, comfortable/uncomfortable, care/careless, heat/preheat). c. Use a known root word as a clue to the meaning of an unknown word with the same root (e.g., company, companion). d. Use a known root word as a clue to the meaning of an unknown word with the same root (e.g., company, companion). Demonstrate understanding of word relationships and nuances in word meanings. (L.3.5.)(DOK 1,2,3) a. Distinguish the literal and nonliteral meanings of words and phrases in context (e.g., take steps). Aug. Sept. Oct. Nov. Dec. Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. a. 6. Identify real-life connections between words and their use (e.g., describe people who are friendly or helpful). b. Distinguish shades of meaning among related words that describe states of mind or degrees of certainty (e.g., knew, believed, suspected, heard, wondered). Acquire and use accurately gradeappropriate conversational, general academic and domain-specific words and phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner that night we went looking for them). (L.3.6.)(DOK 1,2) Language Arts Depth-Of-Knowledge Definitions - Writing Level 1 Recall of Information Level 1 requires the student to write or recite simple facts. This writing or recitation does not include complex synthesis or analysis but basic ideas. The students are engaged in listing ideas or words as in a brainstorming activity prior to written composition, are engaged in a simple spelling or vocabulary assessment or are asked to write simple sentences. Students are expected to write and speak using Standard English conventions. This includes using appropriate grammar, punctuation, capitalization and spelling. Some examples that represent but do not constitute all of Level 1 performance are: Use punctuation marks correctly. Identify Standard English grammatical structures and refer to resources for correction. Level 2 Basic Reasoning Level 2 requires some mental processing. At this level students are engaged in first draft writing or brief extemporaneous speaking for a limited number of purposes and audiences. Students are beginning to connect ideas using a simple organizational structure. For example, students may be engaged in note-taking, outlining or simple summaries. Text may be limited to one paragraph. Students demonstrate a basic understanding and appropriate use of such reference materials as a dictionary, thesaurus, or web site. Some examples that represent but do not constitute all of Level 2 performance are: Construct compound sentences. Use simple organizational strategies to structure written work. Write summaries that contain the main idea of the reading selection and pertinent details. May Level 3 Complex Reasoning Level 3 requires some higher level mental processing. Students are engaged in developing compositions that include multiple paragraphs. These compositions may include complex sentence structure and may demonstrate some synthesis and analysis. Students show awareness of their audience and purpose through focus, organization and the use of appropriate compositional elements. The use of appropriate compositional elements includes such things as addressing chronological order in a narrative or including supporting facts and details in an informational report. At this stage students are engaged in editing and revising to improve the quality of the composition. Some examples that represent but do not constitute all of Level 3 performance are: Support ideas with details and examples. Use voice appropriate to the purpose and audience. Edit writing to produce a logical progression of ideas. Level 4 Extended Reasoning Higher-level thinking is central to Level 4. The standard at this level is a multi- paragraph composition that demonstrates synthesis and analysis of complex ideas or themes. There is evidence of a deep awareness of purpose and audience. For example, informational papers include hypotheses and supporting evidence. Students are expected to create compositions that demonstrate a distinct voice and that stimulate the reader or listener to consider new perspectives on the addressed ideas and themes. An example that represents but does not constitute all of Level 4 performance is: Write an analysis of two selections, identifying the common theme and generating a purpose that is appropriate for both.