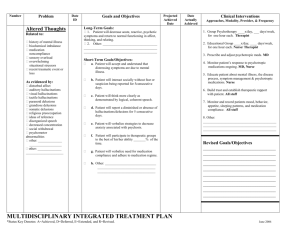
key words schizophrenia
advertisement
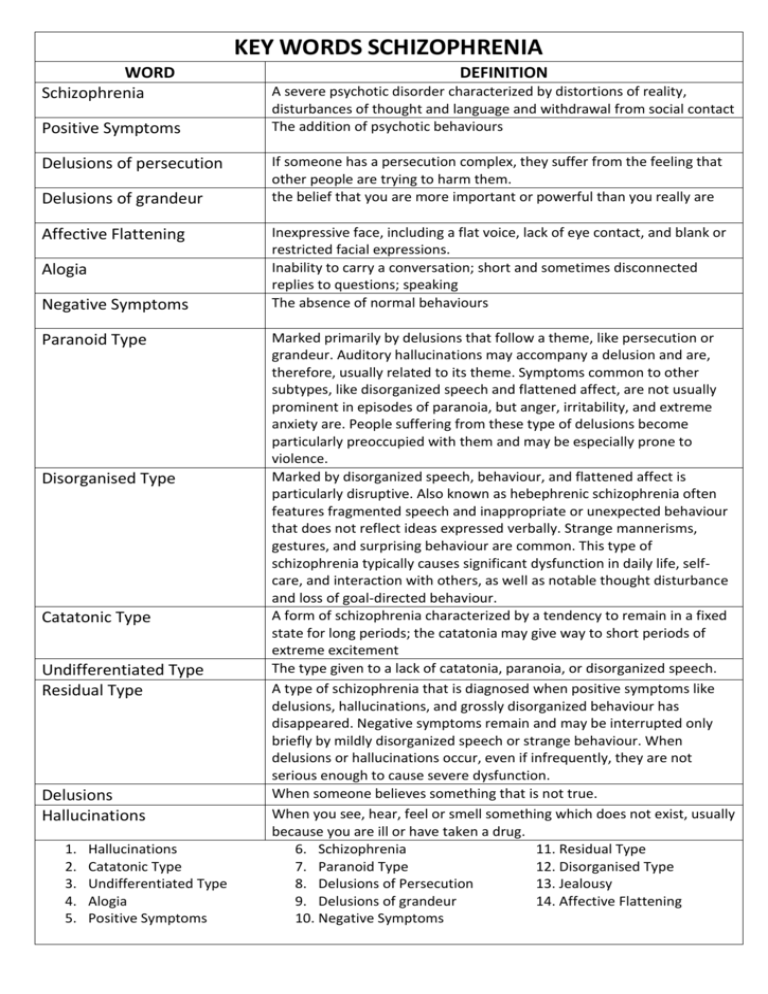
KEY WORDS SCHIZOPHRENIA WORD Schizophrenia Positive Symptoms Delusions of persecution Delusions of grandeur Affective Flattening Alogia Negative Symptoms Paranoid Type Disorganised Type Catatonic Type Undifferentiated Type Residual Type Delusions Hallucinations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Hallucinations Catatonic Type Undifferentiated Type Alogia Positive Symptoms DEFINITION A severe psychotic disorder characterized by distortions of reality, disturbances of thought and language and withdrawal from social contact The addition of psychotic behaviours If someone has a persecution complex, they suffer from the feeling that other people are trying to harm them. the belief that you are more important or powerful than you really are Inexpressive face, including a flat voice, lack of eye contact, and blank or restricted facial expressions. Inability to carry a conversation; short and sometimes disconnected replies to questions; speaking The absence of normal behaviours Marked primarily by delusions that follow a theme, like persecution or grandeur. Auditory hallucinations may accompany a delusion and are, therefore, usually related to its theme. Symptoms common to other subtypes, like disorganized speech and flattened affect, are not usually prominent in episodes of paranoia, but anger, irritability, and extreme anxiety are. People suffering from these type of delusions become particularly preoccupied with them and may be especially prone to violence. Marked by disorganized speech, behaviour, and flattened affect is particularly disruptive. Also known as hebephrenic schizophrenia often features fragmented speech and inappropriate or unexpected behaviour that does not reflect ideas expressed verbally. Strange mannerisms, gestures, and surprising behaviour are common. This type of schizophrenia typically causes significant dysfunction in daily life, selfcare, and interaction with others, as well as notable thought disturbance and loss of goal-directed behaviour. A form of schizophrenia characterized by a tendency to remain in a fixed state for long periods; the catatonia may give way to short periods of extreme excitement The type given to a lack of catatonia, paranoia, or disorganized speech. A type of schizophrenia that is diagnosed when positive symptoms like delusions, hallucinations, and grossly disorganized behaviour has disappeared. Negative symptoms remain and may be interrupted only briefly by mildly disorganized speech or strange behaviour. When delusions or hallucinations occur, even if infrequently, they are not serious enough to cause severe dysfunction. When someone believes something that is not true. When you see, hear, feel or smell something which does not exist, usually because you are ill or have taken a drug. 6. Schizophrenia 11. Residual Type 7. Paranoid Type 12. Disorganised Type 8. Delusions of Persecution 13. Jealousy 9. Delusions of grandeur 14. Affective Flattening 10. Negative Symptoms