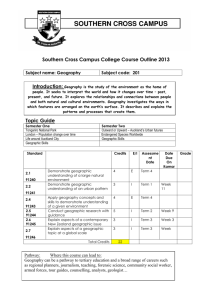
“Unwrapped” Standards Steps 1
advertisement
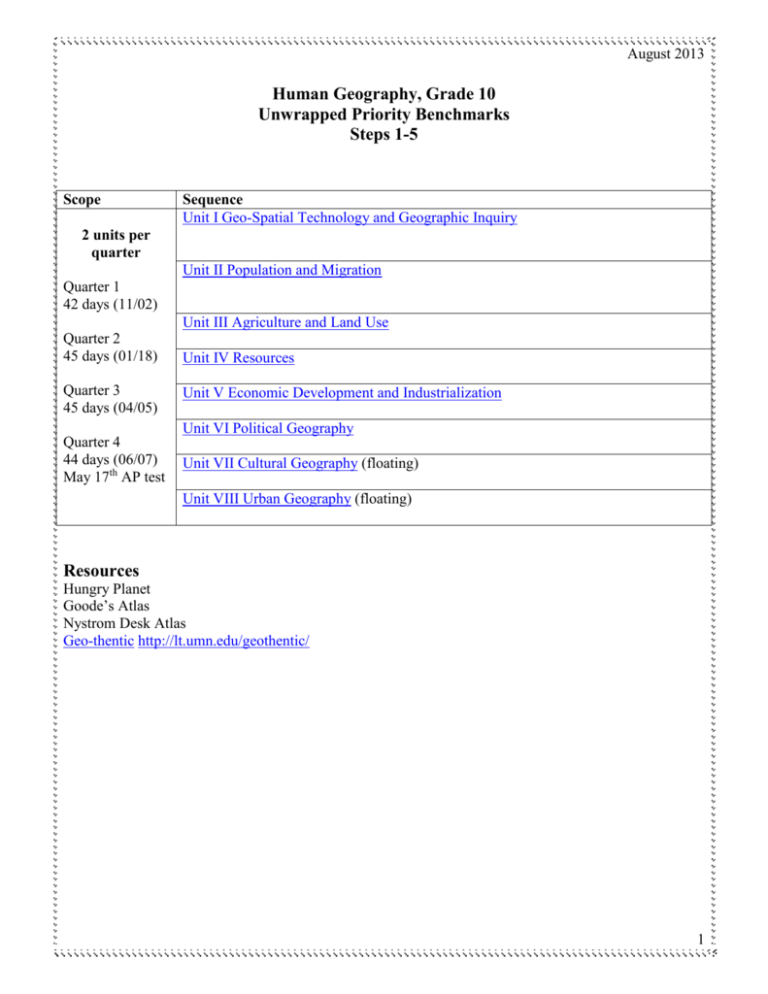
August 2013 Human Geography, Grade 10 Unwrapped Priority Benchmarks Steps 1-5 Scope Sequence Unit I Geo-Spatial Technology and Geographic Inquiry 2 units per quarter Unit II Population and Migration Quarter 1 42 days (11/02) Unit III Agriculture and Land Use Quarter 2 45 days (01/18) Quarter 3 45 days (04/05) Unit IV Resources Unit V Economic Development and Industrialization Unit VI Political Geography Quarter 4 44 days (06/07) May 17th AP test Unit VII Cultural Geography (floating) Unit VIII Urban Geography (floating) Resources Hungry Planet Goode’s Atlas Nystrom Desk Atlas Geo-thentic http://lt.umn.edu/geothentic/ 1 August 2013 Unit I: Geo-Spatial Technology and Geographic Inquiry Priority benchmarks: Concepts 9.3.1.1.1 Apply geographic information from a variety of print and electronic sources to interpret the past and present and plan for the future; provide rationale for using specific technologies for each application Skills (Bloom) Interpret Rationale Provide 9.3.1.1.2 Use geospatial technologies to develop plans for analyzing and solving local and regional problems that have spatial dimensions Geography Map skills Geographic information Geospatial GIS 9.3.2.3.1 Make inferences and draw conclusions about the physical and human characteristics of places based on a comparison of maps and other geographic representations and geospatial technologies Physical Human Region Infer Conclude Big Ideas Statements of enduring ideas Analyze Solve Overarching/Essential Questions Establishes learning goals Resources: Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Maps are an essential source of geographic information. How do we use different maps for different information? http://www.whydontyoutrythis.com/2013/04/thetrue-size-of-africa-erroneousmap.html#sthash.gGrOj3mK.dpbs Geospatial technologies are an essential tool for geographers. How do we analyze maps for data, purpose and author intent? What are geospatial technologies? How can we make inferences about places and regions using maps and geospatial technology? Arcgis.com Esri BAO (business analyst online) APP Return to top of document Learning Targets * I can analyze a variety of maps for geographic information. * I can use geo-spatial technologies to learn about places and regions. 2 August 2013 Unit II: Population and Human Migration: Chapters 2 and 3 Priority benchmarks: Concepts 9.3.3.5.1 Describe the patterns of human population distribution in the United States and major regions of the world. 9.3.3.5.3 Compare the population characteristics of places at a range of scales using population pyramids, birth and death rates, and other key demographic variables. 9.3.3.5.2 Use the demographic transition model to analyze and explain the impact of changing birth and death rates in major world regions. 9.3.3.5.4 Explain migration patterns in the modern era at a range of scales, local to global. Skills (Bloom) Where? Why? Population pyramids Demographics IPAT Equation (human Impact= Population (x) Affluence (x) Technology) Birth/death rate Demographic Transition Model Birth/death rate Migration Push Pull Human Trafficking Describe Compare Analyze Explain Explain Unit I Priority Benchmarks 9.3.1.1.1, 9.3.1.1.2, 9.3.1.2.1, 9.3.2.3.1 Big Ideas Statements of enduring ideas Humans choose to live based on resources, climate and culture. Population pyramids and demographics are tools for comparing populations. Population impacts the environment. Overarching/Essential Questions Establishes learning goals Where do humans live and why? Demographics change over time. How does the Demographic Transition Model explain or not explain the impact of changing birth rates and death rates? How do we compare populations using population pyramids and demographics? How does population impact the environment? Resources Census.gov population pyramid data Population Reference Bureau Case Study of China, India, Brazil etc. Urban Agriculture. 3 August 2013 Push and pull factors affect why and where people move. Return to top of document What are motivating factors for migration? Learning Targets * I can describe where people live and why. * I use demographics to compare populations from local to national to global. * I can explain/analyze impact of birth rates and death rates using the DTM. * I can use push and pull factors to explain varieties of migration. Unit III: Agriculture and Land Use: Chapter 10 Priority benchmarks: Concepts 9.3.2.4.3 Explain how technological and managerial changes associated with the third agricultural revolution, pioneered by Norman Bourlaug, have impacted regional patterns of crop and livestock production. 9.3.2.4.4 Describe patterns of production and consumption of agricultural commodities that are traded among nations 1st and 2nd agricultural revolutions 3rd agricultural revolution crops livestock subsistence commercial Von Thunen Production Consumption commodities Skills (Bloom) Explain Describe Unit I Priority Benchmarks 9.3.1.1.1, 9.3.1.1.2, 9.3.1.2.1, 9.3.2.3.1 Big Ideas Statements of enduring ideas Agriculture has evolved through three Overarching/Essential Questions Establishes learning goals Resources How has agriculture changed over time? 4 August 2013 revolutions. Modern agriculture is based on production, trade and consumption. What commodities are produced, traded and consumed? USDA.gov Return to top of document Learning Targets * I can describe the 1st and 2nd agricultural revolutions. * I can explain how the 3rd agricultural revolution has impacted global agriculture today. * I can describe the production, trade and consumption of at least one agricultural product. * I can describe WHY at least one agricultural product is grown where it is. *I can describe at least two different types of farming. Unit IV: Resources: Chapter 14 Priority benchmarks: Concepts 9.3.4.9.1 Analyze the interconnectedness of the environment and Human environment-interaction human activities (including the use of technology), and the impact Renewable resources of one upon the other. Non-renewable resources Carbon footprint 9.3.4.10.1 Describe patterns of production and consumption of Fossil fuels fossil fuels that are traded among nations Trade Carbon footprint OPEC Big Ideas Statements of enduring ideas Skills (Bloom) Analyze Describe Overarching/Essential Questions Establishes learning goals Human affect and in turn, are affected by the environment. How does human use of resources impact the environment? Fossil fuels are a major world commodity. What global role does production, trade and consumption of fossil fuels play? Resources: OPEC US Energy Information Administration EIA.gov 5 August 2013 Top of the Document Learning Targets * I can explain impact of human-environmental interaction on humans and the environment. * I can describe the global production, trade and consumption of at least one fossil fuel. Unit V: Economic Development and Industrialization: Chapter 9 and 11 Priority benchmarks: Concepts Skills (Bloom) 9.3.2.4.1 Apply geographic models to explain the location of economic activities and land use patterns in the United States and the world. Von Thuenen (see Ag) Weber Core-Periphery Globalization Apply Explain 9.3.2.4.2 Identify the primary factors influencing the regional pattern of economic activities in the United States and the world. Development indicators (literacy, GDP, HDI) Primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary Levels of development Identify Unit I Priority Benchmarks 9.3.1.1.1, 9.3.1.1.2, 9.3.1.2.1, 9.3.2.3.1 Big Ideas Statements of enduring ideas Geographic models can explain how and where humans use the land and resources. Economic development varies among countries and regions. Overarching/Essential Questions Establishes learning goals Resources How can models explain economic activities and land use? Why does economic development vary among countries? 6 August 2013 Return to top of document Learning Targets * I can explain at least one geographic economic model and apply it to at least one place. * I can use demographics to explain the causes of differing levels of development. * I can describe the effects of globalization on different scales. * I can describe different types of jobs in relation to levels of development. Unit VI: Political Geography: Chapter 8 and 7 Priority benchmarks: 9.3.3.8.1 Define the concepts of nationalism and sovereign political states and explain how sovereignty is impacted by international agreements. 9.3.3.8.2 Describe the effects of nationalism and supranationalism on the establishment of political boundaries and economic activities. 9.3.3.8.3 Analyze the impact of colonialism on the emergence of independent states and the tensions that arise when the boundaries of political units do not correspond to the nationalities or ethnicities of the people living within them. Unit I Priority Benchmarks 9.3.1.1.1, 9.3.1.1.2, 9.3.1.2.1, 9.3.2.3.1 Big Ideas Statements of enduring ideas Nationalism and sovereignty affect nations and states. Overarching/Essential Questions Establishes learning goals What are nationalism and sovereignty? Concepts nationalism sovereignty treaties State Nation Stateless nation Nation-State Political Boundaries/Borders Supranationalism European Union Colonialism Ethnicities Skills (Bloom) Define Explain Describe Analyze Resources 7 August 2013 The European Union is a supranational organizations European colonialism impacted the nationalism and political boundaries of future political units. Return to top of document What are states, nations, stateless nations and nation-states? How does nationalism affect boundaries? What is supranationalism? How did colonialism lead to civil conflict? Learning Targets * I can connect nationalism and sovereignty to nations and states. * I can use nationalism and supra-nationalism to explain current geopolitical issues. * I can explain how colonialism affects countries today. Unit VII: Cultural Geography: Chapter 4,5 and 6 Priority benchmarks: 9.3.3.7.1 Explain the spread of culture using the concept of diffusion and diffusion models. 9.3.3.7.2 Describe the spatial distribution of significant cultural and/or ethnic groups in the United States and the world and how these patterns are changing. 9.3.3.7.3 Explain how social, political and economic processes influence the characteristics of places and regions. Concepts Trans-Culture Diffusion (Expansion, Relocation, Hierarchial, Contagious) Language v. Dialect Popular and Folk Religion, Food World Religions Ethnic Ex. Latino Skills (Bloom) Explain Describe Explain Globalization 9.3.1.1.1, 9.3.1.1.2, 9.3.1.2.1, 9.3.2.3.1 8 August 2013 Big Ideas Statements of enduring ideas Culture is spread through diffusion Overarching/Essential Questions Establishes learning goals How do cultures diffuse? There are cultural patterns of ethnic spatial distribution. Globalization has affected the culture of places and regions. How are ethnic groups distributed throughout the world and the U.S.? How has globalization impacted the cultural landscape in places and regions? Resources Projects.nytimes.com Return to top of document Learning Targets * I can explain cultural diffusion * I can describe ethnic group distribution in the United States and around the world. * I can explain the influence of globalization on cultural diffusion. * How does language or religion unite or divide people? Unit VIII: Urban Geography: Chapter 12 and 13 Priority benchmarks: 9.3.3.5.5 Describe the factors influencing the growth and spatial distribution of large cities in the contemporary world. 9.3.3.5.6 Analyze how transportation and communication systems have affected the development of systems of cities. 9.3.3.5.7 Describe how changes in transportation and communication technologies affect the patterns and processes of urbanization of the United States. 9.3.3.5.8 Describe the factors (transportation, government policies, economic development, and changing cultural values) that shape and change urban and suburban areas in the United States. 9.3.3.6.1 Use generally accepted models to explain the internal spatial structure of cities in regions of the United States and other regions in the world 9.3.1.2.1 Use geospatial technologies to make and justify decisions about the best location for facilities Concepts Central Place Theory – Christaller Primate cities Concentric Ring Theory Von Thuen Peripheral model Suburbs Urban sprawl Infrastructure Urban Renewal Gentrification Concentric zone Sector model Multiple nuclei Urban Planning GIS Google Earth Geo-thentic Skills (Bloom) Describe Analyze Describe Describe Explain Justify 9 August 2013 9.3.1.1.1, 9.3.1.1.2, 9.3.1.2.1, 9.3.2.3.1 Big Ideas Statements of enduring ideas Cities have spatial distribution. Urban areas grow due to transportation and communication. Geospatial technologies assist in city planning. Overarching/Essential Questions Establishes learning goals What determines the spatial distribution of cities around the world? What causes urban areas to grow? Resources What is urban planning? Return to top of document Learning Targets: * I can explain the function and spatial distribution of cities. * I can explain how transportation and communication influence the growth of urban areas. * I can describe the process of urban planning. 10 August 2013 American Studies Opening Week Items to Review in Content Session As a Teacher Lead, you were part of the process of prioritizing benchmarks and drafting a scope and sequence. Lead your colleagues through the scope and sequence to make sure any inconsistencies are caught. There is a district calendar in your folder. * Should Cultural Geography and Urban Geography be made ‘floating’ units that allow PLCs to place them where they think they fit best? * Should Population and Migration be two separate units? * Should Agriculture and Land Use be two different units? * Using the 2012-2013 calendar, what is the Scope for each unit? * Review the units with their priority benchmarks for… * Any changes to unit titles * PD needed for teaching a unit/benchmark 11