GEOGRAPHY and ANCIENT CHINA
advertisement

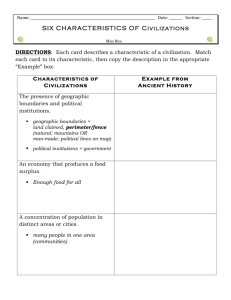
GEOGRAPHY AND ANCIENT CHINA Seventh Grade, Concord Middle School The land and people of China created one of the world’s oldest continuous civilizations. The distinctive features of this civilization were shaped by both its access to arable land along two river valleys and its isolation from its neighbors. By applying the five themes of geography to this part of the world, the movement of people and their interactions with their environment are revealed as key factors in influencing their culture. The five themes of geography provide a pragmatic approach to studying an immense region with tremendous diversity. China’s location is a significant factor on its history. China has been historically cut off from its neighbors to the west by natural features. As a result, China developed a distinct civilization from South and Southwest Asia. In due course, its neighbors to the east were strongly influenced by China. China’s land today can be divided into several distinctive regions. For the sake of narrowing our focus to ancient China, we will look at China in terms of four zones: north and south, east and west. It is imperative that we understand the geographic features of each zone in order to understand the interaction of people in China’s early history. Within China, the people of the north and south competed for land and resources, creating a history of movement and conflict. Beginning with a close study of China’s geographic features, students will describe the attributes of the civilizations that grew along two of its river valleys. Using the five themes of geography, a framework and vocabulary familiar to students, they will use a variety of sources to draw conclusions about the river valley civilizations. Initially we will study the themes of “location”, “region”, and “place.” As they explore these civilizations through primary source materials, readings, and film clips, students will reflect on their conclusions. Using critical thinking skills, students will be expected to construct support for how the final two geographic themes of Ancient China: “humanenvironment interaction” and “movement” were key factors in shaping its history and culture. Essential Questions Where is China? How do maps enable us to learn about history and culture? What are the characteristics of the land that shaped the Chinese civilization? Learning Objectives 1) Identify the absolute and relative locations of China 2) Create big maps of China to identify the following geographic features and predict their impact on the development of civilization. a. Physical b. Climate c. Natural Resources d. Cultural (Ethnic/Language Groups) e. Early Chinese Civilizations (5000-1700 BC) 3) Locate and describe the origins of Chinese civilization in the Huang-He Valley during the Shang Dynasty. Day One: Location Essential Question Where is China? Student Outcome Identify the absolute and relative locations of China Materials • Six Globes • Classroom Wall Map of World (Pacific Rim perspective) • Six Nystrom World Atlases • 30 East Asia map worksheets • 30 Location worksheets • Transparency of Location worksheet • Overhead projector Procedure 1) Arrange desks into six table groups with a globe and atlas for each table. 2) Location worksheets should be distributed as students enter the classroom with a reminder to read the directions after filling in their names. 3) Go over definitions for absolute and relative locations, generating examples from students. 4) Direct students to locate China on the globes at each table 5) “Which continent is China part of?” 6) “With your table groups, fill in your observations for #2 and complete the location worksheet” 7) Allow twenty minutes for students to complete worksheet in their groups. 8) Go over worksheet by having students from each group fill in transparency on overhead for #2-5. 9) List volunteer student responses for #6. 10) Distribute East Asia map assignment and remind students of map expectations for class. China Absolute and Relative Location Warm-Up (to be completed as soon as you take your seat) 1. Define the following terms: a. Absolute __________________________________________________ b. Relative __________________________________________________ Relative Location (to be completed as directed by your teacher) 2. Describe China’s relative position on the globe _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ 3. Shade in the U.S.A. and China below QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Describe China’s relative position to the United States using this map and the wall map of the world _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ Absolute Location 4. Using the atlas, identify the farthest absolute location points of China North N South N E E East N West N E E 5. What are the absolute locations for each of the following cities in China? Beijing N E Shanghai N E Hong Kong N E Drawing Conclusions 6. What do these coordinates and its relative location tell us about China? _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ Political Map Assignment East Asia Directions: Use the Nystrom Atlas and your textbook to complete the map 1. Label the following political characteristics with horizontal labels: China Japan North Korea South Korea Nepal India Mongolia Russia Bhutan Taiwan Mynamar Vietnam Laos Thailand Hainan 2. Color in the labeled nations 3. Title the map and create a key Shanghai Hong Kong Philippines Beijing Tokyo Nanjing Xi’an Zhengzhou Taipei KEY http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/Asiaweb/blankmap.htm Day Two: Creating Big Maps (Place and Region) Essential Questions How do maps enable us to learn about history and culture? What are the characteristics of the land that shaped the Chinese civilization? Student Outcome Create big maps of China to identify the following geographic features and predict their impact on the development of civilization. Physical Climate Natural Resources Cultural (Ethnic/Language Groups) Early Chinese Civilizations (5000-1700 BC) Materials 2 Overhead projectors 2 transparencies of blank outline map of China 6 black permanent markers (thick) 5 large sheets of butcher paper (3’ x 4’) 2 large foam core boards 25 copies of blank map (8.5”x11”) Laptops with internet access Primary Source geography information packet Procedure 1) Before students arrive in class, tape one piece of butcher paper to your whiteboard and hang one piece of foam board on a bulletin board. 2) Position the overhead projectors so the overhead transparency of the blank China map is projected onto each. Trace the corners of the transparency (to keep the alignment accurate). Both projectors should be positioned away from high traffic areas of the classroom. 3) Students are divided into five groups. They may be divided as follows – a. By ability level with map topics pre-selected by teacher OR b. heterogeneous groups may select map topics by interest 4) The “physical features” map group is assigned to the foam board projection and another group is assigned to the other projection. 5) The rest of the class is directed to exchange maps of East Asia and correct each other’s work. 6) The tracing groups should take turns so that each member has a chance to trace the projection. 7) Each group should begin the worksheet for their topic as the tracings continue. 8) Teacher checks in with groups as they brainstorm approaches to completing the Big Map. PHYSICAL FEATURES What are topographical or elevated maps? Use the Nystrom Atlas, your textbook, and these sites: relief map, national geographic as research sources. In this table, list the physical features of China you will include on your big map: Mountains Highlands Plains Rivers Deserts With your group, brainstorm approaches to creating a map that reflects varied elevations. Be prepared to discuss your ideas with your teacher. CLIMATE Define climate Use the Nystrom Atlas, your textbook, and relief /climate map, as research sources. Describe the climates of the following regions in China Northeast North South Southeast Southwest Northwest With your group, brainstorm approaches to creating a map that reflects the varied climates. Be prepared to discuss your ideas with your teacher. NATURAL RESOURCES What are natural resources? Use the Nystrom Atlas and your textbook as research sources. List the natural resources your group will be identifying on your map: What is the percentage of arable land in China? __________% With your group, brainstorm approaches to creative representations of different resources. Be prepared to discuss your ideas with your teacher. CULTURAL What is an ethnic group? How many language and ethnic groups are there in China? List them in the table below along with their percentage of the whole population. With your group, brainstorm approaches to representing these different groups on a map. Be prepared to discuss your ideas with your teacher. EARLY CHINESE CIVILIZATIONS Use the Nystrom World History Atlas, your textbook, and Metropolitan Museum of Art: Timeline of History, China, 8000-2000 BCE as resources. Where did the Yangshao and Longshan civilizations settle? Why? Your map should include descriptive information for each civilization. Your group must determine how to represent the locations and achievements of these civilizations. Be prepared to discuss your ideas with your teacher. Days Three and Four: Creating Big Maps (Place and Region) Essential Questions How do maps enable us to learn about history and culture? What are the characteristics of the land that shaped the Chinese civilization? Student Outcome Create big maps of China to identify the following geographic features and predict their impact on the development of civilization. Physical Climate Natural Resources Cultural (Ethnic/Language Groups) Early Chinese Civilizations (5000-1700 BC) Materials Cardboard Old newspapers Paint Colored plasticene or clay Markers (including blue and black permanent) Glue Sponges Procedure Students work in groups to complete big maps Day Five: Presenting Big Maps (Human-Environment Interaction and Movement) Essential Questions What are the characteristics of the land that shaped the Chinese civilization? Student Outcome Create big maps of China to identify geographic features and predict their impact on the development of civilization Materials 25 copies “Drawing Conclusions” Procedure 1. Set up desks into five tables to display Big Maps to simulate a museum exhibit. 2. Distribute “Drawing Conclusions” to students 3. Direct students to rotate to each table and fill in sheets with 2-3 facts per category. 4. When students finish gathering facts, have them sit on the floor in the center of the room in a semi-circle facing the projector screen. 5. Project image of Basin (Gansu province) from Yangshao period 6. “Take a few minutes to study the features of this basin. It was found in Northern China and dates from 3200-2700 BC. What are its features? What is it made from? What was it used for? Based on what you know about the geographic features of Northern China, what can you tell me about the culture that created this basin?” 7. Direct students to fill in center box titled “People of the North” 8. Project image of ritual object (bi), Neolithic period, Liangzhu culture, ca. 2700–2500 B.C. 9. “Again, let’s take a few minutes to study this image closely. This object dates from 2700-2500 BC and was found in Jiangsu or Zhejiang Province, China. What are its features? What is it made from? What was it used for? Based on what you know about the geographic features of Southern China, what can you tell me about the culture that created this object?” 10. Direct students to fill in center box titled “People of the South” 11. Read the instructions on the back of the sheet aloud to students. 12. Respond to any questions. Drawing Conclusions: Gathering Facts from Big Maps List 2-3 facts from each map for features of the north and south NORTH SOUTH WRITING TASK You are a museum curator that must create a description to introduce an exhibit titled “Ancient Civilizations of China: Geographic Influences.” In your description, you must include four to five details from the front of this sheet to support your claim of how geography shaped the ancient civilizations of China. The description will be reviewed by colleagues at the museum before its display on a large sign at the start of the exhibit.