Slope Criteria for Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
advertisement

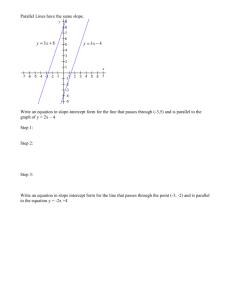
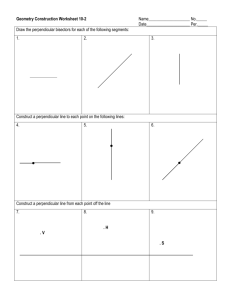
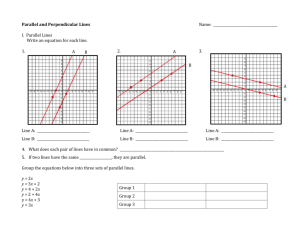
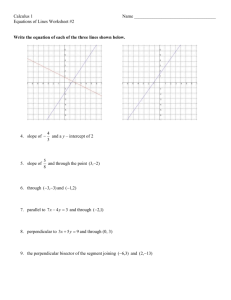
Lesson Title: Proving Slope Criteria for Parallel & Perpendicular Lines Course: CC Geometry, Unit 1 Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Start/end times: _________________________ Lesson Standards/Objective(s): What mathematical skill(s) and understanding(s) will be developed? Which Mathematical Practices do you expect students to engage in during the lesson? G.GPE.B.5 Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems (e.g., find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point). G.CO.A.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc. This lesson will engage students in the following mathematical practices: MP2: Reason abstractly and quantitatively. MP6: Attend to precision. MP8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Lesson Launch Notes: Exactly how will you use the first five minutes of the lesson? Assess students’ prior knowledge of slopes and the properties of rectangles using these questions. 1. What is true about the opposite sides in any rectangle? 2. Plot the following three points on graph paper, labeling and connecting them with segments as you go: A (3,4), B (0,0), and C (6, -4). 3. Find the coordinates of a fourth point D that would create Rectangle ABCD when segments are drawn to it from the other points plotted. 4. Find the slope of one side of the rectangle. 5. Find the length of one side of the rectangle using the distance formula. Lesson Closure Notes: Exactly what summary activity, questions, and discussion will close the lesson and connect big ideas? List the questions. Provide a foreshadowing of tomorrow. Have the students complete a summary sheet for parallel and perpendicular lines, listing everything they know about each, including the slope criteria. For example, Parallel Lines Equidistant apart (do not intersect) Equal slopes No solution in a system of equations Perpendicular Lines Intersect at right angles Product of slopes is -1 (or slopes are negative reciprocals) Lesson Tasks, Problems, and Activities (attach resource sheets): What specific activities, investigations, problems, questions, or tasks will students be working on during the lesson? Be sure to indicate strategic connections to appropriate mathematical practices. 1. Divide students into small groups of 3- 4 students to work at stations. 2. Create four stations for investigating the slope of parallel and perpendicular lines. You may have to set up more than one station of each type, depending on class size. (See the Parallel and Perp. Lines Stations document.) Look for evidence of math practices (MP) indicated while students work. Station A- Students will use the distance formula to verify lines are parallel by finding the constant distance between them. Then they will find the slopes of the lines. Look for evidence of MP6 as students calculate distances and find slopes. (Use rectangles drawn in a coordinate plane for the investigation. See Station A activity sheet.) Station B- Students will use Patty Paper to investigate slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines. Tell students, “Be sure to discuss patterns you see after finding the slopes of these lines.” (MP8) Station C- Students will investigate slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines using Geometers’ Sketchpad. Have one pair in each group work as partners on Part I and the other pair on Part II. Look for evidence of MP2 as students analyze measurements and make conjectures at this station. (Note: Set up this activity in advance. Create the sketches for Parts I and II beforehand by doing HCPSS Secondary Mathematics Office (v2.1); adapted from: Leinwand, S. (2009). Accessible mathematics: 10 instructional shifts that raise student achievement. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Lesson Title: Proving Slope Criteria for Parallel & Perpendicular Lines Course: CC Geometry, Unit 1 Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Start/end times: _________________________ and saving Steps 1-3 as a file, and have the students do the remaining steps at this station.) Station D- Students will investigate slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines formed by similar right triangles that share a common vertex. Look for evidence of MP6 as students find measures. 3. Allow students to have about 5 minutes per station. Each member of the group will do a different problem so that there is only one problem per student completed at each station. Once students have rotated through all four stations, have them work in their small groups to discuss their findings and write a conjecture about the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines. 4. Conduct a class discussion about the results of the investigations students completed at stations. 5. Verify the criteria for slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines by giving students the formal rules. Evidence of Success: What exactly do I expect students to be able to do by the end of the lesson, and how will I measure student success? That is, deliberate consideration of what performances will convince you (and any outside observer) that your students have developed a deepened and conceptual understanding. By the end of the lesson, students should be able to state that the slope criteria are (1) for parallel lines, the slopes are equal and (2) for perpendicular lines, the product of the slopes is -1 or the slopes are negative reciprocals. They should be able to use the slope criteria to solve geometric problems (e.g., find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point). Notes and Nuances: Vocabulary, connections, anticipated misconceptions (and how they will be addressed), etc. Vocabulary: Parallel, Perpendicular, Slope, Distance, Rectangle, Right Triangle, Opposite sides Note: This lesson may take more than one day. Resources: What materials or resources are essential for students to successfully complete the lesson tasks or activities? Homework: Exactly what follow-up homework tasks, problems, and/or exercises will be assigned upon the completion of the lesson? Graph paper Straightedge “Parallel and Perp. Lines Stations” Worksheets Computer or Tablets for Sketchpad Investigation Patty Paper For homework, assign problems involving application of the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines (e.g., have them find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point and use the criteria in real world problems). Lesson Reflections: How do you know that you were effective? What questions, connected to the lesson standards/objectives and evidence of success, will you use to reflect on the effectiveness of this lesson? How well did these explorations help develop students’ conceptual understanding of the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines? Are students able to state and apply the criteria accurately? Are students able to identify the criteria when presented in different applications? Can all students apply the criteria in problem-solving situations, i.e. related to writing the equation of a line or solving systems of equations? What real world applications or extensions to learning can I introduce to help students make meaningful connections for this concept? HCPSS Secondary Mathematics Office (v2.1); adapted from: Leinwand, S. (2009). Accessible mathematics: 10 instructional shifts that raise student achievement. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann.