Syllabus
advertisement

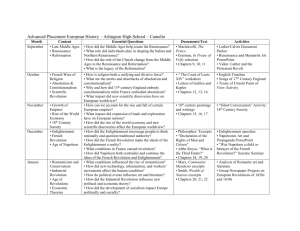
AP European History Syllabus Course Description: This course is designed to prepare students for the AP exam in European History while increasing their understanding and appreciation of Western civilization from 1450 to 2001. Through inquiry and analysis of primary and secondary materials, students will expand their knowledge of the history of the Europe. In addition to providing a narrative of historical events, the goals of AP European History are to enhance college level reading and writing skills. These skills will be developed by document analysis, historical interpretation, essay writing, and the articulation of principal themes in modern European history. Text: Spielvogel, Jackson J. Western Civilization. Thomson Wadsworth, 2009. Supplemental Materials: Gregory, Candace. Documents of Western Civilization. Vol. I & II. Thomson Wadsworth, 2006. Kosso, Cynthia. Map Workbook for Western Civilization. Vol. I & II. Wadsworth Thomson Learning, 2000. Link, Jere. AP European History Exam. New Jersey: Research & Education Assoc., 2007. McKay, John P. A History of Western Society Since 1300. New York: Houghton Mifflin Co., 2006. William, Williams. DBQ: AP Style Document Based Questions. California: Social Studies School Services, 2005. Unit 1: Renaissance, Reformation, and the Age of Discovery Readings: Spielvogel chapters 11-14 Supplemental materials Chapter 11: Review, pp.303-335 Manor, Feudalism, & Church 100 Years War & The Black Death Chapter 12: 337-371 Making Renaissance Society Italian States in the Renaissance Intellectual Renaissance in Italy Artistic Renaissance European State in the Renaissance Church in the Renaissance 1 Chapter 13: 373-408 Prelude to Reformation Martin Luther and the Reformation Spread of the Protestant Reformation Social Impact of the Protestant Reformation Catholic Reformation Politics and the Wars of Religion in the Sixteenth Century Chapter 14: 410-441 On the Brink of the New World New Horizons the Portuguese and Spanish Empires New Rivals on the World Stage The Impact of European Expansion Toward a World Economy Unit 2: State Building, Science, and the Age of Reason Readings: Spielvogel chapters 15-17 Supplemental materials Chapter 15: 443-481 Social Crises, War, and Rebellions The Practice of Absolutism: Western Europe Absolutism in Central, Eastern, and Northern Europe Limited Monarch and Republics The Flourishing of European Culture Chapter 16: 483-508 Background to the Scientific Revolution Toward a New Heaven: A Revolution in Astronomy Advances in Medicine and Chemistry Women in the Origins of Modern Science Toward a New Earth: Descartes, Rationalism, and a New View of Humankind The Scientific Method and the Spread of Scientific Knowledge Chapter 17: 509-537 The Enlightenment Culture and Society in the Enlightenment Religion and the Churches Chapter 18 : 538-569 The European States Wars and Diplomacy Economic Expansion and Social Change The Social Order of the Eighteenth Century 2 Unit 3: Readings: The Age of Revolution Spielvogel chapters 19-21 Supplemental materials Chapter 19: 571-602 Background to the French Revolution The French Revolution The Age of Napoleon Chapter 20: 604-631 The Industrial Revolution in Great Britain The Spread of Industrialization The Social Impact of the Industrial Revolution Chapter 21: 632-663 The Conservative Order (1815-1830) The Ideologies of Change Revolution and Reform (1830-1850) The Emergence of an Ordered Society Culture: The Mood of Romanticism Unit 4: Readings: The Emerging Modern World Spielvogel chapters 22-24 Supplemental materials Chapter 22: 665-697 The France of Napoleon III National Unification: Italy and Germany The National State in the Mid-century Industrialization and the Marxist Response Science and Culture in an Age of Realism Chapter 23: 698-729 The Growth of Industrial Prosperity The Emergence of a Mass Society The National State Chapter 24: 731-766 Intellectual and Cultural Developments Politics: New Directions and New Uncertainties The New Imperialism International Rivalry and the Coming of War 3 Unit 5: Readings: The World at War Spielvogel chapters 25-27 Supplemental materials Chapter 25: 768-802 The Road to World War I The War War and Revolution The Peace Settlement Chapter 26: 803-827 An Uncertain Peace The Democratic States The Authoritarian and Totalitarian States The Expansion of Mass Culture and Mass Leisure Cultural and Intellectual Trends in the Interwar Years Chapter 27: 839-873 Prelude to War (1933-1939) The Course of World War II The New Order The Home Front Aftermath of the War Unit 6: Readings: Cold War to the Present Spielvogel chapters 25-27 Supplemental materials Chapter 28: 875-908 Development of the Cold War Europe and the World: Decolonization Recovery and Renewal in Europe Postwar Society and Culture in the Western World Chapter 29: 909-933 A Culture of Protest A Divided Western World The Cold War: The Move to Détente Society and Culture in the Western World Chapter 30: 935-965 Toward a New Western Order New World Order or Age of Terrorism? New Directions and New Problems in Western Society Western Culture Today The Digital Age Toward a Global Civilization 4