Key Terms for The Gilded Age Exam
advertisement

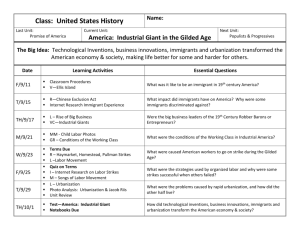
Key Terms for The Gilded Age Exam How did the forces of innovation, urbanization, industrialization and immigration change America during the time known as the Gilded Age? The Expansion of Industry (pp 230 – 235) What made the expansion of industry possible and how did industrialization change American? How did inventions of the time change the way Americans lived? Bessemer process, Thomas Edison, Alexander Graham Bell, industrialization, factories, assembly lines The Age of the Railroads (pp 236 – 240) How did the growth of railroads facilitate commerce in America? What are some ways that railroad companies abused their power? Transcontinental railroad, George M. Pullman, Credit Mobilier, Munn v. Illinois, Interstate Commerce Act, time zones, Central pacific, Union Pacific Big Business and Labor (pp 241 – 249) How did Social Darwinism provide justification for the rise of big business at the expense of labor? What were some obstacles facing unions in their attempts to organize for workers’ rights? Andrew Carnegie, vertical and horizontal integration, Social Darwinism, monopoly, vertical integration, Triangle Shirtwaist Fire, Phillip Armour, J.P. Morgan, Gustavus Swift, Andrew Carnegie, John Rockefeller, Cornelius Vanderbilt, Knights of Labor, UMW, Samuel Gompers, American Federation of Labor (AFL), Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), Big Bill Haywood, Eugene Debs, Haymarket Affair , Mary Harris Jones, Sherman Antitrust Act, Pullman Strike, robber barons, captains of industry, laissez faire capitalism, Wobblies, trusts, mergers, yellow dog contracts, statistics describing distribution of wealth The New Immigrants (pp 254 – 261) What were push and pull factors driving immigration during the Gilded Age? What were some of the challenges and obstacles immigrants faced when attempting to immigrate to the US?. How were immigrants from Europe, Asia and Latin America regarded differently? What challenges did these immigrant groups face when attempting to “assimilate” to the dominant culture Ellis Island, Angel Island, tenements, nativism, settlement houses, melting pot, Americanization movement, urbanization, Jane Addams, Social Gospel movement, Chinese Exclusion Act, Denis Kearney, Anti-Chinese movement and methods of exclusion, Gentlemen’s Agreement, patterns of immigration up to the 1920s The Challenges of Urbanization (pp 262 – 266) How did the works of Jane Addams, Jacob Riis and proponents of the Social Gospel movement act as a critique of Social Darwinism? Urbanization, Americanization movement, tenements, mass transit, Social Gospel movement, urban problems (multiple), settlement house, Jane Addams, Jacob Riis Segregation and Discrimination (pp 286 – 291) How were new immigrants and people of color restricted from assimilating fully into US society as a result of “legal” exclusionary laws and practices? What were some reactions to those practices by people of color? Ida B. Wells, poll tax, grandfather clause, segregation, Jim Crow laws, Plessy v. Ferguson, debt peonage Expanding Public Education (pp 284-285) How did Booker T. Washington and W.E.B. Du Bois differ in their approaches to achieving equality for African Americans? Booker T. Washington, WEB Dubois The Dawn of Mass Culture (pp 292 – 299) What were some of the early hallmarks of American mass culture that have been adopted around the world? Susan B. Anthony, Joseph Pulitzer, William Randolph Hearst, Ashcan school, Mark Twain, rural free delivery (RFD), Coney Island, amusement parks, public parks, baseball, cycling and bikes, department stores Additional Sources Reading excerpt from Destiny of the Republic (key terms include antisepsis and Centennial Exhibition) Article: "The Coal Mining Industry" (key terms include: anthracite coal and place where most anthracite is mined, Breaker boys, black lung disease) Films: "Matewan" (See film study guide handout for key terms and characters) Quotes from textbook, readings and films