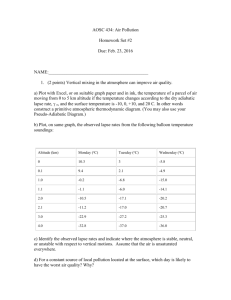
3U-Unit 3-A-Shapes
advertisement
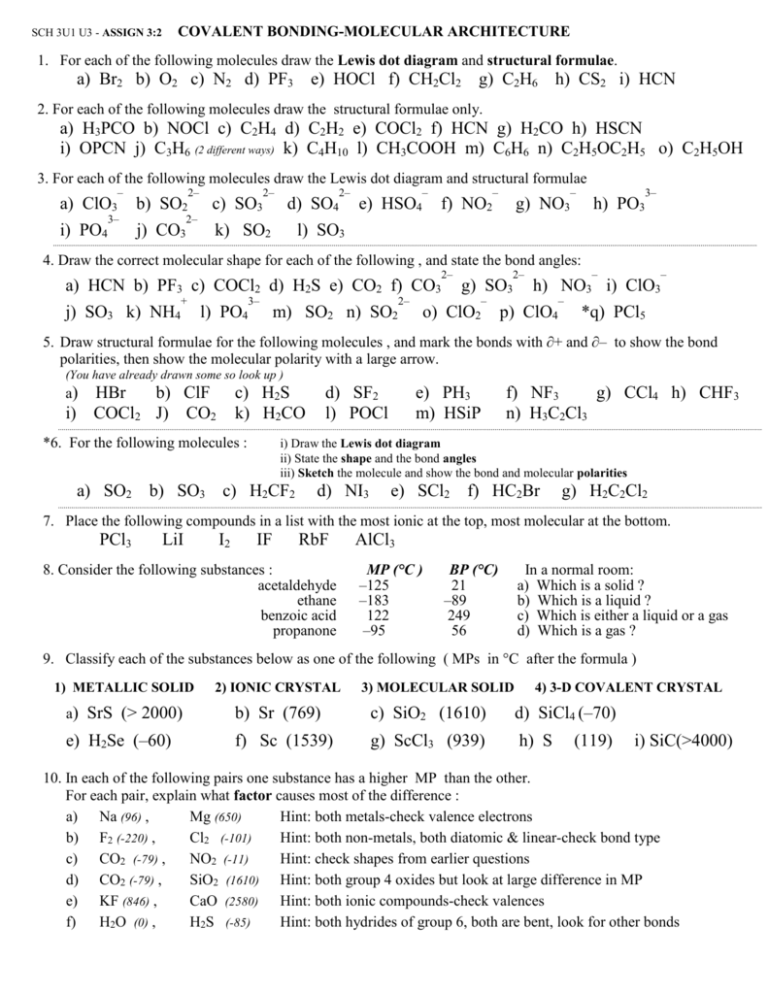
COVALENT BONDING-MOLECULAR ARCHITECTURE SCH 3U1 U3 - ASSIGN 3:2 1. For each of the following molecules draw the Lewis dot diagram and structural formulae. a) Br2 b) O2 c) N2 d) PF3 e) HOCl f) CH2Cl2 g) C2H6 h) CS2 i) HCN 2. For each of the following molecules draw the structural formulae only. a) H3PCO b) NOCl c) C2H4 d) C2H2 e) COCl2 f) HCN g) H2CO h) HSCN i) OPCN j) C3H6 (2 different ways) k) C4H10 l) CH3COOH m) C6H6 n) C2H5OC2H5 o) C2H5OH 3. For each of the following molecules draw the Lewis dot diagram and structural formulae – a) ClO3 i) PO4 3– b) SO2 j) CO3 2– 2– c) SO3 2– d) SO4 k) SO2 2– e) HSO4 – f) NO2 – g) NO3 – h) PO3 3– l) SO3 4. Draw the correct molecular shape for each of the following , and state the bond angles: a) HCN b) PF3 c) COCl2 d) H2S e) CO2 f) CO3 j) SO3 k) NH4 + l) PO4 3– m) SO2 n) SO2 2– 2– 2– g) SO3 – o) ClO2 – – h) NO3 i) ClO3 p) ClO4 – *q) PCl5 5. Draw structural formulae for the following molecules , and mark the bonds with ∂+ and ∂– to show the bond polarities, then show the molecular polarity with a large arrow. (You have already drawn some so look up ) a) HBr b) ClF i) COCl2 J) CO2 c) H2S k) H2CO *6. For the following molecules : d) SF2 l) POCl e) PH3 m) HSiP f) NF3 g) CCl4 h) CHF3 n) H3C2Cl3 i) Draw the Lewis dot diagram ii) State the shape and the bond angles iii) Sketch the molecule and show the bond and molecular polarities a) SO2 b) SO3 c) H2CF2 d) NI3 e) SCl2 f) HC2Br g) H2C2Cl2 7. Place the following compounds in a list with the most ionic at the top, most molecular at the bottom. PCl3 LiI I2 IF RbF 8. Consider the following substances : acetaldehyde ethane benzoic acid propanone AlCl3 MP (°C ) –125 –183 122 –95 BP (°C) 21 –89 249 56 In a normal room: a) Which is a solid ? b) Which is a liquid ? c) Which is either a liquid or a gas d) Which is a gas ? 9. Classify each of the substances below as one of the following ( MPs in °C after the formula ) 1) METALLIC SOLID 2) IONIC CRYSTAL 3) MOLECULAR SOLID 4) 3-D COVALENT CRYSTAL a) SrS (> 2000) b) Sr (769) c) SiO2 (1610) d) SiCl4 (–70) e) H2Se (–60) f) Sc (1539) g) ScCl3 (939) h) S (119) i) SiC(>4000) 10. In each of the following pairs one substance has a higher MP than the other. For each pair, explain what factor causes most of the difference : a) Na (96) , Mg (650) Hint: both metals-check valence electrons b) F2 (-220) , Cl2 (-101) Hint: both non-metals, both diatomic & linear-check bond type c) CO2 (-79) , NO2 (-11) Hint: check shapes from earlier questions d) CO2 (-79) , SiO2 (1610) Hint: both group 4 oxides but look at large difference in MP e) KF (846) , CaO (2580) Hint: both ionic compounds-check valences f) H2O (0) , H2S (-85) Hint: both hydrides of group 6, both are bent, look for other bonds