LAB: F = ma - mrwilterdink
advertisement
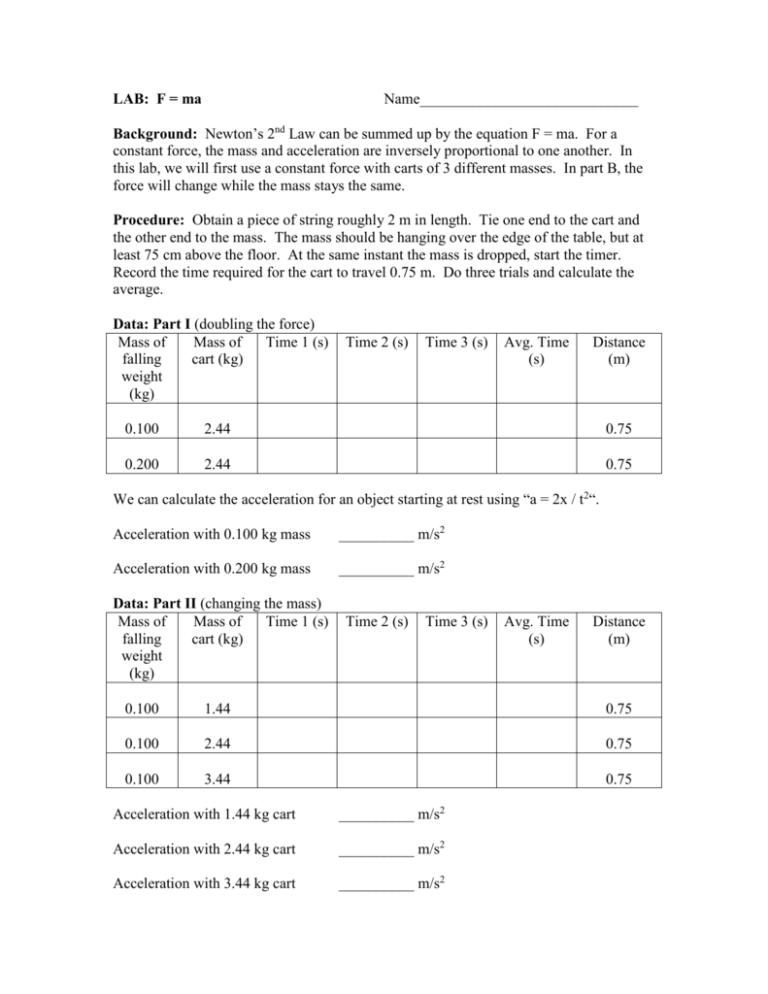
LAB: F = ma Name_____________________________ Background: Newton’s 2nd Law can be summed up by the equation F = ma. For a constant force, the mass and acceleration are inversely proportional to one another. In this lab, we will first use a constant force with carts of 3 different masses. In part B, the force will change while the mass stays the same. Procedure: Obtain a piece of string roughly 2 m in length. Tie one end to the cart and the other end to the mass. The mass should be hanging over the edge of the table, but at least 75 cm above the floor. At the same instant the mass is dropped, start the timer. Record the time required for the cart to travel 0.75 m. Do three trials and calculate the average. Data: Part I (doubling the force) Mass of Mass of Time 1 (s) falling cart (kg) weight (kg) Time 2 (s) Time 3 (s) Avg. Time (s) Distance (m) 0.100 2.44 0.75 0.200 2.44 0.75 We can calculate the acceleration for an object starting at rest using “a = 2x / t2“. Acceleration with 0.100 kg mass __________ m/s2 Acceleration with 0.200 kg mass __________ m/s2 Data: Part II (changing the mass) Mass of Mass of Time 1 (s) falling cart (kg) weight (kg) Time 2 (s) Time 3 (s) Avg. Time (s) Distance (m) 0.100 1.44 0.75 0.100 2.44 0.75 0.100 3.44 0.75 Acceleration with 1.44 kg cart __________ m/s2 Acceleration with 2.44 kg cart __________ m/s2 Acceleration with 3.44 kg cart __________ m/s2 Lab: F=ma follow up questions 1. Determine the amount of force being applied to the cart in each trial using Newton’s 2nd Law (F = ma). 2. The motion of the cart could best be described as having a (constant, changing) velocity and a (constant, changing) acceleration? 3. How did the mass of the cart and its contents affect the acceleration of the cart? Explain. 4. How did the amount of force applied to the cart (by the falling weight) affect the acceleration when the mass of the cart was unchanged? Explain. 5. Could we use the mass of the falling weight times 9.80 to determine the force applied to the cart (Hint: Draw a free body diagram for the falling weight.)? Try it for one of your trials and compare it to the mass x acceleration calculated above in question #1.