COMPETENCY AND INDONESIAN QUALIFICATION FRAMEWORK
advertisement
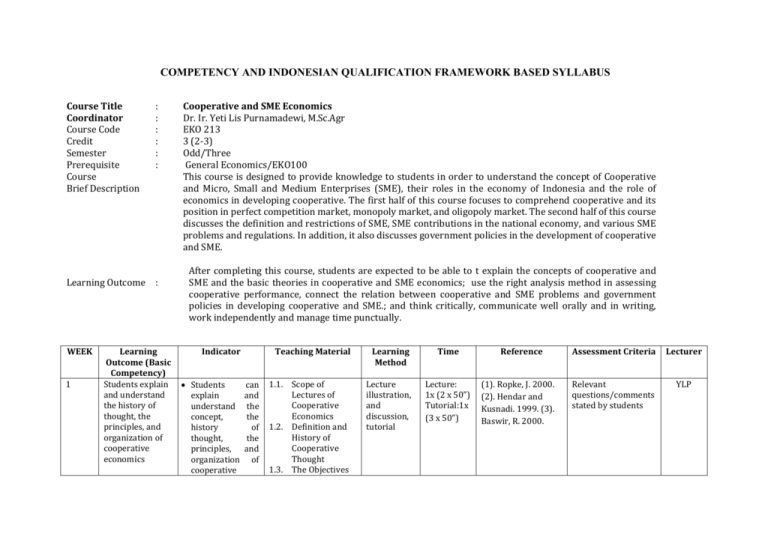
COMPETENCY AND INDONESIAN QUALIFICATION FRAMEWORK BASED SYLLABUS Course Title Coordinator Course Code Credit Semester Prerequisite Course Brief Description : : : : : : Learning Outcome : WEEK 1 Learning Outcome (Basic Competency) Students explain and understand the history of thought, the principles, and organization of cooperative economics Cooperative and SME Economics Dr. Ir. Yeti Lis Purnamadewi, M.Sc.Agr EKO 213 3 (2-3) Odd/Three General Economics/EKO100 This course is designed to provide knowledge to students in order to understand the concept of Cooperative and Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (SME), their roles in the economy of Indonesia and the role of economics in developing cooperative. The first half of this course focuses to comprehend cooperative and its position in perfect competition market, monopoly market, and oligopoly market. The second half of this course discusses the definition and restrictions of SME, SME contributions in the national economy, and various SME problems and regulations. In addition, it also discusses government policies in the development of cooperative and SME. After completing this course, students are expected to be able to t explain the concepts of cooperative and SME and the basic theories in cooperative and SME economics; use the right analysis method in assessing cooperative performance, connect the relation between cooperative and SME problems and government policies in developing cooperative and SME.; and think critically, communicate well orally and in writing, work independently and manage time punctually. Indicator Students explain understand concept, history thought, principles, organization cooperative can and the the of the and of Teaching Material Learning Method Time 1.1. Scope of Lectures of Cooperative Economics 1.2. Definition and History of Cooperative Thought 1.3. The Objectives Lecture illustration, and discussion, tutorial Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) Reference (1). Ropke, J. 2000. (2). Hendar and Kusnadi. 1999. (3). Baswir, R. 2000. Assessment Criteria Lecturer Relevant questions/comments stated by students YLP economics 2 Students explain the organization, management, capital and guidelines in setting up a cooperative 3. Students explain various relationships in cooperative and cooperative advantage prerequisite Students can explain the organization, management, capital and guidelines in setting up a cooperative Students can explain various relationships in cooperative and cooperative advantage prerequisite and Principles of Cooperative 1.4. Theoretical Concept Need in Cooperative Analysis and the Scope of Cooperative Economics 2.1. Organization, Management and Capital of Cooperative 2.2. Guidelines to Set up Cooperative: 2.2.1. Form and Position of Cooperative 2.2.2. Government Role in Setting up Cooperative 2.2.3. Preparation to Set up Cooperative 2.2.4. Setting up Cooperative 3.1. Various Relationships in Cooperative and Reasons to Become Member of Cooperative 3.2. Cooperative in Strategic Triangle 3.3. Cooperative Advantage Lecture illustration, tutorial Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1) Hendar and Kusnadi. 1999. (2) Act Number 17 year 2012 Relevant questions/comments stated by students ; presentation based on field study report assignment on cooperative case per group YLP Lecture illustration, and discussion, , tutorial Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1) Hendar and Kusnadi. 1999. (2) Act Number 17 year 2012 Relevant questions/comments stated by students and structured assignment YLP Prerequisite and the General Requirement for Organization Development Success 4 Students explain the concept of cooperative efficiency Students can explain the concept of cooperative efficiency 4.1. Profit Maximization Model 4.2. Cooperative Types and Efficiency 4.3. Integrated Cooperative Efficiency Lecture illustration, and discussion, , tutorial Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1) Hendar and Kusnadi. 1999. Relevant questions/comments stated by students and structured assignment AA 5 Students explain the existence of cooperative in market system Students can explain the existence of cooperative in market system 5.1. Lecture illustration, and discussion, , tutorial Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1). Ropke, J. 2000. (2). Hendar and Kusnadi. 1999. Relevant questions/comments stated by students and structured assignment AA 6 Students explain the concept of member participation in cooperative Students can explain the concept of member participation in cooperative Lecture illustration, and discussion, , tutorial Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1). Ropke, J. 2000. (2). Hendar and Kusnadi. 1999. (3). Baswir, R. 2000. Relevant questions/comments stated by students and structured assignment AA The Power and Weaknesses of Cooperative in Market System 5.2. Cooperative in Trading System Chain 5.3. Vertical Integrated Target through Cooperative 5.4. Attitudes on Cooperative Price Policy 6.1. Definition of Participation 6.2. Definition of the Importance of Participation 6.3. How to Improve Participation 6.4. Participation Stimulation 6.5. Participation Cost 7 Students explain the existence of cooperative and cooperative strategy in the perfect competition market Students can explain the existence of cooperative and cooperative strategy in the perfect competition market 8 Students explain the existence of cooperative and cooperative strategy in monopoly and oligopoly markets Students can explain the existence of cooperative and cooperative strategy in monopoly and oligopoly markets 9 Students explain the definition and success Students can explain the definition and 7.1. Cooperative Target 7.2. Cooperative in the Perfect Competition Market 7.3. Short-run Analysis 7.4. Long-run Analysis Lecture illustration, and discussion, , tutorial MID-TEST (35%) 8.1. Potential Lecture Competitors of illustration, Cooperative and 8.2. Cooperative and discussion, , Natural tutorial Monopoly 8.3. Definition of Oligopoly Market 8.4. Strategy in Oligopoly Market 8.5. Restrictions to Enter the Market 9.1. Definition of Cooperative Entrepreneurship Lecture illustration, and Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1). Ropke, J. 2000. (2). Hendar and Kusnadi. 1999.. Relevant questions/comments stated by students and structured assignment AA Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1). Ropke, J. 2000. (2). Hendar and Kusnadi. 1999. Relevant questions/comments stated by students and structured assignment AA Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (1). Hendar and Kusnadi. 1999. Relevant questions/comments stated by students ; MF prerequisite of cooperative entrepreneurship success prerequisite of cooperative entrepreneurship 9.2. Competitive Advantage in Cooperative 9.3. Responsibilities of Cooperative Entrepreneursh ip 9.4. The Soul and Spirit of Cooperative Entrepreneursh ip 9.5. The Principles of Innovation discussion, tutorial (3 x 50”) presentation based on field study report assignment on cooperative case per group 10 Students explain the definition, characteristics, and contributions of SME Students can explain the definition, characteristics, and contributions of SME 10.1. Definition and Restrictions of SME 10.2. SME Characteristics 10.3. SME Contributions in the Economy Lecture illustration, and discussion, tutorial Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1) Act Number 20 Year 2008. (2) Ministry of Cooperatives and Small-Medium Enterprises (2005). Relevant questions/comments stated by students; presentation based of field study report assignment on cooperative case per group MF 11 Students explain the concept of business partnership Students can explain the concept of business partnership 11.1. Government Regulation on Business Partnership 11.2. The Principle in Business Partnership 11.3. The Rights and Obligations in Conducting Business Partnership Lecture illustration, and discussion, tutorial Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1) Indonesian Government Regulation No 44 year 1997 (2) Ministry of Cooperatives and Small-Medium Enterprises (2005). Relevant questions/comments stated by students ; presentation based on field study report assignment on cooperative case per group MF 12 Students explain various obstacles in cooperative and SME development Students can explain various obstacles in cooperative and SME development 13 Students explain the concept of cooperative performance and choose the right cooperative performance measurement method Students can explain the concept of cooperative performance and choose the right cooperative performance measurement method 14 Students explain government policies in developing cooperative and SME Students can explain government policies in developing cooperative and SME 12.1. 12.2. 12.3. 12.4. 12.5. 12.6. 12.7. 12.8. 13.1. Funding Marketing Raw Material Technology Management Bureaucracy Infrastructure Partnership Definition, Objectives and Advantages of Cooperative Performance Assessment 13.2. Cooperative Performance 13.3. Cooperative Performance Variables and Indicators 13.4. Cooperative Performance Measurement Method 14.1. Cooperative and SME Development 14.2. Challenges in the Development of Cooperative and SME 14.3. Direction, Strategies, Policies and Programs of Lecture illustration, and discussion, tutorial Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1) Ministry of Cooperatives and Small-Medium Enterprises (2005), (2) Firmansyah(2001) Lecture illustration, and discussion, , tutorial Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1). Ropke, J. 2000. (2). Hendar and Kusnadi. 1999. Lecture illustration, and discussion, tutorial Lecture: 1x (2 x 50”) Tutorial:1x (3 x 50”) (1) Hendar and Kusnadi. 1999. (2) Act Number 17 year 2012, (3) Act Number 20 Year 2008, (4) Ministry of Cooperatives and Small-Medium Enterprises (2005). Relevant questions/comments stated by students ; presentation based on field study report assignment on cooperative case per group Relevant questions/comments stated by students ; presentation based on field study report assignment on cooperative case per group Relevant questions/comments stated by students ; presentation based on field study report assignment on cooperative case per group MF YLP YLP Cooperative and SME Development FINAL TEST/UAS (35%) ASSIGNMENT (PAPER & PRESENTATION) (30%) Literature Reference: (1). Ropke, J. 2000. Ekonomi Koperasi, Teori dan Manajemen. Translated by Hj. Sri Djatnika S. Arifin. SE. M.Si. Penerbit Salemba Empat (2). Hendar dan Kusnadi. 1999. Ekonomi Koperasi. Lembaga Penerbit Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Indonesia. (3). Baswir, R. 2000. Koperasi Indonesia BPFE Yogyakarta. (4). Act Number 17 Year 2012 on Cooperative (5) Act Number 20 Year 2008 on Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (6) Indonesian Government Regulation No 44 Year 1997 on Partnership (7) The Ministry of Cooperative and Small Medium Enterprises (2005), The Development of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises and Cooperative. Jakarta. (8) Firmansyah, 2001. Dinamika Usaha Kecil dan Menengah. LIPI. Jakarta. Lecturer Team: (1). Dr. Yeti Lis Purnamadewi (YLP) as coordinator (2) Dr. Alla Asmara (AA) as a member of lecturer team (3) Dr Muhammad Findi A (MFA) as a member of lecturer team Assignment Design Assessment Format : conduct tutorial including field study to cooperative, case per group (during mid-test lectures), and make the report to be presented during final test lectures each week, each group consisting of 5-6 students; : Mid-test (UTS) : 35 % Final Test (UAS) : 35 % Assignment (Paper) and Presentation : 30 %





