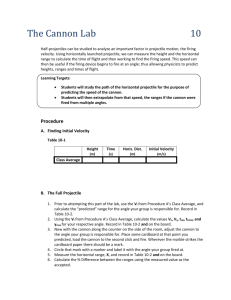
PhET Projectile Motion

Physics PhET Projectile Motion Lab
1. Go to the “phET” physics website by googling “phET
2. Go to simulations ---physics----motion----projectile motion
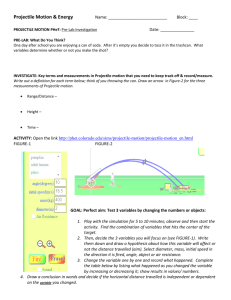
3. Set up the simulation (as shown opposite) with the height of the cannon 13m above ground level (person’s feet) and the angled at 0 degrees (horizontal). Select pumpkin as the projectile. Use the tape measure to check the height. If you fire the cannon it should show -13.0 m in the box if you set it right.
4. Again use the tape measure to set the center of the target 17 away from the center line of the cannon
(as shown above).
5. Fire the projectile at various initial speeds. Does this change the time that the projectile is in the air?
Explain why or why not!
_______because ______________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
6. What determines the time that the projectile is in the air? ___________________________________
7. What determines the range of the projectile? _____________________________________________
8. Using physics theory calculate the time the projectile is in the air. Show your work! Then check with the simulation.
Work:
9. Now calculate the initial horizontal speed that the projectile (pumpkin) has to be fired at in order to hit the center of the target (17m away). Then check with the simulation. You should see “score” if successful.
Work:
10. If you fired the projectile horizontally at twice the initial speed, what would happen to i) the time in the air and ii) its horizontal range? How many times does each increase? i) _________________________________ ii) _____________________________________
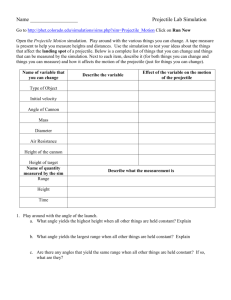
11. Reset the screen and put the target at the same height as the projectile is fired from (not ground height) and positioned 17m away (see diagram opposite). The initial velocity should be set to 18 m/s.
12. Play with the angle setting until you find two angles of launch that allow the projectile to hit the center of the target. angle 1 = _____________ angle 2 = ______________
13. Which launch angle gives the most time in the air? __________________
Which launch angle gives the biggest horizontal speed? _______________
14. Why do you think there are two launch angles that give the same range? Hint: R = v
H
t
_____________________________________________________________________________________
15. Without worrying about hitting the target which angle (0 – 90 deg) gives the most height?_______
This is because ___________________________________________________________________
Without worrying about hitting the target which angle (0 – 90 deg) gives the most range? _______
This is because ___________________________________________________________________
16. Calculate the hang time (time to return to the firing line) using angle 1 and an initial velocity of 18 m/s. Hint: Draw a scale vector diagram to determine the projectile’s initial vertical velocity.
Work:
17. Calculate the range (for the projectile returning to the firing line), using the hang time and an initial velocity of 18 m/s. Hint: Draw a scale vector diagram to determine the projectile’s initial horizontal velocity. Check your answer.
Work: