c5th GradeResource Correlation
advertisement

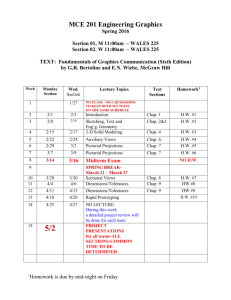
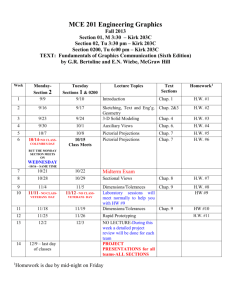
5th Grade Science Grade Level Expectations Unit: Nature of Science Understand: 1. Science attempts to explain how and why things happen in the natural world by collecting evidence and developing theories that explain natural phenomena. 2. The Scientific Method is a systematic problems solving approach to collect data and evidence 3. Scientists use the scientific method and experiments to collect the data / evidence that might help them answer a question or solve a problem. Know: 1. The steps of the scientific method: State the problem or question Form a testable hypothesis Design an experiment Collect and analyze data Draw conclusions Communicate results 2. The skill scientist use when conducting experiments: Observe Predict Classify Model Compare and contrast 3. Key scientific definitions: Law Theory Hypothesis System 4. How to design an experiment 5. What tools scientist use to collect data 6. Lab safety procedures Be Able To: 1. Write and analyze questions that can be answered by conducting scientific experiments 2. Design and conduct an experiment using the scientific process and scientific skills 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Select and use appropriate tools and techniques to gather and display data Measure in both U.S. Customary and International Systems of measurement Explain the difference between observation and inference Demonstrate proper lab safety procedures Compare and contrast a law, theory and hypothesis Identify systems Read and follow technical instructions Unit: Earth’s Systems Understand: 1. The earth is a dynamic system undergoing constant change. 2. We develop theories to explain how the earth system works based on evidence. 3. Rocks and minerals are nonrenewable resources that move through a cycle. 4. Nonliving things can be classified based on their defining characteristics Know: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. The layers of the earth (PH Inside Earth) The Theory of Plate Tectonics (PH Inside Earth) How the ocean floors are effected by plate tectonics (PH Inside Earth) The causes of earthquakes (PH Inside Earth) How volcanoes and islands are formed (PH Inside Earth) The stages of the Rock Cycle (PH Inside Earth) The classification of rocks (STC Rocks and Minerals Kit) The properties of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks (STC Rocks and Minerals Kit) Be Able To: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Classify and sort rocks Compare/contrast and define types of rocks Record characteristics to determine types of rocks Diagram rock cycle Interpret information from tables, graphs, maps, and charts Observe, illustrate, discuss, describe, and interpret changes in earth’s systems 7. Create models and maps to study changes in earth’s systems 8. Read and follow technical directions 9. Identify the differences between renewable and non-renewable resources Vocabulary: Renewable- A resource that is easily replaced or renewed Nonrenewable- A resource that is difficult to replace Technology- Tools, things built with tools or methods used to accomplish a practical purpose Hypothesis- A prediction that can be tested Inference- The use of facts, data and observation to draw a conclusion about a specific event Theory- A well tested explanation of something that occurs based on extensive empirical evidence Law- A rule describing a consistent pattern in nature, it happens every time all the time Unit: Biology of Living Systems Understand: 1. Cells are the basic units of all living organisms. Some organisms are made of one cell while others are made up of systems of cells. 2. Cell characteristics are one of the ways we use to classify things as plants or animals. 3. Plants manufacture their own food through the process of photosynthesis which also cycles carbon and oxygen into and out of the atmosphere. 4. All living things inherit traits from their parents in a molecule called DNA. Some of those traits are very common while others are rare. 5. Species evolve traits to help them survive Know: 1. The cell is the basic living unit of all organisms. (HMS Unit A Chap. 1) 2. The parts and function of an animal cell. (HMS Unit A Chap. 1) 3. The parts and function of a plant cell. (HMS Unit A Chap. 1) 4. The structural differences between plants and animal cells (HMS Unit A Chap. 1) 5. That plant convert energy from the sun through photosynthesis. (HMS Unit A Chap. 2) 6. Photosynthesis recycles oxygen and carbon (HMS Unit A Chap. 2) 7. Cells organized into systems (HMS Unit A Chap. 2) 8. The plant systems required to accomplish photosynthesis (HMS Unit A Chap. 2) 9. The definition of an inherited trait. (HMS Unit A Chap. 3) 10. Common traits (HMS Unit A Chap. 3) 11. How traits are passed (HMS Unit A Chap. 3) 12. How traits can enhance an organisms survival (HMS Unit A Chap. 3) Be Able To: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Use microscopes to observe cells Compare and contrast the structural differences between plant and animal cells Model plant and animal cells. Explain how plants convert energy from the sun through photosynthesis Diagram the process of photosynthesis. Explain the concept that traits are passed from parents to offspring List several inherited traits. Describe how traits can help an organism survive Vocabulary: Biology- Study of living things (Ch.1) Photosynthesis- The process by which plants use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars and oxygen (Ch.2) Traits- Characteristics, inherited from parents, an organism develops after it is born (CH. 3) Unit: The Structure of Matter Understand: 1. The Atom is the basic unit of matter and can be classified on the periodic table according to its properties. 2. Two or more atoms can chemically combine to make compounds. 3. A chemical change results in a change in the characteristics of the matter. Physical change causes only a change in the appearance of the matter. 4. Matter changes state when the energy is added or removed. Know: 1. Atoms are the basic unit of matter (HMS Unit E Chap 12) 2. What elements are (HMS Unit E Chap 12) 3. What system we use to classify elements (periodic table) (HMS Unit E Chap 12) 4. What a molecule and compound are (HMS Unit E Chap 12) 5. The difference between a mixture and solution (HMS Unit E Chap 13) 6. The physical and chemical properties of matter (HMS Unit E Chap 13) 7. The difference between a physical and chemical change (HMS Unit E Chap 13) 8. That matter is conserved during any change (HMS Unit E Chap 13) 9. The states of matter (HMS Unit E Chap 14) 10. The relative position of the atoms in any state (HMS Unit E Chap 14) 11. That energy is required to change the state of matter (HMS Unit E Chap 14) Be Able To: 1. Create a model of an atom identifying components and charge 2. Explain how we classify atoms 3. Compare and contrast mixtures and solutions 4. Differentiate between physical and chemical changes 5. Diagram the relative position of atoms / molecules in the 3 states of matter 6. Observe and record changes in matter 7. Create and interpret tables and charts 8. Describe the difference among elements, compounds, and mixtures 9. Create a model or diagram of an element, a compound, and a mixture 10. Describe the form of a matter in its solid, liquid, and gaseous state Vocabulary: Atom- The smallest of an element that still has the properties of that element (ch.12) Electron- A particle that orbits around an atom’s nucleus that has a negative charge (ch.12) Element- A substance that can not be broken down into other substances (ch.12) Neutron- A particle in the nucleus of an atom that has no charge (ch.12) Nucleus- Storehouse of the cell’s most important chemical information or the central core of an atom (ch.12) Proton- A particle in the nucleus of an atom that has a positive charge (ch.12)