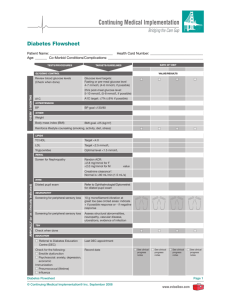
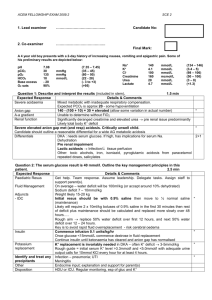
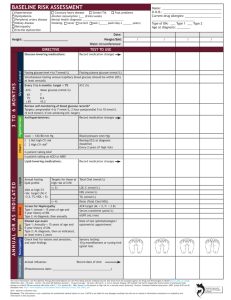
20130320-231928
advertisement

THE MINISTRY OF PUBLIC HEALTH OF UKRAINE VINNITSIA NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY named after M.I.PIROGOV EDUCATIONAL-METHODICAL RECOMMENDATION FROM PATHOPHYSIOLOGY FOR THE 3RD YEAR MEDICAL FACULTY STUDENTS Module N 1 GENERAL PATHOLOGY Practical training N 3 TYPICAL VIOLATIONS OF METABOLISM VINNITSIA - 2012 1 The manual from Pathophysiology is approved and confirmed for the introduction into the educational process at Pathophysiology department meeting. Protocol N 1 Сompilers: Head of Department from 30.08.2011 N.A. Rikalo as. S.G. Polinkevich as. O.Y. Guminska The manual is recommended for the foreign students of medical faculty (3rd course). 2 Theme: VIOLATION of WATER-ELECTROLYTE METABOLISM. Actuality of the theme. The changes of water and electrolytes maintenance in the organism and their redistribution between the separate sectors of water violate such major parameters of homeostasis, constancy of volume, osmotic and ionic composition of blood, extracellular and intracellular liquid. It can cause violation of blood circulation, retraction of heart function, edema, changes of acid basic balance and other. Violations of water-electrolyte metabolism can be the result not only external influencing but also internal disorders. A lot of diseases and the pathological states accompanied with the changes of waterelectrolyte homeostasis parameters which complicates their course. The effective correction of water-electrolyte homeostasis changes is possible only on condition of etiology and mechanisms of their development knowledge. General purpose of the lesson To learn violation of water-electrolyte metabolism, reason for origin and mechanisms of their development. Learn reasons and mechanisms of edema development. For this it is necessary to know: 1. To select principal reasons for violations of water-electrolyte metabolism. 2. To explain the mechanisms of their development. 3. To modulate different pathogenetic forms of edema, to be able to explain the mechanisms of their development. For realization of purpose of lesson it is necessary to have the base knowledgesskills. 1. Metabolism of water between blood and tissues after Starling (Normal Physiology Department). 2. Contents of electrolytes in blood plasma in a norm (Normal Physiology Department). 3. Regulation of water-electrolyte metabolism (Normal Physiology Department) Information that is necessary for addition to knowledges-abilities of bases on these questions, can be found in the followings textbooks: Materials from normal physiology course. The checking of primary level of knowledges Give the answer to the followings questions: 1. What is «positive water balance»? 2. What is «negative water balance»? 3. Hormones which take part in regulation of water-electrolyte metabolism. 4. What is «dehydration»? 5. Types of dehydration. 6. What is «isoosmolar dehydration»? 7. What reasons for isoosmolar dehydration origin? 8. What is «hypoosmolar dehydration»? 3 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 4 Reasons for hypoosmolar dehydration origin. What is «hyperosmolar dehydration»? Reasons for hyperosmolar dehydration origin. What is «hyperhydration»? Types for hyperhydration. What is «isoosmolar hyperhydration»? Reasons for isoosmolar hyperhydration origin. What is «hypoosmolar hyperhydration»? Reasons for hypoosmolar hyperhydration origin. What is «hyperosmolar hyperhydration»? Reasons for hyperoosmolar hyperhydration origin. What is edema? What is «dropsy»? Kind of dropsy. Types of edema according to pathogenesis. Mechanism of oncotic edema development. Mechanism of osmotic edema development. Mechanism of hydrostatical edema development. Mechanism of membranogenic edema development. Mechanism of lymphatic edema development. Quantity of sodium in blood plasma in a norm. Quantity of potassium in blood plasma in a norm. Quantity of calcium in blood plasma in a norm. Quantity of phosphorus in blood plasma in a norm. Standards of answers: It is the state at which entering of fluid in organism exceeds its excreting. It is the state at which excreting of fluid from an organism exceeds its receipt. Aldosteron, vasopresin (antidiuretic hormone), atrial Na-uretic factor. Diminishing of volume of extracellular fluid. А) Isoosmolar B) Hypoosmolar C) Hyperosmolar It is a type of dehydration in case of which osmotic pressure of extracellular liquid does not change. А) Polyuria B) Diarrhea C) First hours after hemorragia. It is a type of dehydration, with exceed loss of salts, which is accompanied the decrease of osmotic pressure of extracellular liquid. А) Vomiting B) Diarrhea C) Sweating It is a type of dehydration, with exceed loss of water which is accompanied the increase of osmotic pressure of extracellular liquid. А) Hyperventilation B) Increased sweating 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. C) Hypersalivation D) Diarrhea E) Vomiting Increasing of volume of extracellular liquid. А) Isoosmolar B) Hypoosmolar В) Hyperosmolar It is a type of hypergidration, in case of which osmotic pressure of extracellular fluid does not change. Surplus introduction of isotonic solutions. It is a type of hypergidration, in case of which osmotic pressure of extracellular fluid is decreased. А) Reflectory anuria B) Acute kidney insufficiency It is a type of hypergidration, in case of which osmotic pressure of extracellular fluid is increased. The use for drink of sea water. It is a surplus accumulation of liquid in intercellular space as a result of water metabolism violation between blood and tissues. It is an accumulation of liquid in cavities. А) Oncotic B) Osmotic C) Hydrostatic D) Membranogenic E) Lymphogenic А) In the condition of reduced blood plasma oncotic pressure (the deficiency of proteins in organism at starvation, violation of liver protein syntesis function, loss of albumens with urine at pathology of kidney) B) In the condition of promoted oncotic pressure in tissues (output of albumens in the tissues in case of increased permeability of vascular wall, at the damage of cell) In the condition of increased osmotic pressure in the tissues. In the condition of increased venous hydrostatical pressure. In the condition of increased permeability of vascular wall (action of biologically active substances, endo- and exotoxins on a vascular wall). In the condition of lymphostasis. 135 - 155 mmol/L 3,5 - 5,5 mmol/L 2,1 - 3,1 mmol/L 0,9 - 1,2 mmol/L 5 Theoretical questions for FMC №1. 1. Basic types of water-electrolyte metabolism violations. 2. Dehydration. Kinds. Reasons. Mechanisms of development. Value for an organism. 3. Reasons for dehydration development at children. Consequences of dehydratation. Principles of pathogenetic treatment of dehydratation different forms. 4. Hyperhydration. Kinds. Reasons. Mechanisms of development. Value for an organism. 5. Edema, determination of concept. Pathogenetic factors of edema development. 6. Pathogenesis of edema is at the diseases of heart, kidney, liver, inflammation, allergy, starvation. 7. Violation of sodium metabolism. Reasons for origin, mechanisms of development, consequences. 8. Violation of potassium metabolism. Reasons for origin, mechanism of development, consequences. 9. Violation of calcium metabolism. Reasons for origin, mechanisms of development, consequences. 10. A value of violations of water-electrolyte metabolism for organism. Principles of pathogenetic therapy. Literature: Handbook of general and Clinical Pathophysiology/ Edited by prof.A.V.Kubyshkin, CSMU, 2005.p.152-159, 167-171 2. Pathophysiology/ Edited by prof.Zaporozan, OSMU, 2005.p.154-162 3. General and clinical pathophysiology/ Edited by Anatoliy V/ Kubyshkin – Vinnytsia: Nova Knuha Publishers – 2011. p.333-343 1. Testing according system “Krok-I” Tests of an open database (2010) 1. A 56 year old patient suffering from cardiac insufficiency has edema of feet and shins, edematous skin is pale and cold. What is the leding mechanism of edema pathogenesis? A Rise of hydrostatic pressure in venules B Drop of oncotic pessure in capillaries C Increase of capillary permeability D Disorder of lymph outflow E Positive water balance 2. A patient with nephrotic syndrome has massive edemata of his face and limbs. What is the leading pathogenetic mechanism of edemata development? A Drop of oncotic blood pressure B Increase of vascular permeability C Rise of hydrodynamic blood pressure D Lymphostasis E Increase of lymph outflow 6 3. A patient was stung by a bee. Examination revealed that his left hand was hot, pink, edematic, there was a big red blister on the site of sting. What is the leading mechanism of edema development? A Increased vessel permeability B Reduced vessel filling C Injury of vessels caused by the sting D Drop of oncotic pressure in tissue E Drop of osmotic pressure in tissue 4. A patient ill with enteritis accompanied by massive diarrhea has low water rate in the extracellular space, high water rate inside the cells and low blood osmolarity. What is such disturbance of water-electrolytic metabolism called? A Hypo-osmolar hypohydration B Hyperosmolar hypohydration C Osmolar hypohydration D Hypo-osmolar hyperhydration E Hyperosmolar hyperhydration 5. A patient was admitted to the infectious department. His symptoms: dry skin, decreased skin turgor, rice-water stool. The patient was diagnosed with cholera. What disorder of water-electrolytic balance is most often observed in this disease? A Isoosmotic hypohydration B Hyperosmotic hyperhydration C Hypoosmotic hypohydration D Hyperosmotic hypohydration E Hypoosmotic hyperhydration 6. Edema was modeling to the white rat by the injection of adrenalin. What pathogenetic mechanism of edema development? A. Oncotic B. Hydrodynamic C. Membranogenic D. Lymphogenic E. Colloid-osmotic 7. Patient of D., 35 years, complains about permanent thirst, decrease of appetite, headache and convulsion. He drinks 9 l during a day. Day's diuresis is increased, urine without pathological changes, specific gravity - 1005. The reason of development such pathology is the damage of: A. The epithelium of kidney tubule B. Adenohypophis C. Epyphis D. Hypothalamic nucleus E. Basal membrane of glomerulus capillaries 7 8. Inflamation is characterised by increasing penetration of vessels of microcirculation stream, increasing of their fluid dynamic blood pressure. Increasing of the osmotic concentration and dispersity of protein structures present in the intercellular fluid. What kind of edema will appear in this case? A Mixed B Hydrodynamic C Colloid-osmotic D Lymphogenic E Membranogenic 9. Inflammation of a patient's eye was accompanied by accumulation of turbid liquid with high protein at the bottom of anterior chamber that was called hypopyon. What process underlies the changes under observation? A Disturbance of microcirculation B Primary alteration C Secondary alteration D Proliferation E 10. A patient who suffers from severe disorder of water-salt metabolism experienced cardiac arrest in diastole. What is the most probable mechanism of cardiac arrest in diastole? A Hyperkaliemia B Hypernatremia C Organism dehydratation D Hypokaliemia E Hyponatremia 11. An animal with aortic valve insufficiency got hypertrophy of its left heart ventricle. Some of its parts have local contractures. What substance accumulated in the myocardiocytes caused these contractures? A Calcium B Potassium C Lactic acid D Carbon dioxide E Sodium 12. A patient who suffers from heart failure has enlarged liver, edemata of lower extremities, ascites. What is the leading mechanism in the development of this edema? A Hydrodynamic B Colloid osmotic C Lymphogenous D Membranogenic E - 8 13. Periodic renal colics attackes are observed in the woman with primery hyperparathyroidizm. Ultrasonic examination revealed small stones in the kidneys. What is the cause of the formation of the stones? A Hypercalcemia B Hyperphosphatemia C Hypercholesterinemia D Hyperuricemia E Hyperkalemia 14. Transmural myocardial infarction in the patient was complicated with progressive acute left ventricle insufficiency. What is the most typical for this state? A Edema of the lungs B Edema of the extremities C Cyanosis D Ascites E Arterial hypertension 15. Patient suffered from cirrhosis of liver was intravenous injected 500 ml of 5% glucose solution. What disturbances of water-salt balance may appear in this patient? A. Hypoosmolar hyperhydration B. Hyperosmolar hyperhydration C. Isoosmolar hyperhydration D. Hypoosmolar hypohydration E. There is no dyshydration 16. A person, who has been on vegetable diet for along time, has edemas. What is the main mechanism of edema development in this case? A. Hypoaminoacidemia B. Hypoproteinemia C. Decrease of quantity of microelements in blood D. Hypoglycemia E. Anemia 17. Persons, 32, during 4 years suffers on chronic glomerulonephritis. Edemas are marked on face, lately edemas appeared in trunk, that glomerulonephritis with a nephrotic syndrome. What pathogenetic factor of edemas development for this patient? A. Increase of tissue liquid oncotic pressure B. Difficulty of lymph outflow C. Decrease of oncotic blood pressure D. Increase of hydrodynamic blood pressure in capillaries E. Increase of capillaries permeability 9 (2009) 18. As a result of continuous starvation the glomerular filtration rate has increased by 20%. The most probable cause of the glomerular filtration alteration under the mentioned conditions is: A. Increase in the systemic arterial pressure B. Increase in the permeability of the renal filter C. Increase of the renal blood flow D. Decrease in the oncotic pressure of blood plasma E. Increase of the filtartion quotient (2006-2008) 19. After a surgery a 36-year-old woman was given an intravenous injection of concentrated albumin solution. This has induced intensified water movement in the following direction: A. From the intercellular fluid to the cells B. From the intercellular fluid to the capillaries C. No changes of water movement will be observed D. From the cells to the intercellular fluid E. From the capillaries to the intercellular fluid 20. A patient has osmotic pressure of blood plasma at the rate of 350 mOsmol/l (norm is 300 mOsmol/l). This will cause hypersecretion of the following hormone: A. Cortisol B. Adrenocorticotyropin C. Vasopressin D. Natriuretic E. Aldosterone 21. Patient, 62 years, during 15 years suffers on insufficiency of mitral valve. Last month the edema of lower extremities began to arise up. What is the mechanism of edema development? A. Increase of permeability of capillaries B. Decrease of oncotic blood pressure C. Increase of oncotic pressure of tissue liquid D. Violation of lymphatic vessels E. Increase of hydrostatical blood pressure 22. A patient with chronic cardiac insufficiency have edema of lower extremities. What is the leading link of their pathogenesis? A. Hypothalamo-hypophysar system B. Renin-angiotensin-aldosteron system C. Sympato-adrenal system D. Parasympathetic system E. Kalikrein-kinin system 10 23. A person, after the long period of starvation has edema. What is the main mechanism of edema development in this case? A. Decrease of oncotic pressure in the blood B. Increase of oncotic pressure in tissues C. Increase of hydrostatic pressure of venous blood D. Decrease of hydrostatic pressure of tissues E. Decrease of blood circulating volume 24. Pulmonary hypertension and right-ventricle heart insufficiency with ascites and edemas develop in a patient suffered from pneumosclerosis. What is the main mechanism of edema development in this case? A. Increase of hydrostatic pressure in veins B. Increase of oncotic pressure of tissues C. Decrease of oncotic pressure of blood D. Reduction of heart stroke volume E. Increase of vascular permeability 25. Which of followings may cause the isoosmolar hypohydration? A. Acute blood loss B. Diarrhea C. Vomiting D. Perspiration E. Hyperventilation 26. A patient has uneasiness in the chest and difficult breathing after physical exertion. Some time later cough with foamy liquid phlegm appears. Significant cyanosis develops in the patient. What is the leading mechanism for edema development in this case? A. Hydrodynamic B. Colloid C. Membranogenous D. Lymphogenic E. Osmotic 27. Development of toxic edemat is predefined: A. Hypoproteinemia B. By the promoted permeability of vessels C. Hypernatriemia D. Acidosis E. By the promoted hydrostatic pressure 28. Patient had trauma, hyperemia of skin is appeared in place of damage, she became hot. Pain, limitation extremity motions, edema appeared. Name the initiating pathogenetic factor of inflammatory edema? A. Increase of microvessels permeability B. Decrease of oncotic blood pressure C. An increase of blood pressure in capillaries D. Violation of lymph outflow E. An increase of osmotic pressure in the region of inflammation 11 29. A patient with severe nephropathy accompanied by severe oedema syndrome that develops as complication of bronchiectasis. Laboratory examination of this patient displays abundant proteinuria, cylinderuria, distinct decrease of protein content in blood serum, hyperlipidemia, hypokalemia, and other pathological changes. What is the most important link in development of edemas in this patient? A. Decrease of oncotic pressure of blood B. Increase of osmotic pressure of interstitial fluid C. Increase of hydrostatic pressure of blood D. Blockade of lymphatic drainage E. Increase of microvessel permeability 30. At complete starvation (with taking water) generalized edemas develop. What is the leading pathogenic factor in this case? A. Increase of oncotic pressure of interstitial fluid B. Decrease of osmotic pressure of blood plasma C. Decrease of oncotic pressure of blood plasma D. Increase of osmotic pressure of interstitial fluid E. Decrease of hydrostatic pressure of interstitial fluid 31. What is the leading factor of edema development in case of nephrotic syndrome? A. Increase of hydrostatic pressure in capillaries B. Increase of vascular permeability C. Hypoalbuminemia D. Dynamic lymphatic insufficiency E. Increase of blood volume 32. A patient complain about a muscular weakness, feeling of weight in the epigastral area. At an inspection found out taxicardia, arterial hypotension, on ECG lengthening the interval of PQ, decrease of T voltage. What violation of mineral metabolism causes development of these disorders? A. Hypernatriemia. B. Hypokaliemia C. Hyperkaliemia. D. Hyponatriemia. E. Deficit of iron. 33. A patient was admitted to the infectious hospital with complaints about unrestrained vomit. What violations of water-salt metabolism are there? A. Isoosmolar dehydration B. Hyperosmolar dehydration C. Hypoosmolar hyperhydration D. Hyperosmolar hyperhydration E. Hypoosmolar dehydration 12 34. People found themselves on the island after a catastrophe in the ocean, without fresh water. What form of water-salt metabolism violations will develop? A. Hyperosmolar hyperhydration B. Isoosmolar hypergidration C. Hypoosmolar hyperhydration D. Hyperosmolar dehydration E. Hypoosmolar dehydration 35. Osmotic diuresis develops at diabetes mellitus. What violations of waterelectrolyte balance are observed? A. Isotonic dehydration B. Hypoosmolar dehydration C. Hyperosmolar hyperhydration D. Hyperosmolar dehydration E. Isoosmolar hyperhydration 36. Patient carried heavy infectious disease, after that appeared the signs of diabetes insipidus. Day's diuresis was increased to 10l. Afterwards dehydration of organism purchased threatening character. What mechanism of development? A. Increase of ultrafiltrate osmolarity B. Braking of water suction in the intestine C. Decrease of reabsorbtion of water in kidney D. Decrease of reabsorbtion of sodium in kidney E. Decrease of plasma oncotic pressure 37. Patient 43 years, appeared the signs of cardiac activity decompensation with the origin of edema and ascyt after the sharpening of rheumatic heart disease. The increase of production of what matter may cause those violation A. Aldosteron B. Insulin C. Cortisol D. Vasopresin E. Corticothropin 38. At a examination the edema is discovered in the area of left forearm, which arose up after the bite of bee. Name the leading pathogenetic mechanism of this edema: A. Hydrodynamic B. Oncotic C. Osmotic D. Lymphogenic E. Membranogenous 13 39. When treating for dehydration by means of salt-poor fluids at the background of sharply reduced excretory renal function resulted from tubular necrosis the worsening of general condition, confused consciousness, convulsive readiness, and brain edema with vomiting develop. What kind of water-salt metabolism disturbances takes place in this case? A. Hypoosmolar hyperhydration B. Isoosmolar hyperhydration C. Hyperoosmolar hyperohydration D. Hypoosmolar hypohydration E. Hyperosmolar hypohydration 40. Edemas are developed in a patient with renal disease. High quantity of albumen in the analyses of urine. What mechanism is it possible to explain the origin of edemas for such patient? A. By the decrease of lymph oncotic pressure B. By the decrease of filtration pressure in buds C. By the decrease of blood plasma oncotic pressure D. By the decrease of interstitial oncotic pressure E. By the increase of blood plasma osmotic pressure 41. Person, 64years, complain about the dysphnoe, frequent heart beating, rapid fatigueability. In the evening edemas appear on legs. What main pathogenetic factor in the development of edemas? A. Increase of tissue liquid oncotic pressure B. Violation of lymph outflow C. Decrease of oncotic blood pressure D. Increase of hydrodynamic pressure E. Increase of capillaries permeability 42. Edema of Kvinke (common edema of tissues) developed in the patient with allergy. What pathogenetic factor is starting in this case? A. Decrease of hydrostatical pressure in tissues B. Decrease blood plasma oncotic pressure C. Increase of permeability of capillaries walls D. An increase of hydrodynamic blood pressure E. An increase of osmotic pressure in tissues 43. Considerable part of alimentar starvation cases are accompanied with edema. What is the main pathogenetic factor of edema in this case? A. Decrease of tissues hydrostatical pressure B. Decrease of blood plasma oncotic pressure C. Increase of blood osmotic pressure D. Increase of intercellular liquid oncotic pressure E. Increase of blood hydrodynamic pressure 14 44. Patient with burn shock next to anaestetic drugs it is vitally necessary to enter antishock solutions in connection with water-electrolyte metabolism violations. What water-electrolyte metabolism violation most probably arise up at burn illness? A. Hypoosmolar of hypohydria B. Hypoosmolar hyperghydration C. Isoosmolar dehydration D. Hyperosmolar dehydration E. Hyperosmolar hyperhydria 45. Patient, 35 years, carried hepatitis and continued to adopt an alcohol, the signs of liver cirrhosis developed with ascyt and edemata of lower extremities. What blood composition changes did become deciding in development of edema? A. Hypokaliemia B. Hypoglobulinemia C. Hypoalbuminemia D. Hypocholesterinemia E. Hypoglycemia 46. Patient carried operative interference concerning intestinal impassability, after the signs of considerable dehydration appeared. What blood ions must be appointed in the first turn for water-salt balance correction? A. Chlor B. Cuprum C. Sodium D. Calcium E. Magnesium 47. A woman ate orange, after she has edema of palpebra, lips, neck, and tongue. Before on oranges there were pouring out on a skin, itch. What pathogenetic mechanism lies in development of edema? A. An increase of hydrodynamic blood pressure in capillaries B. Violation of lymph outflow C. Increase of capillaries permeability D. Decrease of oncotic blood pressure E. Increase of tissue fluid oncotic pressure 48. Patient, 35 years, who drinks alcohol often, has strong muscular and cardiac weakness, vomit, diarrhea, AP-100/60 mm Hg. All those symptoms developed during diuretics treatment. Reason of such state is the increased selection with urine: A. Phosphates B. Na C. К D. Cl E. Ca 15 49. Hypertensive solution of glucose was intravenously entered a patient. It will increased motion of water: A. From intercellular liquid to the capillaries B. There were no changes C. From capillaries to the intercellular liquid D. From cell to the intercellular liquid E. From intercellular liquid to the cell 50. Patient has reduced synthesis of vasopresin, that why he has polyuria and dehydration of organism. In what does consist mechanism of polyuria development of polyuria? A. Increase of glomerular filtration speed B. Decrease of water reabsorbtion in tubuls C. Decrease of Na+ reabsorbtion in tubuls D. Decrease glucose of reabsorbtion E. Decrease of protein reabsorbtion in tubuls 1-A 11-A 21-E 31-C 41-D 2-A 12-A 22-B 32-B 42-C 3-A 13-A 23-A 33-E 43-B 4-A 14-A 24-A 34-A 44-C Correct answers 5-A 6-B 15-A 16-A 25-A 26-A 35-D 36-C 45-C 46-C 7-D 17-C 27-B 37-A 47-C 8-A 18-D 28-E 38-E 48-C 9-A 19-B 29-A 39-A 49-D 10-A 20-C 30-C 40-C 50-B Situational tasks: 1. The worker of hot workshop had the unendurable feeling of thirst, increase of body temperature and brief loss of consciousness. 1) Type of water-electrolyte metabolism violation. _____________________________________________________________________ 2) What measures of prophylaxis need to be taken, to prevent this violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3) What water-electrolyte metabolism violation will develop if patient will drink water without the salt? ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Patient suffers from insufficiency of the mitral valve, patient marks the presence of edemas on lower extremities in the evening after work. 1) What is the mechanism of this edema development? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 16 2) Explain their localisation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. A child had dehydration of organism in the result of diarrhea. Isotonic solution of sodium chloride and desoxycortikosteron (mineralocortikoid) were appointed intravenous. Muscular weakness developed after some time. The level of Na in plasma is - 180 mmol/L (in a norm - 135-155 mmol/L), to potassium - 3,4 mmol/L (in a norm - 3,5-5,5 mmol/L). 1) What is the mechanism of complication? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 2) Is the medical tactic correct? Explain. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4. A 0,1% solution of adrenalin was injected to the white rat intraabdominal in dose 1 мg/100g of body mass. In 30 minutes, breathing became frequent and superficial, then sharp and convulsive, than foamy liquid appeared from the nose cavity, there was acrocyanosis. At appearance of sharp edema of lungs an animal die. What pathogenetic mechanism of edema development? 1) What mechanism of edema development takes place in this case? Explain. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 5. Patient D. 35 years, complain about permanent thirst, decrease of appetite, headache, convulsions. He drinks 9 l during a day. Diuresis is increased, urine without pathological changes, specific gravity - 1005. 1) What is the disease at the patient? _______________________________________________________________________ 2) Reasons for its origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3) Explain the mechanisms of its development. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4) What forms of this disease do you know? 17 ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 5) What is the treatment of the disease? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 6. Patient D., 82, delivered in a hospital with chronic cardiac insufficiency in the decompensate state. Taxycardia, arterial pressure is decreased/ There is edema of lower extremities. 1) What are the main pathogenetic factors in development of edemas at cardiac insufficiency. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Practical work: „EXPERIMENTAL EDEMA” Object of work: to show formation of frog back arms edema at the passing through the vascular net of solution of lactic acid; to show development of lungs edema at a white rat after intraperitoneal introduction of adrenalin. EXPERIMENT № 1. Prepare preparation of back arms of frog. Dissect an abdominal region by the longitudinal slit, extract internals. Place ligature under an aorta, incise an aorta, insert into a glass cannula and fix it by ligature. The upperparts of trunk is chopped off. Fill a cannula by Ringer’s solution for cool-blooded animals and unite it with the apparatus which consists of two Marriott’s tubes connected with a T-joint by rubber tubing with pressed-on clamps. Fill one burette by solution of Ringer and another one by lactic acid solution painted by methylene-blue. At first pass Ringer’s solution through the preparation of arms vessels and count up the amount of drops. Close the clamp of burette with Ringer’s solution and open the clamp of burette with lactic acid solution. Count up the amount of drops. Pass a few times by turns Ringer’s solution and lactic acid solution. Look after development of frog back arms edema. 18 № 1 2 3 4 Amount Ringer’s solution drops Amount lactic acid solution drops Conclusion:______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 19 EXPERIMENT № 2. Count up the initial respiration rate at a rat. Make the intraperitoneal injection of adrenalin on the basis of 0,5 ml a 0,1% solution on 100g of rat weight. Look after the changes of breathing during 10-15 min. After animals death extract the lungs, weigh it. Counted up a pulmonary coefficient (ratio of lungs weight in g to the rat’s body weight in kg). In a norm a pulmonary coefficient is equal 3-4. Conclusion:______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 20 Theme: VIOLATION of the ACID-BASIC BALANCE. Actuality of the theme. Constancy of pH of internal environment is the necessary condition of existence of higher organisms. It is provide certain correlation of acids and bases (acid-basic balance ABB) in biological environments, at violation of which an organism perishes. Violations of ABB are observed at many diseases and complicate their course. Knowledge of indemnification mechanisms of ABB violations and their support is one of major steps in the prophylaxis of many diseases complications. General purpose of the lesson. To learn reasons and mechanisms of basic acid-basic state (ABS) violations development, and also indexes which characterize these violations. For this it is necessary to know: 1. To interpret the main reasons which result in the origin of ABB. 2. To expose the mechanisms of ABB violations development. 3. To explain compensate possibilities of organism which are included at the different forms of ABB violations. 4. To design violation of the ABB. For realization of purpose of lesson it is necessary to have the base knowledgesskills: 1. Concept about the buffer systems. (Normal Physiology Department); 2. Concept about blood pH (Normal Physiology Department). Information that is necessary for addition to knowledges-abilities of bases on these questions can be found in the followings textbooks: Materials from normal physiology course The checking of primary level of knowledges Give the answer to the followings questions: 1. Acid-basic balance, definition. 2. What index of blood active reaction and what is it evened? 3. Chemical buffer systems of organism. 4. What physiological systems take part in supportion of ABB? 5. How does the system of the external breathing take part in regulation of ABB? 6. How does the kidney take part in regulation of ABB? 7. What is acidogenesis? 8. What is amoniogenesis? 9. Mian forms of ABB violation. 10. Acidosis, definition. 11. Alkalosis, definition. 12. How does divide acidosis and alkalosis depending on the pH changes? 13. How does divide acidosis and alkalosis after the mechanisms of development? 14. Main reasons for gas acidosis origin. 15. Main reasons for gas alkalosis origin. 21 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 22 Types for nongas acidosis. Types fon nongas alkalosis. What are the reasons of metabolic acidosis origin? What are the reasons for exogenous acidosis origin? What are the reasons for excretory acidosis origin? What are the reasons for hypochloremic alkalosis origin? What are the reasons for hypokaliemic alkalosis origin? What are the reasons for exogenous alkalosis origin? Standards of answers. It is permanent correlation between hydrogen and OH ions in the internal environment of organism. pH = 7,36 - 7,44 А) Hydrocarbonatic B) Phosphatic C) Hemoglobin D) Protein А) System of the external breathing B) Kidney C) Digestive system Supports pressure of CO2 in arterial blood. А) Acidogenesis B) Amoniogenesis C) Reabsorbtion of hydrocarbonat Synthesis and secretion in the kidney tubules H + ions. Synthesis and secretion in the kidney tubules the ammonium ion. А) Acidosis B) Alkalosis It is an absolute or relative accumulation of acids in the internal environment of organism. It is an absolute or relative accumulation of bases in the internal environment of organism. А) Compensated (if pH keeps in physiological norm) B) Uncompensated (if pH goes outside physiological norm) А) Gas (caused the primary changes of CO2 pressure in blood) B) Non gas (caused an accumulation in the organism of non-flying products of acid or alkaline character) А) Hypoventilation of lungs, that is accompanied violation of CO 2 destroying from the organism B) Breathing in air with high maintenance of СО2 А) Hyperventilation of lungs B) Incorrectly guided artificial respiration А) Metabolic B) Excretory C) Exogenous А) Excretory (hypochloremic, hypokaliemic) B) Exogenous (hypernatriemic) 18. An accumulation in the organism of non-flying acids as a result of metabolic disturbances: lactatatsidosis, ketoacidosis. 19. Hit in the organism of exogenous non-flying acids. 20. Loss of hydrocarbonat by an organism at kidney function violation and digestive disorders. 21. Repeating vomit which is accompanied the loss of Cl-. 22. Hyperaldosteronism, that is accompanied the loss of potassium ions with urine. 23. Hit in the organism of exogenous bases (for example, introduction of hydrocarbonat during wrong correction of nongas acidosis). Theoretical questions for FMC №1. 1. Classification of ABB violations. 2. Acidosis, definition of concept. Kinds. Reasons and mechanisms of development. 3. Compensation and violation of functions at acidosis. 4. Alkalosis, determination of concept. Kinds. Reasons and mechanisms of development. 5. Violation of functions and compensation of the different types of alkalosis. 6. Main indexes of the acid-basic state. Changes of indexes at different ABB violations. Literature: Handbook of general and Clinical Pathophysiology/ Edited by prof.A.V.Kubyshkin, CSMU, 2005.p.160-166 2. Pathophysiology/ Edited by prof.Zaporozan, OSMU, 2005.p.162-166 3. General and clinical pathophysiology/ Edited by Anatoliy V/ Kubyshkin – Vinnytsia: Nova Knuha Publishers – 2011. p.343-348 1. Testing according system “Krok-I” Tests of an open database (2010) 1. Trauma of the head brain a patient is accompanied by repeated vomiting and shortness of breathing. At an inspection it is marked: рН = 7,62; pСО2 = 40 mm of Hg. What is violation of the acid-basic state at a patient? A Ungas alkalosis B Gas alkalosis C Ungas acidosis D Gas acidosis E - 23 2. Hypoxemia and hypercapnia are educed at the research of blood gas composition at the patient with the chronic disease of respiratory system on a background of the shortness of breathing, tachicardia and cyanosys.Because of what violations of the external breathing these changes were arise up? A Hypoventilation B Hyperventilation C Hyperperfusion D Hypoperfusion E Hyperdiffusion 3. A newborn child with pylorostenosis has often repeating vomiting accompanied by apathy, weakness, hypertonicity, sometimes convulsions. What disorder form of acidbase balance is it? A Nongaseous alkalosis B Gaseous alkalosis C Gaseous acidosis D Metabolic acidosis E Excretory acidosis 4. After taking poor-quality food a patient developed repeated episodes of diarrhea. On the next day he presented with decreased arterial pressure, tachycardia, extrasystole. Blood pH is 7,18. These abnormalities were caused by the development of: A Nongaseous acidosis B Gaseous acidosis C Nongaseous alkalosis D Gaseous alkalosis E Metabolic alkalosis 5. Disorder of the airways passage in small and middle bronchi was revealed in the patient. What disorder of the acid-base equilibrium can be detected in the blood? A Respiratory acidosis B Metabolic acidosis C Respiratory alkalosis D Metabolic alkalosis E -6. 48 y.o. patient with diabetes mellitus was admitted to the hospital in severe precoma state. When examining of acid-base balance metabolic acidosis was revealed. What is the main possible mechanism of found changes development? A. Disorders of O2 using in cells B. Disorders of buffer systems of blood C. Decrease of CO2 removing D. Excretion of alkali elements with urine E. Formation of products of incomplete oxydation 24 7. A group of mountain climbers went through the blood analysis at the height of 3000 m. It revealed decrease of HCO 3_ to 15 micromole/l (standard is 22-26 micromole/l). What is the mechanism of HCO 3_ decrease? A Hyperventilation B Intensification of acidogenesis C Hypoventilation D Decrease of ammoniogenesis E Decrease of bicarbonate reabsorption in kidneys 8. For a patient with respiratory insufficiency рН of blood is 7,35. Determination of рСО2 showed the presence of hypercapnia. At research of рН of urine the increase of her acidity is marked. What form of violation of the acid-basic state in this case? A Compensated gas acidosis B Compensated metabolic acidosis C Decompensated metabolic acidosis D Compensated gas alkalosis E Decompensated gas alkalosis 9. Toxicosis with the heavy repeated vomiting for a day long developed at a pregnant woman. After twenty-four hours tetaniform convulsions and dehydration of organism began to show up. What change of pH caused the described changes? A Excretory alkalosis B Gas alkalosis C Gas acidosis D Metabolic acidosis E Secretory acidosis (2006-2009) 10. In a patient with diabetes mellitus metabolic acidosis developed as a result of accumulation of keton bodies. Arterial blood pH is: A. 7,40 B. 7,32 C. 7,48 D. 7,56 E. 7,66 11. Patient of D., 48 y.o., which suffers from obesity, conducted the course of medical starvation in home terms. The deep, noisy breathing appeared on 10 day, arterial pressure went down to 90/60 mm Hg, a selection of urine diminished, urine with the smell of acetone. What is conditioned described? A. Non gas alkalosis B. Hyperglycemia C. Ketosis D. Hypoglycemia E. Gas acidosis 25 12. A 65-years-old patient with multiple fractures of ribs was admitted to the hospital. What type of acid-base balance disorder may develop in him? A. Gas acidosis B. Gas alkalosis C. Non-gas acidosis D. Non-gas alkalosis E. There are no disorders of acid-base balance 13. A pregnant woman has toxicosis, which accompanied by prolonged vomiting. Data of her biochemical analyses show: pH of blood – 7.38, pCO2 of arterial blood – 46 mmHg, SB – 17 mmol/L, BE – (+ 6 mmol/L). What type of acid-base balance disorder takes place in this case? A. Compensated non-gas alkalosis B. Decompensated non-gas alkalosis C. Compensated non-gas acidosis D. Decompensated non-gas acidosis E. Compensated gas alkalosis 14. A 58-years-old female patient was admitted to the hospital in severe state. Data of her biochemical analyses show: pH of blood – 7.33, pCO2 of arterial blood – 36 mmHg, SB – 17 mmol/L, BE – ( - 6 mmol/L). What type of acid-base balance disorder takes place in this case? A. Compensated non-gas alkalosis B. Decompensated non-gas alkalosis C. Compensated non-gas acidosis D. Decompensated non-gas acidosis E. Compensated gas alkalosis 15. What is the reason for gas alkalosis? A. Pulmonary hyperventilation B. Loss of gastric juice C. Loss of intestine juice D. Pulmonary hypoventilation E. Hyperaldosteronism 16. What kind of acid-base balance disturbances may be observed in case of diabetes mellitus? A. Non-gas acidosis B. Gas acidosis C. Gas alkalosis D. Non-gas alkalosis E. Excretory acidosis 26 17. At examination of patient following were found: hyperglycemia, ketonuria, polyuria, hyperstenuria, and glucosuria. What kind of acid-base balance disturbances occurs in this case? A. Gas alkalosis B. Non-gas alkalosis C. Metabolic alkalosis D. Metabolic acidosis E. Gas alkalosis 18. At getting up in mountains euphoria, head pain, dizziness, heart beating, dyspnoe, which was alternated from apnoe, developed for an alpinist. What did violation of the acid-basic state develop for an alpinist? A. Metabolic alkalosis B. Gas alkalosis C. Non gas alkalosis D. Gas acidosis E. Non gas acidosis 19. Respiratory alkalosis developed in group of alpinists during ascending to on Everest. Thus pressure of СО2 in arterial blood: A. 40 mm Hg B. 50 mm Hg C. 60 mm Hg D. 70 mm Hg E. 30 mm Hg 20. A patient suffered from diabetes mellitus was admitted to the hospital because of worsening of his condition. He has general malaise, polyuria, lethargy, and sleepiness. Kussmaul respiration, heart arrhythmia, and acetone scent in expired air are noticed in this patient. What kind of shift of acid-base balance contributes these symptoms? A. Gas alkalosis B. Gas acidosis C. Non-gas metabolic alkalosis D. Non-gas metabolic acidosis E. Non-gas excretory alkalosis 21. What violation of the acid-basic state does take place at blood pH 7,48? A. Alkalosis decompensate B. Alkalosis compensated C. Metabolic decompensated acidosis D. Acidosis compensated E. Acidosis excretory decompensated 27 22. What acid –basic balance disorder can develop in 2 hours after repeated vomiting? A. Excretory acidosis B. Excretory alkalosis C. Eczogenic alkalosis D. Metabolic acidosis E. Eczogenic acidosis 23. Patient, who suffers from severe diarrhea, was admitted to the hospital with consequences disorder, Kussmaul respiration. Blood pH 7,30, deficiency of base. Acidic reaction of urine, contain many phosphates and ammonium salts. What is acid-basic balance disorder develop in this case? A. Non-gas alkalosis B. Non-gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas alkalosis E. Gas acidosis 24. Repeated vomiting occurs in patient suffered from pylorostenosis which is bring to severe state. Appeared appation, weakness, increased muscular tonus, cramps. What is acid-basic balance disorder develop in this case? A. Non-gas alkalosis B. Non-gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas alkalosis E. Gas 25. In the case of development of mountain disease compensatory lung hyperventilation is developed. What is acid-basic balance disorder develop in this case? A. Non-gas alkalosis B. Non-gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas alkalosis E.Gas acidosis 26. During bronchial asthma attack patient developed gas acidosis (hypercapnia). What type of acid-base balance disorder takes place in this case? A. Gas alkalosis B. Gas acidosis C. Non-gas metabolic alkalosis D. Non-gas metabolic acidosis E. Non-gas excretory alkalosis 28 27. Patient was appointed solution of glucose intravenously with potassium bicarbonat. Such indexes are determined: pH- 7,43; рСО2 - 61 mm Hg; SB - 31,5 mecv/l; BB - 59 mecv/l; BE +8,5 mecv/l . What ABB violation does take place in this case? A. Non gas alkalosis B. Non gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas acidosis E. Gas alkalosis 28. Patient had such laboratory parameters – pH-7,32, pCO2 35 mm Hg, SB16,5mecv/l, BB – 35,0 mecv/l, BE – 9,0 mecv/l, TK day urine - 8,0 mecv/day. What is acid-basic balance disorder develop in this case? A. Non-gas alkalosis B. Non-gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas alkalosis E. Gas acidosis 29. Patient get head trauma, which accompanied with repeated vomiting and dyspnoe. Laboratory tests: pH -7,48, pCO2 – 30 mm Hg, SB – 27 mecv/l, BB- 50,0 mecv/l., BE -+ 3,0 mecv/l. What is acid-basic balance disorder develop in this case? A. Non-gas alkalosis B. Non-gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas alkalosis E. Gas acidosis 30. For a patient with nefrotic syndrome polyuria observed, hyponatriemia (patient gets diacarb). Patient had such laboratory parameters: pH - 7,30; рСО2 - 36 mm Hg;SB- 17,0 mecv/l; BB - 42 mecv/l; BE - 8,0 mecv/l. What ABB violation does take place in this case? A. Non gas alkalosis B. Non gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas acidosis E Gas alkalosis 31. Patient in comatose state. Laboratory tests: keton bodies – 58 mg%, TK day urine- 40 mecv/day, pH – 7,30, p CO2 – 50 mmHg, SB – 15,5 mecv/l, BB – 38,0 mecv/l, BE – 13,0 mecv/l. What is acid-basic balance disorder developing in this case? A. Non-gas alkalosis B. Non-gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas alkalosis E. Gas acidosis 29 32. Patient suffers from severe toxic damage of kidney with anuria. Laboratory tests: lactic acid – 20 mg%, pH -7,25, p CO2 - 47 mecv/l, SB -18,5 mecv/l, BB – 40,5 mecv/l, BE -70 mecv/l. What is acid-basic balance disorder develop in this case? A. Non-gas alkalosis B. Non-gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas alkalosis E. Gas acidosis 33. An operation is conducted with artificial ventilation of lungs. Patient had such laboratory parameters: pH -7,47; рСО2-75 mm Hg; SB-27,0 mecv/l; BB-49,0 mecv/l; ВЕ+3,5 mecv/l. What ABB violation does take place in this case? A. Non-gas alkalosis B. Non-gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas alkalosis E. Gas acidosis 34. An operation is conducted with artificial ventilation of lungs. Patient had such laboratory parameters: pH -7,32; рСО2-25 mm Hg; SB-20 mecv/l; BB-40 mecv/l; ВЕ+3,0 mecv/l. What ABB violation does take place in this case? A. Non-gas alkalosis B. Non-gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas alkalosis E. Gas acidosis 35. Patient suffers from sharp insuffiency of left ventricle of heart. Edema of lung developed. Patient had such laboratory parameters: pH - 7,32; рСО2 - 51 mm Hg; SB - 18,0 mecv/l; BB - 45 mecv/l; BE +8.0 mecv/l. What ABB violation does take place in this case? A. Non-gas alkalosis B. Non-gas acidosis C. Excretory alkalosis D. Gas alkalosis E. Gas acidosis 36. For a patient with diabetes mellitus hyperglicemia, ketonuria, glycosuria is marked, hyperstenuria and polyuria. What form of ABB violation does take place in this situation? A. Gas acidocic B. Metabolic acidosis C. Gas alkalosis D. Non gas alkalosis E. Excretory alkalosis 30 1-A 10-B 19-E 28-B 2-A 11-C 20-D 29-C 3-A 12-A 21-A 30-B 4-A 13-A 22-B 31-B Correct answers 5-A 6-E 14-D 15-A 23-B 24-C 32-B 33-E 7-A 16-A 25-D 34-D 8-A 17-D 26-B 35-B 9-A 18-B 27-A 36-B Situational tasks: 1. An alpinist frequency and breathing depth was sharply increased. After some time breathing depressed and loss of consciousness came suddenly. 1) What type of ABB violation take place in this patient? _____________________________________________________________________ 2) What are possible reasons for it origin? ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3) Explain the mechanism of frequent and deeply breathing at getting up on a height. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4) Why did breathing stimulation change its depression? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 5) What does a patient need to appoint - the breathing by clear oxygen or carbogen? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Patient get head trauma, which accompanied with repeated vomiting and frequent breathing. During inspection found out the followings indexes of ABB: pH - 7,56; рСО2 = 30mm Hg; SB = 28 mmol/L; BB = 50 mmol/L; BE = +5 mmol/L. 1) What type of ABB violation takes place in this patient? ______________________________________________________________________ 2) What are possible reasons of origin? ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3) What are the mechanisms of functions compensation in this case? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4) What possible violations can arise up? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 5) How to correct ABB violation in a patient? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 31 3. A pregnant woman has toxicosis, which accompanied by prolonged vomiting. Data of her biochemical analyses show: pH of blood – 7.38, pCO2 of arterial blood – 46 mmHg, SB – 38 mmol/L, BE – (+ 6 mmol/L). 1) What type of ABB violation takes place in this patient? _____________________________________________________________________ 2) What are the mechanisms of functions compensation in this case? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3) What possible violations can arise up? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 4) How to correct ABB violation in a patient? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. Patient with diabetes mellitus has violation of acid-basic state, which developed as a result of keton bodies accumulation. Blood pH 7,32. 1) What type of ABB violation takes place in this patient? ______________________________________________________________________ 2) What possible violations can arise up from the side of different organs and systems? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3) How to correct ABB violation in a patient? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 5. A 58-years-old patient was admitted to the hospital in severe state. Data of her biochemical analyses show: pH of blood – 7.33, pCO2 of arterial blood – 36 mmHg, SB – 17 mmol/L, BE – (- 6 mmol/L). 1) What type of ABB violation takes place in this patient? _____________________________________________________________________ 2) What are the mechanisms of functions compensation in this case? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3) What possible violations can arise up from the side of different organs and systems? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4) How does to correct ABB violation in a patient? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 32 6. Patient with bronchial asthma has disturbances of airways passage at the level of small and medium bronchi. 1) What type of ABB violation takes place in this patient? _____________________________________________________________________ 2) What possible violations can arise up from the side of different organs and systems? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3) How to correct ABB violation in a patient? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 7. Patient suffers from bronchial asthma. рН 7,35 рСО2, mm Hg 52 SВ, mmol/l 22 ВВ, mmol/l 45 ВЕ, mmol/l +2 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 8. An operation with using of artificial blood circulation is performed to the patient. рН 7,34 рСО2, mm Hg 37 SВ, mmol/l 14 ВВ, mmol/l 29 ВЕ, mmol/l -12 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 33 9. Primary diagnosis of the patient is “diabetes mellitus”. pН 7,36 рСО2 mm Hg 36 SB, mmol/l 19,5 ВВ, mmol/l 39 BE, mmol/l -5 TA, mmol/l 37 NH+4, mmol/l -17 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 10. Primary diagnosis of the patient is “chronic glomerulonephritis, acute phase”. pН 7,28 рСО2 mm Hg 35 SB, mmol/l 16,5 ВВ, mmol/l 35 BE, mmol/l 9 TA, mmol/l 8 NH+4, mmol/l 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 11. Small intestine fistula with loss of intestine juice was diagnosed at the patient. рН 7,35 рСO2, mm Hg 36 SB, mmol/l 14 ВВ, mmol/l 24 BE, mmol/l -8 LA, mg% -28 NH+4, mmol/l -15 TA, mmol/l -8 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 34 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 12. Patient suffers from severe form of toxic injury of the liver and kidneys with oliguria. рН 7,25 рСO2, mm Hg 47 SB, mmol/l 18,5 ВВ, mmol/l 40,5 BE, mmol/l -7 LA, mg% NH+4, mmol/l TA, mmol/l 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 13. Patient suffers from acute left ventricle insufficiency complicated by the lung edema. рН 7,47 рСO2, mm Hg 25 SB, mmol/l 20 ВВ, mmol/l 40 BE, mmol/l 2 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 35 14. An operation with using of artificial blood circulation is performed to the patient. рН 7,47 рСO2, mm Hg 25 SB, mmol/l 20 ВВ, mmol/l 40 BE, mmol/l 2 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 15. Patient suffers from uncontrolled vomiting, tetany. рН 7,50 рСО2, mm Hg 36 SB, mmol/l 28 ВВ, mmol/l 57 BE, mmol/l +5,5 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 16. Patient suffers from brain concussion with uncontrolled vomiting and dyspnea. рН 7,56 рСО2, mm Hg 30 SB, mmol/l 28 ВВ, mmol/l 50 BE, mmol/l +5 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 36 17. Patient suffers from acute blood loss. рН 7,19 рСО2, mm Hg 25 SB, mmol/l 11 ВВ, mmol/l 27 BE, mmol/l -17 Ht 0,36 LA, mg% 23 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 18. Patient is in the state after the operative removing of the clot from the abdominal part of aorta. рН 7,35 рСО2, mm Hg 49 SB, mmol/l 19,5 ВВ, mmol/l 44 BE, mmol/l -3,0 Ht LA, mg% 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 19. Patient suffers from hemolytic anemia of unknown reason. рН 7.31 рС02, mm Hg 35 SB, mmol/l 18 ВВ, mmol/l 42 ВЕ, mmol/l -5.5 TA, mmol/l 12 LA, mg% -12 Ht 0,30 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 37 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 20. Patient suffers from brain concussion with uncontrolled vomiting. рН 7,43 рС02, mm Hg 28 SB, mmol/l 25 ВВ, mmol/l 48 ВЕ, mmol/l +4,0 TA, mmol/l LA, mg% Ht 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 21. The blood was taken from the patient after the episode of the hysteria. рН 7,42 рСО2, mm Hg 30 SB, mmol/l 20,0 ВВ, mmol/l 50,5 ВЕ, mmol/l -0,5 Ht 0,40 TA, mmol/l -18 LA, mg% -25, 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 38 22. Patient was hospitalized 9 days before with diagnosis “acute myocardial infarction”. рН 7,22 рСО2, mm Hg 51 SB, mmol/l 15 ВВ, mmol/l 38 ВЕ, mmol/l -12,5 Ht TA, mmol/l LA, mg% 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 23. Patient suffers from purulent peritonitis. рН 7,48 рСО2 49 mm Hg SB 26,5 mmol/l ВВ 52,5 mmol/l ВЕ +6 mmol/l TA 18 mmol/l 1. Name the type of ABB violation at the patient. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the reasons of described violation origin. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to correct the described violation? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Practical work: “VIOLATION of the ACID-BASIC STATE” Object of work: to define titratable acidity of urine at acidosis and alkalosis. EXPERIMENT № 1. Take 5 ml of urine, add 2 drops of phenolphthalein. Titrate by the drops of decinormal solution of NaOH till the colour of solution become to rose. 39 Titratable acidity – it’s the amount of alkali (ml), which we use for neutralization of 1 liter of urine acidic products. In a norm this index is equal 200-400 ml. For titration of 5 ml of urine we used ______ ml of alkali. 5 ml of urine - _______ ml of alkali 1000 ml of urine – X ml of alkali X = ____________________________ ml Conclusion:______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 40 Theme: PATHOLOGY OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Actuality of the theme. Violation of carbohydrate metabolism is the leading link in pathogenesis of many diseases (nervous, cardio- vascular systems, liver). Most frequent and the most heavy form of pathology of carbohydrate metabolism is diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus - one of the most widespread diseases with steady tendency to growth. From data of WHO, frequency of him on the average hesitates from 1,5 to 3-4%, considerably growing in the developed countries of the world (to 5-6%). Growth of morbidity, heavy invalidization consequences and high lethality, especially among capable of working population develops due to diabetes mellitus and it complications. Fight against diabetes mellitus is delivered to the medico-social problems. Understanding of reasons which influence on growth of morbidity on diabetes finding out of thin mechanisms of its development, understanding of prophylactic, sanitary educational measures on morbidity of population of Ukraine on diabetes mellitus, has an irrefutable value. General purpose of the lesson Learn reasons and mechanisms of development of basic types hypo- and hyperglycemia. To study etiology, pathogenesis, mechanism of development of basic displays of diabetes mellitus, its pathogenic treatment. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. For this it is necessary to know: To expose the typical forms of violations of carbohydrate metabolism. To define reasons and mechanisms of hypo- and hyperglycemia development. To expose reasons and mechanisms of hypo- and hyperglycemia development at the children of different age, value of these changes for child's organism. To explain the modern views of reasons and pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. To explain intercommunication between disorders of metabolism and basic functional violations at diabetes mellitus. To expose features, which is typical for diabetes mellitus at children. Transfer the base moments of the first aid during hypo- and hyperglycemic states. For realization of purpose of lesson it is necessary to have the base knowledgesskills. 1. Role of carbohydrates in an organism (department of biochemistry). 2. Intercommunication between carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism (BiochemistryDepartment). 3. Neurohumoral regulation of carbohydrate metabolism (Normal Physiology Department) 41 The checking of primary level of knowledges. Give the answer to the followings questions: 1. Hormones which take part in regulation of carbohydrate metabolism. 2. Participation of the nervous system in the carbohydrate metabolism regulation. 3. Contrinsular hormones. 4. Where is the place of insulin production? 5. What is hyperglycemia? Kinds. 6. What is hypoglycemia? Kinds. 7. What is glycosuria? 8. What is a kidney threshold for glucose? Why is it evened? 9. What is diabetes mellitus? Definition. 10. Types of diabetes mellitus. 11. Commas which arise up at diabetes mellitus, mechanisms of their development 12. Ketoacidotic coma, reasons. 13. Hyperosmolar coma, reasons. 14. Reasons of hypoglycemic coma development at diabetes mellitus? 15. What are consequences of hypoglycemia? 16. What are complications of diabetes mellitus? 17. What are the experimental models of diabetes mellitus? Theoretical questions for FMC №1. 1. Typical forms of violations of carbohydrate metabolism. 2. Hyperglycemia, kinds, reasons of origin, mechanisms of development. Value for organism. 3. Children’s hyperglycemia. Reasons and mechanisms of development. Value for child's organism. 4. Hypoglycemia, reasons of origin, mechanisms of development. Value for an organism. 5. Child kidneys hypoglycemia. Reasons and mechanisms of development. Value for the children of different age. 6. Diabetes mellitus. Modern view of etiology and pathogenesis. Classification. 7. Childkidneys diabetes mellitus. Reasons, mechanisms of development. Communication with the antigens of HLA. 8. Mechanisms of development of diabetes mellitus main manifestations. 9. Metabolic disorders at diabetes mellitus. 10. Coma, determination of concept. Pathogenesis of basic types of comas which can arise at diabetes mellitus, pathogenic treatment. 11. Basic experimental models of diabetes mellitus. Literature is necessary for theoretical questions . 1. Handbook of general and Clinical Pathophysiology/ Edited by prof.A.V.Kubyshkin, CSMU, 2005.p.146-151 2. Pathophysiology/ Edited by prof.Zaporozan, OSMU, 2005.134-144 3. General and clinical pathophysiology/ Edited by Anatoliy V/ Kubyshkin – Vinnytsia: Nova Knuha Publishers – 2011. p.294-321 42 Nota bene! Glycated hemoglobin - (НвА1с) - contains glucose, attached to terminal valin in every ß chain. It is permanent index of the compensative state of diabetes mellitus. The concentration of it is increased in patients with decompensate diabetes mellitus. Normal index of НвА1с in blood: 5-7% from the general level of hemoglobin. THEMES of reports for individual work of students: 1. Modern view in mechanisms of development of microangiopathy at diabetes mellitus. 2. Modern view in mechanisms of development of macroangiopathy at diabetes mellitus. 3. Modern view in mechanisms of development of diabetic coma. Pathogenetic treatment. 4. Modern view in mechanisms of development of hyperosmolar coma. Pathogenetic treatment. Testing according system “Krok-I” Tests of an open database (2010) 1. A patient, 24, suffers from dryness in a mouth, decline of waight on the base of the increased appetite, increase of urine amount. What test for the diagnosis is it necessary to make first of all? A Determination of glucose level in the day's amount of urine B Analysis of urine according to Zimnitskyy C General analysis of urine D Research of albuminous factions of the blood serum E Coagulograme 2. Apatient with a diabetes mellitus delivered in a hospital in the state of unconsciousness. Kussmaul’s breathing, blood pressure 80/50 mmHg, the smell of acetone from a mouth. By accumulation of what substances in the organism it is possible to explain the origin of these disorders? A Keton bodies B Modified lipoproteids C Lactic acid D Coal acid E Complete carbohydrates 3. Glucose was founded in the purine of patient who suffers from polyuria and polydipsia. Content of dlucose in the blood plasma is normal. What is the mechanism of glucosuria development for a patient? A Violation of glucose reabsorption in the tubulis. B Violation of glucose filtration in the glomerulis. C Insufficient production of insulin by a pancreas. D Resistance of cell receptors to insulin. E Hyperproduction of glucocorticoids by the adrenal gland. 43 4. A woman 26 years suffers from dryness in to the mouth, thirst. At an inspection: a level of glucose in the blood is 6,5 mmol/l, glucosuria. For what from the marked below states these symptoms are most characteristic for? A Kidney diabetes B Steroid diabetes C Diabetes insipidus D Alimentary glucosuria E Diabetes mellitus 5. Insulin was entered to a patient with insulindepended diabetes mellitus. After some time general weakness, irritability, increase of sweating arose up. What basic mechanism of of hypoglycemic comma development? A Carbohydrate starvation of brain. B Intensification of glycogenolysis. C Intensification of ketogenesis. D Intensification of lipogenesis. E Diminishing of glyconeogenesis. 6. A 12-year-old teenager has significantly put off weight within 3 months; glucose concentration rose up to 50 millimole\l. He fell into a coma. What is the main mechanism of its development? A Hyperosmolar B Hypoglycemic C Ketonemic D Lactacidemic E Hypoxic 7. A child 12 years after the carried rubella had loss of weight, permanent feeling of thirst, increase of appetite, polyuria. Objectively: diuresis 6 l, glucose of blood - 17,8 mmol/L, in urine found out glucose and acetone. What pathology can be assumed for a patient? A. Diabetes mellitus Ι type B. Diabetic nephropathy C. Diabetes mellitus ІІ type D. Violation of tolerance to glucose E. Diabetes insipidus 8. Patient with diabetes didn't get insulin injection in time that caused hyperglycemic coma (glucose in the blood 50mmol/L). What mechanism is prevalent in the development of the coma? A Hyperosmia B Hypokaliemia C Hypoxia D Hyponatremia E Acidosis 44 9. A woman, aged 58, was admitted to the hospital in severe condition. She has confused consciousness; dry skin, hollow eyes, cyanosis, and scent of acetone from her mouth. At laboratory examination of her: glucose in blood – 15.2 mmol/L, ceton bodies – 100 mcmol/l. What is the most possible reason for this condition? A. Hypoglycemic coma B. Ketoacidotic coma C. Hypovolemic coma D. Uremic coma E. Anaphylactic shock 10. A patient was admitted to the hospital. Objectively: the state is heavy, consciousness is absent, adynamia. Skin is dry, hollow eyes, cyanosis, taxicardia, smell of acetone from a mouth. Results of analyses: glucose of blood -20,1 mmol/L (normal -3,3-5,5 mmol/L), in urine -3,5% (normal - 0). What the most reliable diagnosis? A. Sharp alcoholic poisoning B. Hypoglycemic coma C. Аnaphylactic shock D.Hyperglycemic coma E. Cardiac insufficiency 11. A patient suffering from pheochromocytoma complains of thirst, dry mouth, hunger. Blood test for sugar revealed hyperglycemia. What type of hyperglycemia is it? A Adrenal B Hypercorticoid C Alimentary D Somatotropic E Hypoinsulinemic (2006-2009) 12. Patient has diabetes mellitus. Hyperglycemia over 7,2 mmol/L. The level of what protein of plasma does allow retrospectively (previous 4-8 weeks to an inspection) to estimate the level of glycemia? А. Ceruloplasmin В. Glycated hemoglobin С. Fibrinogen D. С-reactive protein E. Albumen 13. In a patient with diabetes mellitus loss of consciousness and cramps were observed after insulin injection. What is a possible result of blood test for glucose in this case? A. 5.5 mmol/L B. 3.3 mmol/L C. 8.0 mmol/L D. 10 mmol/L E. 1.5 mmol/L 45 14. At diabetes mellitus can develop ketosis as a result of activation of lipid acids oxygenation. What violations of ABB can bring accumulation of keton bodies in blood? А. Respiratory acidosis В. Respiratory alkalosis С. Exogenous acidosis D. Metabolic acidosis Е. Excretory acidosis 15. Content of glucose in patient’s blood is: on an empty stomach - 5,6 mmol/l, in 1 hour after taking sugar - 13,8 mmol/l, and in 3 hours -9,2 mmol/l. What pathology such indexes characterise? А. Healthy person В. Аcromegaly С. Ichenko- Kushinga disease D. Diabetes mellitus Е. Thyreotoxycosis 16. Content of glucose in patient’s blood is: on an empty stomach – 5.65 mmol/l, in one hour after taking sugar – 8.55 mmol/l, and in two hours after taking sugar – 4.95 mmol/l. These signs are characteristic for: A. Healthy person B. Person suffered from hidden diabetes mellitus C. Person suffered from non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus D. Person suffered from insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus E. Person suffered from thyrotoxicosis 17. Newborn has been refusing food, having vomiting and diarrhea, and some time later its crystalline lens become opaque. At examination of newborn: glucose in blood – 8.5 mmol/L and in urine – 1%. What is the most possible diagnosis? A. Galactosemia B. Phenylketonuria C. Tyrosinosis D. Cystinuria E. Alkaptonuria 18. Introduction of adrenalin in the experiment to the animal causes the increase of glucose in blood. A result of what hormone action is this hyperglycemia? A. Increase of absorption of glucose in intestine B. Decrease of glicogenesis C. Activation of gluconeogenesis D. Activation of glycogenolysis in the liver E. Decrease of hexokinase activation 46 19. At the inspection of patient glycemia -16 mmol/L, acetone bodies - 0,52 mmol/L, at urine - 2% glucose, acetone bodies + + +, diures 10 l in day. About what disease it is possible to think? A. Illness of Itsenko-Kuching B. Steroid diabetes C. Kidney diabetes D. Diabetes mellitus E. Diabetes insipidus 20. During examination the increase of glucose level is marked in students blood. What mechanism linked in this case? A. Increase of products of glucagons B. Increase of products of STH C. Increase of insulin production by pancreas D. Activating of the sympato-adrenal system E. Increase of tonus of the parasympathic nervous system 21. To the patient with diabetes mellitus with the purpose of hyperglycemic effect appointed insulin. What mechanism of insulin action? A. Warning of suction of glucose in a thin intestine B. Activation of gluconeogenesis C. Increasing of selection of endogenous insulin by pancreas D. By the assistance of penetration of glucose to the cell and its utilization E. Activation of anaerobic glicolis 22. A patient was admitted to the hospital in comatose state with the smell of acetone from mouth. Level of glucose in plasma of blood - 18 mmol/L. What type of coma is the most possible in this patient? A. Ketoacidotic B. Toxic C. Hyperosmolar coma D. Lactic acidosis E. Hypoglycemic coma 23. Patient has hyperglycemia, polyuria, hyperstenuria, ketonuria, glucosuria. What nosology can connect all these indexes? A. Diabetes mellitus B. Diencephalic obesity C. Diabetes insipidus D. Glikogenosis E. Kidney diabetes 47 24. A patient suffers from frequent head aiche, somnolence, crabbiness. At laboratory tests the level of glucose of blood is on an empty stomach - 2,8 mmol/L, after taking sugar the maximal concentration of glucose 4,7 mmol/L. The contents of insulin in blood in 10 times exceeds normal indexes, that characteristically for insulinoma. Activity of which processes is most promoted at this pathology? A. Lipolis B. Suction of glucose in an intestine C. Absorption of glucose by cell D. Synthesis of glicogenes E. Litogenesis 25. A man, aged 38, is under the course of treatment for schizophrenia at in-patient department. Contents of glucose, ketone bodies, and urea in his blood are normal. Shock therapy with regular injections of insulin has led to development of insular coma, and after that state of patient becomes better. What is the most possible reason for insulin coma? A. Glucosuria B. Dehydration of tissues C. Hypoglycemia D. Metabolic acidosis E. Ketonemia 26. Man, 28 years, suffers diabetes mellitus from 6 years age, he hospitalized in the comatose state which arose up after the physical loading. Skin moisture, tone of muscles and reflexes of tendons promoted, breathing is superficial, taxicardia, low blood pressure, level of glucose in blood - 1,88 mmol/L. This symptoms most characteristic for? A. Diabetic ketoacidosis B. Lactic acidosis C. Hypoglycemic coma D. Collapse E. Hyperosmolar coma 27. Man, 43years, delivered to the hospital in the comatose state. Objectively: a skin is dry, breathing is superficial frequent, the smell of acetone is absent, taxicardia, hypotension. Level of glucose in blood - 48 mmol/L, the reaction of urine on the acetone is negative. These symptoms most characteristic for? A. Hypertensive cris B. Ketoacidotic coma C. Lactic coma D. Collapse E. Hyperosmolar coma 48 28. Person, 42, was admitted to the hospital in the comatose state. Objectively: a skin is dry, pale, smell of acetone from the mouth, Kussmaul respiration, taxicardia, low blood pressure, level of glucose in blood - 27,7 mmol/L. What kind of coma has developed in this patient? A. Starvation B. Ketoacidotic coma C. Hyperosmolar coma D. Lactic coma E. Alcoholic intoxication 29. Woman, 45 years, the symptoms of diabetes are absent, but the level of glucose on an empty stomach determined in blood (7,5 mmol/L). What index must be conducted for clarification of presence of diabetes? A. Remaining nitrogen of blood B. Glucose of blood on an empty stomach C. Acetone bodies in urine, blood D. Tolerance to glucose E. Glycated hemoglobin 30. Patient with the Itsenko-Cushing syndrome has hyperglycemia because of hyperprodaction of glycocorticoids. What leading mechanism of hyperglycemia in this case? A. Decrease of activity of hexokinas B. Activating of glycogenolisis in liver C. Activating of glyconeogenesis in liver D. Strengthening of absirbtion of glucose in an intestine E. Activating of insulinase in liver 31. A patient with diabetes mellitus did not take the dose of insulin in time. Thus hyperglycemic coma developed (content of glucose in patient’s blood is 50 mmol/L). What is the leading factor for such coma development? A. Hyperosmolarity of blood plasma B. Hypokalemia C. Hypoxia D. Hyponatremia E. Acidosis 32. On the second week after gastrectomia for a patient in a hour after taking sweat food on the empty stomach develop sharp hypoglycemic state. What phenomenon does lie in basis of this state? A. Alimentar hypoglycemia B. Glikogenos C. Phermentopatia D. Adrenal insufficiency E. Dumping-syndrome 49 33. During the experiment rat was injected with 5% alloxan solution in dose 200 mg per kg of rat weight. What kind of pathology arises in this case? A. Arterial hypertension B. Acute renal failure C. Diabetes insipidus D. Diabetes mellitus E. Hepatic failure 34. After the break of diet (taking the easy for assimilation carbohydrates) in a woman, who has been suffering from diabetes mellitus for a long time, general malaise and increase of blood pressure gradually develop and hallucinations and cramps appear. Woman has dry skin and distinct signs of dehydration. What is the reason for worsening of patient’s condition? A. Hypoglycemic coma B. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic coma C. Diabetic ketoacidosis D. Heart failure E. Respiratory failure 35. What is the reason for glucosuria appearance under diabetes mellitus? A. Hyperglycemia B. Increase of renal threshold C. Rise of hexokinase activity D. Increase of glomerular membrane permeability E. Polyuria 36. A patient, aged 50, complains of increased appetite, thirst, and loss of body weight, weakness. At laboratory examination rise of amount of glucose in his blood revealed. What type of cells is injured in case of this disease development? A. Lipotropocytes B. Thyrocytes C. B-cells of Langerhans islets D. A-cells of Langerhans islets E. Pancreatocytes 37. A patient address to a doctor with complaints of constant thirst. Hyperglycemia, polyuria and increased content of 17-ketosteroids in urine were revealed. What is the most probable disease in this case? A. Addison’s disease B. Mychedema C. Glycogenosis of I type D. Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus E. Steroid diabetes 50 38. A patient was admitted to the hospital in comatose state. Accompanying people said that hi lost consciousness at training while he was finishing the Marathon distance. What sort of coma is the most possible in this patient? A. Hyperglycemic B. Hypoglycemic C. Hypothyroid D. Hepatic E. Diabetic ketoacidosis 39. In 18-years-old patient, while laboratory examining presence of glucose in urine and normal concentration of glucose in blood plasma were revealed. What disorder is the most possible cause of these changes? A. Disorders of glomerular filtration B. Disorders of tubular secretion C. Disorders of glucocorticoids secretion D. Disorders of insulin secretion E. Disorders of tubular reabsorption 40. A 19-years-old patient has suffered from diabetes mellitus since he was 8. He took cure irregularly. He was admitted to the hospital in connection to diabetes ketoacidosis development. What kind of respiration is the most possible in this condition? A. Kussmaul respiration B. Biot’s respiration C. Chane-Stocks respiration D. Inspiratory breathlessness E. Expiratory breathlessness 41. In a patient, who has poisoning with flodzine, glucosuria was revealed; concentration of glucose in patient’s blood is 5.6 mmol/L. What is the mechanism of glucosuria in this case? A. Disturbances of tubular reabsorption B. Reduction of glomerular filtration C. Increase of glomerular filtration D. Disorders of tubular secretion E. Rise of oncotic pressure of blood 42. Woman, 45 years disease of Kuchinga - steroid diabetes. At a biochemical inspection: hyperglycemia, hypochloremia. What processes is activated first of all? A. Glicogenolis B. Тransportation of glucose in a mew C. Glicolis D. Gluconeogenesis E. Reabsorption of glucose 51 43. A patient suffers from neurodermitis for a long time, use prednisolon. During examination increase of glucose in blood was found. In what link of carbohydrate metabolism prednisolon influence ? A. Increase of suction of glucose in an intestine B. Activation of gluconeogenesis C. Decrease of synthesis of glicogen D. Activating of breaking up of insulin E. Activating of glycogenogenesis 44. Patient with diabetes mellitus. In blood increase of level of free lipid acids. Reason of what it can be: A. Increase of thriglyceridlipase of adipocytes activity B. Accumulation in cytosolum palmitin-KoA C. Activating of apolipoprotein А-1, А-2, А-4synthesis D. Decrease of activity of phosphatidilcholin –cholesterin - acetyltransferase of plasma E. Activating of utilization of keton bodies 1-A 10-D 19-D 28-B 37-E 2-A 11-A 20-D 29-B 38-B 3-A 12-B 21-D 30-C 39-E 4-A 13-E 22-A 31-A 40-A Correct answers 5-A 6-A 14-D 15-D 23-A 24-C 32-E 33-D 41-A 42-D 7-A 16-A 25-C 34-C 43-B 8-A 17-A 26-C 35-B 44-A 9-B 18-D 27-E 36-C Situational tasks: 1. A patient is delivered to the clinic in the comatose state. Breathing is deep, noisy. Smell of acetone. Level of glucose in blood - 16,1 mmol/L. Found out glucosuria. Reaction of urine on acetone ++++. 1. What disease is described? ______________________________________________________________________ 2. Mechanisms of hyperglycemia? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. Mechanism of glucosuria? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. Mechanism of the appearance of acetone in urine? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 5. Mechanism of the smell of acetone. ________________________________________________________________________ 6. Mechanism of the violation of breathing? ________________________________________________________________________ 7. What is the type of pathological breathing in this case. ______________________________________________________________________ 52 2. Patient, 45 years, which uses an alcohol, feels a weakness, dizziness, thirst last time. He marks appearance of shortness of breathing, acute weakness, sweating after psychical overload. He lost consciousness in a transport. Objectively: skin is pale, AP is 70/45 mm Hg, tachicardia (120/min), violation of breathing (breathing of Chein-Stoks). 1. What additional researches are necessary for diagnosis. ______________________________________________________________________ 2. What form of carbohydrate metabolism pathology in a patient? ______________________________________________________________________ 3. What role of alcohol intoxication in development of this pathology? ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4. During conducting of test with glucose loading was inspected: level of glucose on an empty stomach - 6,66 mmol/L, in two hours after loading - 8 mmol/L. 1. What the results of test testify about? ______________________________________________________________________ 2. How have to maintenance of glucose change in blood for a healthy man through the same time after loading? ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. What is practical value of test with glucose loading? ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Algorithm for skills passing "Analyses of the glucose-tolerance test indexes at the patients with diabetes mellitus" 1. Name the reasons for the GTT Standard answer: - Capillary blood glucose on an empty stomach - more than 5.5 mmol / l - Presence of a diabetes mellitus at the family - Presens of the paradіabetes symptoms (itching of the skin and mucous membranes, often purulent disease, candidiasis) 2. Name the main stages of the GTT Standard answer: - Weigh the patient - Determination of the concentration of glucose in the capillary blood - Peroral intake of glucose at a rate of 1g/kg of body weight - Determination of the glucose concentration in capillary blood of patient after 2 hours 53 3. Appraise the results of GTT in this patient in accordance with the diagnostic criterias of diabetes mellitus and other categories of hyperglycaemia. Standard answer: Conclusion Concentration of glucose in the capillary blood on an empty stomach Diabetes mellitus More than 6.1 mmol/l Disordered glucose tolerance Disordered blood glucose Less than 6.1 mmol/l concentration of glucose in capillary blood after 2 hours after the glucose loading More than or equal to 11.1mmol/L 7,8 - 11.1 mmol/l 5.6 - 6.1 mmol/l Less than 7.8 mmol/l Practical work: “PATHOLOGY OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM” Object of work: to model experimental hypoglicemia for a rabbit. Content of work: determination of glucose concentration in condition of insulin intoxication. EXPERIMENT 1. Students work as brigades. The first brigade carries out the test on determination of glucose in the control samples; the other one carries out the test in experimental samples: before and after insulin introduction. Insulin is entered to the rabbit which was not fed by 24 hours in an amount 10 ME on the 1 kg of weight under the skin of the back. First test is carried out in 15 minutes after insulin introduction, than in 30 min., in 1 hour, in 1,5 hour. Blood for the test in an amount 0,1 ml is taken from an ear regional vein. After taking the blood the 10-15 ml of 30% glucose solution is entered to the rabbit throw the ear regional vein or through the mouth with the purpose to remove of insulin hypoglicemia. COURSE OF ANALYSIS: 1. Fill in two test tubes by 1 ml of decinormal solution of caustic soda and 5 ml of 0,45% solution of sulfuric zinc. 2. Add to one of test tubes 0,1 ml of blood, wash a pipette by solution from a test tube 2-3 times. The second test tube remains the control. 3. Put both test tubes on an water bath on 3 min. 4. Filter the maintenance of test tube through the sterile cotton wool in glass. 5. Wash test tubes twice by 3 ml of the distilled water which is poured on a filter. At the end of filtration the filter is levitated on an edge of bailer. Wait while all liquid will flow from it. Take away the filter from the bailer and shake off the drops of liquid which remained in the bailer in glass. 6. Add to the filtrate 2 ml K3[Fe(CN) 6] 1: 200. 54 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Boil on an water bath during 15 min. Cool glasses and add to each 2 ml of mixture of salts. Add to each glasses 2 ml of 3 % to solution of СН3СООН. Add 2-3 drops of 1 % to solution of starch. Titrate the maintenance of glasses by hyposulphite 1:200 till discolouring. Find the maintenance of glucose at the table by the amounts of hyposulphite which we used for titration. 13. Find the maintenance of glucose in the control tube at the table by the amounts of hyposulphite which we used for titration. 14. Find a difference in the maintenance of glucose in an experimental test tube, take away an error, determine the maintenance of glucose in blood in mg % . For the translation of the got result in mmol/l (international unit) use the coefficient 0,05. An initial maintenance of glucose in the blood before the introduction of insulin is___________mmol/l, after the introduction of insulin : in 15 min. - _________mmol/l, in 30 min. - _________ mmol/l in 90 min. - _________ mmol/l in 120 min.- _________ mmol/l Conclusion:______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 55 Theme: VIOLATION OF PROTEIN AND LIPID METABOLISM. Actuality of the theme. Metabolic disturbances can appear at all levels of biological organization – from molecular and cellular to the organism level. These changes can be investigation of violation of nervous hormonal mechanisms, changes of genetic information, action of pathogenic factors. A primary metabolic disturbance lies in the basis of many diseases, f. ex. diabetes mellitus, obesity, gout and other. The secondary violations accompany the most pathological processes. The studies of reasons, mechanisms of development, displays of metabolic disturbance at different levels, their diagnostics, treatment and prophylactic have great significance in preparation of future doctor. General purpose of the lesson: To learn the basic stages of violations of protein and lipid metabolism. For this it is necessary to know: 1. To expose the typical forms of violations of protein and lipid metabolism. 2. To expose violation of blood protein composition. 3. To explain the mechanisms of development of gout, general pathophysiologycal principles of its treatment. 4. To describe the inherited disorders of amino acid metabolism. 5. To expose main forms of lipid metabolism violations. 6. To explain the main mechanisms of obesity. 7. To define the main classes of lipoproteids and their role in pathology. 8. To explain the role of cholesterol and blood plasma lipoproteids in the origin of atherosclerosis. For realization of purpose of lesson it is necessary to have the base knowledgesskills. 1. Value of protein, lipid for an organism (Biochemistry Department). 2. Regulation of protein and lipid metabolism (Normal Physiology Department). 3. Negative and positive nitrous balance (Biochemistry Department). 4. Protein composition of blood (Normal Physiology Department). 5. A concept about lipoproteids (Biochemistry Department). Information, necessary for addition to knowledges-abilities of bases on these questions, can be found in the followings textbooks: Materials from normal physiology course. The checking of primary level of knowledges Give the answer to the followings questions: 1. What is positive nitrous balance? 2. What is negative nitrous balance? 3. Reasons which lead to the origin of negative nitrous balance? 4. Reasons which lead to the origin of positive nitrous balance? 56 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. What is hypoproteinemia? Make examples. What is hyperproteinemia? Make examples. What is dysproteinemia? Make examples. What is hypernitrogenemia? Make examples. What is products hypernitrogenemia? Make examples. What is retentional hypernitrogenemia? Make examples. What is phenylketonuria? What type of its inheritance? What is alcaptonuria? What type of its inheritance? Gout, mechanisms of development. What acid does accumulate in blood at a gout? What is obesity? Name the types of obesity. What is the secondary obesity? Make examples. Basic classes of blood plasma lipoproteids. What are the „modificated” lipoproteids? Make examples. Make examples of hormonal obesity. Theoretical questions for FMC №1. 1. Main stages of violations of protein metabolism. 2. Violation of protein composition of blood plasma: hypo-, hyper, dysproteinemia, paraproteinemia. 3. Hereditary disorders of aminoacid metabolism. 4. Gout. Reasons and mechanisms of development. Basic pathophysiologycal principles of treatment. 5. Characteristic features of violations of purins bases for children. Hyperurikemia and uraturia of new-born. 6. Main stages of lipid metabolism violations. 7. Obesity, determination. Reasons and mechanisms of obesity different forms development. 8. Basic classes of lipoproteids and their role in pathology. 9. Disorder of cholesterin metabolism for children and adults. Literature. 1. Handbook of general and Clinical Pathophysiology/ Edited by prof.A.V.Kubyshkin, CSMU, 2005.p.142-144 2. Pathophysiology/ Edited by prof.Zaporozan, OSMU, 2005.p.125-133, 145-153 3. General and clinical pathophysiology/ Edited by Anatoliy V/ Kubyshkin – Vinnytsia: Nova Knuha Publishers – 2011. p.286-287, 322-333 THEMES of reports for individual work of students: 1. Inherited disorders of metabolism of amino acid. 2. Pathogenesis of obesity. 3. Gout. Role of eczo- and endogenous factors in its origin. Mechanisms of development. Pathogenic treatment. 4. Modern pictures of pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 5. Obesity and diabetes mellitus. 57 Testing according system “Krok-I” Tests of an open database (2010) 1. A 58-year-old patient suffers from the cerebral atherosclerosis. Examination revealed hyperlipoidemia. What class of lipoproteins will most probably show increase in concentration in this patient’s blood serum? A Low-density lipoproteins B High-density lipoproteins C Fatty acid complexes with albumins D Chylomicrons E Cholesterol 2. A patient who had been working hard under conditions of elevated temperature of the environment, has now a changed quantity of blood plasma proteins. What penomenon is the case? A Relative hyperproteinemia B Absolute hyperproteinemia C Absolute hypoproteinemia D Disproteinemia E Paraproteinemia 3. A patient being treated for viral hepatitis type B got symptoms of hepatic insufficiency. What blood changes indicative of protein metabolism disorder will be observed in this case? A Absolute hypoalbuminemia B Absolute hyperalbuminemia C Absolute hyperfibrinogenemia D Proteinic blood composition is unchanged E Absolute hyperglobulinemia (2009 year) 4. A 1,5-year-old child presents with both mental and physical lag, decolorizing of skin and hair, decrease in catecholamine, concentration in blood. When a few drops of 5% solution of trichloroacetic iron had been added to the child's urine it turned olive green. Such alteration are typical for the following pathology of the amino acid metabolism: A. Tyrosinosis B. Alkaptonuria C. Phenylketonuria D. Albinism E. Xanthinuria 58 5. Nappies of a newborn have dark spots being the evidence of homogentisic acid formation. This is caused by the metabolic disorder of the following substance: A. Cholesterol B. Methionine C.Galactose D. Tyrosine E. Tryptophan (2006-2008) 6. Patient suffers from pellagra. Disorder of metabolism of what amino acid lie in basis of this disease? А. Thrypthofan В. Тhyrosin С. Phenylalanine D. Cystein E. Valin 7. A child with phenylcetonuria suffers from mental insufficiency. What mechanism will be main in development of damage of the central nervous system? А. Increase ecscreation with urine of phenylceton bodies В. Increase of thyrosin synthesis С. Decrease of the synthesis of thyreiod hormones D. Decline of synthesis of melanin Е. Accumulation of phenylalanine in the blood 8. Child, 8 months, found disorders in mental and physical development. What amino acid must be excluded from the meal of child? А. Hystidin В. Leicin С. Тhyrosin D. Thrypthofan Е. Phenilalanin 9. Colouring of sclera, mucous membranes were founded during examination of infant. Darkening of urine in air was determined. Homogenthisin acid was founded in the blood and urine. For what state it is characteristically? А. Cystinuria В. Hystidinemia С. Аlcaptonuria D. Albinism Е. Galakozemia 59 10. Albinos do not carry sun influencing- sunburn does not develop, and burns appear. Violation of what aminoacid lies in a basis of this phenomenon? А. Thrypthofan В. Hystidin С. Меthionin D. Glyutamin acid Е. Phenylalanine 11. To the woman with pathological obesity for the decline of body mass conducted an operation, as a result she lost 30 kg That it was remote during an operation. А. Part of stomach В. Gall blader С. Part of pancreas D. Part of colon Е. Part of thin bowel 12. Man has cerebral obesity developed after the carried encephalitis. What is the leading mechanism of this obesity? А. Decrease of basic metabolism В. Increase converting of glucose into lipids С. Decrease of lipolis D. Hyperinsulinemia E. Bulemia, polyphagia 13. Why develops obesity at hyperinsulinism? А. Decrease of pentozophosphatic way В. Proteins convert into lipids С. Activaiting of glycogenesis D. Glyconeogenes increases Е. Carbohydrates converts into lipids 14. A sportsman after stopping of trainings had obesity. What is pathogenetic mechanism? А. Increase of the tonus of the parasympathetic nervous system В. Decrease of the tonus of the sympathetic nervous system С. Insufficiency of mobilizations lipids from a depo D. Oppressing the center of saturation Е. Uncorrespondence of using energy to the amount of food which is used 15. Child, 10 months (parents has dark hair), has very light skin and blue eyes. During the last 3th months there were violations of cerebral blood circulation. Reason for such state can be: А. Sharp porphyria В. Hystidinemia С. Glicogenom D. Phenilcetonuria Е. Galakozemia 60 16. A patient, 60 years, suffered from pain in the small joints of feet and hands. Joints are increased, have the appearance of the thickened nodes. Maintenance of urats is increased in blood. What metabolism disorders can be the reason of this state? A. Pyrimidin B. Amino acid C. Purins D. Lipid E. Carbohydrates 17. Multiplying maintenance of phenylalanine is discovered in the pregnant women blood. What disorder can arise up in a child? A. Development of oligofrenia B. Development of galaktozemia C. Birth of child is with the Turner syndrome D. Development of Vilson disease E. Birth of child is with the Dawn’s syndrome 18. Man, 65 years, complaints about acute pain in large fingers of legs. He drinks beer often. There was suspicion on a gout. Level of what acid is it necessary to define in blood for confirmation of diagnosis? A. Urinary acid B. Bilirubin C. Keton bodies D. Urea E. Lactate 19. It is known that phenylcetonuria - is result of gene mutation, responsible for transformation of phenylalanine and disintegration of it to the finished products of metabolism - СО2 and Н2О. What way of phenylalanine metabolism will result development of phenylcetonuria? A. Phenylalanine - thyrosin - thyroxin B. Phenylalanine - thyroxin - noradrenalin C. Phenylalanine - thyroxin D. Phenylalanine - phenylpiruvat - keton acid E. Phenylalanine - thyrosin - melanin 20. Sick K., 48 years, suffers from obesity, conducted the course of medical starvation at home. The deep noisy breathing appeared on 10th day, arterial pressure 90/60 mm Hg, a selection of urine diminished, urine with the smell of acetone. What does this phenomenon testify about? A. Nongas alcalos B. Hyperglycemia C. Ketosis D. Hypoglycemia E. Gas acidosis 61 21. Slow physical and psychical development, pale skin, hairs, iris of eye, positive Feling’s test were marked at child 6 months. What inherited disease found out at a child? A. Galaktozemia B. Alcaptonuria C. Illness of Dauna D. Albinism E. Phenylcetonuria 22. Patient suffers from alcaptonuria. Deficiency of what enzyme was present in this case? A. Thyroxinhydroxylase B. Oxydase of homogenthisin acid C. Phenylalaninhydroxylase D. Thyrosinase E. Monoaminooxydase 23. A month ago patient was delete of considerable part of thin bowel. In his blood explored maintenance of albumen in plasma, which made 3,5 g/l. How to classify the changes of albuminous composition of blood? A. Desproteinemia B. Hyperproteinemia C. Paraproteinemia D. Hypoproteinemia E. Hypernitrogenemia 24. The promoted maintenance of low density lipoproteids was founded in the blood at an inspection of patient. What disease can be expected in this patient? A. Pneumonia B. Acute pancreatitis C. Gastritis D. Atherosclerosis E. Damage of kidneys 25. A patient with a fever lost weight during three weeks. Rest nitrogen of blood is 70 mmol/L. What is nitrous balance in a patient? A. Positive B. Negative C. Normal D. Relative 26. The concentration of albumen in patient with infectious disease blood is 120 g/l. What quantitative change of blood albuminous composition is present? A. Hyperproteinemia B. Hypoproteinemia C. Paraproteinemia D. Dysproteinemia E. Hypernitrogenemia 62 27. Maintenance of common protein in the patient with hepatic coma blood is 40 g/l, maintenance of albumen and fibrinogen is reduced, γ-globulin is promoted. Name the changes of blood albuminous composition? A. Hypoproteinemia B. Hyperproteinemia C. Dysproteinemia D. Hypernitrogenemia E. Paraproteinemia 28. The maintenance of lipids in the blood of patient at starvation (in the second period) can increase. What is the form of hyperlipidemia in this case? A. Cerebral B. Retentional C. Transport D. Alimentary E. Diencephalic 29. Ventromedial nucleos of hypothalamus were ruined at animal in an experiment. As a result it has an obesity. What is the type of obesity in this case? A. Alimentary B. Cerebral C. Hormonal D. Hyperplastic E. Hypertrophic 30. Maintenance of urinary acid in a patient blood is promoted, that causes the pain syndrome development as a result of urats deposit in the joints. What is the reason of this acid appearance? A. Catabolism of HEM B. Pirimidin nucleotids disintegration C. Purin bases reutilisation D. Purin nukleotids disintegration E. Protein disintegration 31. Hyperlipidemia was founded at patient 67 years, suffers from atherosclerosis of cerebrum vessels. What class of blood lipoproteids of probably will be promoted at biochemical research? A. Low density lipoproteids B. High density lipoproteids C. α-lipoproteids D. Chilomicrons E. Lipid acids and albumin complexes 63 32. Negative nitrous balance was founded at the inspection of man 45 years, which was long time on a vegetable diet. What is the reason of this phenomenon? A. Insufficient quantity of proteins B. Surplus quantity of water C. Surplus quantity of carbohydrates D. Insufficient quantity of lipids E. Insufficient quantity of lipids and proteins 33. Child, 2 years, was delivered to the hospital with slow mental and physical development, frequent vomiting after taking a meal. Phenylpirovinograde acid was founded in urine. Violation of what metabolism is in this pathology? A. Carbohydrate B. Amino acid C. Water-salt D. Phosphoric-calcium E. Lipid metabolism 34. A prisoner declared starvation. Hypoglycemia, hypoproteinemia, hyperlipemia and ketonemia were founded in his blood after the week of starvation. What form of hyperlipemia developed? A. Alimentary B. Food C. Transport D. Esential E. Retentional 35. Hypotension, muscular weakness, negative nitrous balance were founded at the inspection of woman 50 years, who long time was on a vegetable diet. What factor resulted such state? A. Surplus carbohydrates amount in a food B. Insufficient carbohydrates amount in a food C. Surplus consumption of water D. Insufficient lipids amount in a food E. Insufficient protein amount in a food 36. A patient with normal maintenance of general protein in blood has changes of separate albuminous fractions correlation. Name this phenomenon. A. Hyperproteinemia B. Dysproteinemia C. Paraproteinemia D. Hypoproteinemia E. Monoproteinemia 64 37. Polyunsaturated ω- 3-lipid acids which are contained in marine fish, and preparations, created on their basis, are recommended for the atherosclerosis prophylaxis. What is the mechanism of the lipid acids action? A. In the human organism these acids transform on eycosanoids B. There are vasoconstrictors and activators of trombocytes agregation C. There are vasodilyatators and inhibitors of trombotocytes agregation D. Activate lecitin -cholestirin-acetyltransferase, that is contained in LDLP Е. Inhibitor of Co-A- reductase 38. Apoprotein - is: А. Protein cellular receptors to lipoprotein of blood plasma В. Variant of „modificated” lipoproteids С. Lipoproteins of blood plasma without albuminous part D. Albuminous component of blood plasma lipoproteins Е. Anomal proteins with characteristics of lipoproteins 39. Woman, 62years, suffers from frequent pain in the area of thorax and vertebra, breaks of ribs. A doctor assumed mielom disease (plasmocytoma). What laboratory indexes will have a main diagnostic value? A. Hypoproteinemia B. Paraproteinemia C. Proteinuria D. Hyperalbumenemia E. Hypoglobulinemia 40. The quantity of plasma albumens changed in a man which executed a physical work in the conditions of high temperature. How did quantity of plasma albumins change? A. Relative hyperproteinemia B. Paraproteinemia C. Dysproteinemia D. Absolute hyperproteinemia E. Absolute hypoproteinemia 41. Increase of free lipid acids in patients with diabetes mellitus blood was observed. What is the reason of this state? A. Increase of adipocytes trigliceridlipase activity B. Accumulation of palmytin –Co-A in cytosolum C. Activating of apolipoproteins of А-1, А-2, А-4 synthesis D. Decline of phosphatidilcholin – cholesterin acetyltransferase activity in the blood E. Activating of keton bodies utilization 65 42. Man, 70 years, suffers from atherosclerosis of lower extremities vessels and ischemic heart disease. Violation of lipid composition of blood was founded during examination. What lipoprotein is the main link in atherosclerosis pathogenesis? A. Low density B. Cholesterol C. High density D. Intermediate density E. Chilomicrons 1-A 10-C 19-E 28-C 37-D 2-A 11-E 20-C 29-B 38-D 3-A 12-E 21-E 30-D 39-B 4-C 13-E 22-B 31-A 40-A Correct answers 5-D 6-A 14-E 15-D 23-D 24-D 32-A 33-B 41-A 42-A 7-E 16-C 25-A 34-C 8-E 17-A 26-A 35-E 9-C 18-A 27-C 36-B Situational tasks: 1. Patient, 60 years, suffers from atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, ischemic heart disease. At the investigation hyperlipidemia was founded. 1. What class of lipoproteins od blood plasma will be increased? _____________________________________________________________________ 2. What classes of lipoproteins do you know? Characteristic. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Рrinciples of pharmacocorrection. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Patient, 60 years, suffers from atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, ischemic heart disease. At the investigation hyperlipidemia was founded. 1. What is hyperlipoproteinemia? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Classification of hyperlipoproteinemia. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Рrinciples of pharmacocorrection. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 66 3. Patient has encephalitis. After the disease she suffers from increasing of appetite (polyphagia), increasing of body weight. Obesity developed. 1. What is the type of obesity? _____________________________________________________________________ 2. What are the reasons of its development? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Classification of the obesity according to pathogenesis? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4. Patient has encephalitis. After the disease she suffers from increasing of appetite (polyphagia), increasing of body weight. Obesity developed. 1. Obesity, definition. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the kind of obesity. Explain the answer. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Рrinciples of pharmacocorrection . ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 5. Patient admitted to the clinic at the comatous state. At anamnesis diabetes mellitus II type during 5 years. Objectively: deep and noisy breathing, smell of acetone in the expiratory air. 1. What are the changes of lipid metabolism at the patient? Explain your answer. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 2. For what complication of present disease described symptoms are characteristic? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 6. Patient admitted to the clinic with diagnosis “adenoma of β-cells of pancreas". Obesity is characteristic. 1. What is the reason of obesity in this case? ______________________________________________________________________ 2. What kinds of obesity do you know? 67 ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. What is type of obesity at this patient? ______________________________________________________________________ 4. Рrinciples of pharmacocorrection. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 6. A child complains on general weakness, diarrhea. Depigmentation of the skin was founded. The diagnoses was made: kwashiorkor. 1. Explain the reasons and mechanisms of development of described pathology. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Which else manifestations of kwashiorkor do you know? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Prophylaxis and treatment of this pathology. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 7. Dark spots at the area of the nose, scleras and ears appeared at the child, 2 years old. Urine is become black on the air. 1. Accumulation of what substance in the blood and urine can lead to such changes? _____________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the pathology? _____________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the type of inheritance of this pathology? ________________________________________________________________________ 8. Amount of homogenthisinic acid is increased at the child, 5 years old. 1. What pathology is observed at the patient? ______________________________________________________________________ 2. What enzyme insufficiency takes place at this pathology? ______________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the type of inheritance of this pathology? ________________________________________________________________________ 68 9. A child, 9 monthes. He has light-colored hair (parents are dark-haired) very lightcolored skin and blue eyes. He has physical and mental developmental retardation. Feling’s test is positive. 1. Lever of what amino acid have to be checked? ______________________________________________________________________ 2. Defect of what hormone takes place at this pathology? ______________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the type of inheritance of this pathology? ________________________________________________________________________ 10. A child, 9 monthes. He has light-colored hair (parents are dark-haired) very light-colored skin and blue eyes. He has physical and mental developmental retardation. Feling’s test is positive. 1. Lever of what amino acid have to be checked? ______________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the mechanism of this pathology development? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3. Prophylaxis and treatment of this pathology. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 11. Patient enter to the doctor with complains on the pain at the small joints of the hands and foots. Objectively: increasing of these joints, their deformation. Increased level of the urates in the blood was founded. 1. What is the disease at the patient? ________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the mechanism of described changes? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Prophylaxis and treatment of this pathology. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 69 70