NAME - De Soto Area School District
advertisement

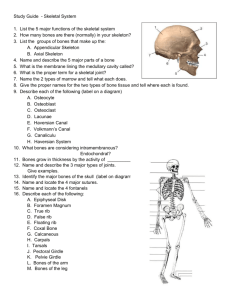
NAME KEY DATE 6th Grade Notes/Skeletal System The skeletal system is the body’s living framework. It consists of living material embedded in a matrix of material. The skeletal system is made up of bones non-living , ligaments , and tendons Cartilage - is dense, fibrous, flexible cartilage . connective tissue. Ligaments together. - are connective tissue that holds Tendons to muscles - are connective tissues that attach bones . The adult skeleton consists of approximately 206 There are 5 functions of the skeletal system. They are: Provide shape Allow movement and support Protects tissues and organs Stores certain materials Produces bones blood cells bones. , Development of bones: Many bones are formed from cartilage It is a stiff, jellylike material that is strong enough to provide support but flexible enough to bend and In newborns, many bones are almost all twist cartilage , . . The process of replacing cartilage with bone begins…. …about 7 months before birth The process continues until the age of 25 . In some places, the cartilage remains unchanged. For instance, places where bone meets knee , bone ankle . For example, at the , or elbow . Two jobs cartilage has are to cushion bones against sudden jolts, and provide a slippery surface for bones to move on without rubbing against each other. Bone Growth: Bone growth takes place…. at both ends of long bones. The growth region is called the growth plate or Epiphyseal Plate. It is in this region that is taking place. The term mitosis for the process of cartilage being replaced by bone is ossification . Structure of Bones: Bones are one of the toughest yet materials in your body, yet they make up barely mass. Bones consist of living non-living of your body’s Osteocytes living cells embedded in a network of tough made up of 14% material embedded in a matrix of material. collagen lightest are the protein fibers called . The non-living part of the bone contains compounds calcium and phosphorous that surround the osteocytes and make bone hard. Bones are covered with a living layer called the periosteum muscles. It also provides a rich which helps to connect them to blood supply to nourish the bone. The middle portion of a typical long bone is called the shaft The shaft contains the filled with central yellow cavity marrow yellow marrow is to store fat by a hard, bony material called compact . which is . The job of the . The central cavity is surrounded bone . There are small channels that run through the compact bone and contain Blood vessels that nourish the osteocytes . The shaft is separated from the ends of the bone by a line that marks the area where growth formerly took place. This is called the Epiphyseal line . In flat bones and ends of long bones, the hard material is very thin. Underneath the hard material is the spongy bone and the potential to injury . This reduces red and , during periods of physical activity. In some bones, the spongy material contains in which shock red white marrow blood , cells are produced. Classification of Bones: Bones are classified according to their bones, such as the arms and and are involved in movement as the underlying and skull organs. The short provide great irregular shape legs , support bones, such as the bones, such as the weight . The flat sternum flexibility . The LONG and , protect wrist and precise ribs bones, such ankles , movements. The and scapula , are adaptations that provide for specific needs involving protection , and/or articulation The adult skeleton consists of approximately into two main divisions: the appendicular framework of support . 206 bones. It is divided axial skeleton and the skeleton. The axial skeleton is the support bones including the and , protection skull , facial bones, central . It consists of 80 vertebral column, and rib cage . The function of the axial skeleton includes: the skull protects the brain; the vertebral column holds the body upright and protects the spinal cord . The rib cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs and the sternum. Each rib is attached to the vertebral column. There are only 7 pairs of “true” ribs – they are attached to the cartilage sternumb by . The other 5 pair of “false” ribs do not attach to the sternum. The function of the rib cage is to protect organs of the thoracic cavity. The appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones in the pectoral girdle, the . and pelvic girdle, and the arms legs The function of the appendicular skeleton includes: the pectoral girdle provides support for the movement. The arms and provides for their broad range of Muscles Attach the pectoral girdle to the axial skeleton. pelvic girdle attaches directly to the lower part of the vertebral column . Skeletal Joints: Any place where two bones come close together is called a joint . Its job is to keep bones far enough apart so they don’t rub against each other. There are six kinds of joints including pivot, ball-and socket, hinge, saddle, gliding, and Ellipsoid. Pivot joints allow for rotation of one bone around another. An example of a pivot joint is the head/neck . Ball-and-socket joints provide for motion . An example of a circular ball-and-socket joint is the in one shoulder . A hinge joint allows movement direction only. An example of a hinge joint is the elbow A gliding joint allows for precise of a gliding joint is the wrist movements . An example . Injuries to the Skeleton: Sprain . - when ligaments get torn or pulled beyond their normal stretching range. Fracture - a break in a bone. Dislocation - when a bone is forced out of its joint.