BLM TEST 1 S2 2015
advertisement
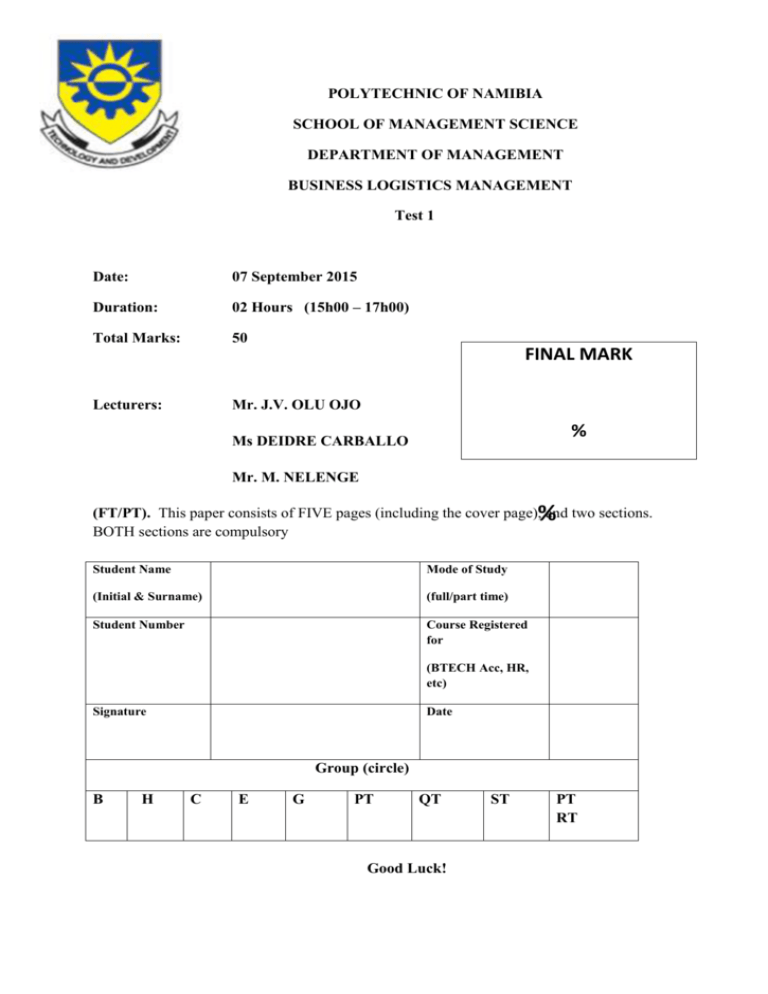
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT BUSINESS LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT Test 1 Date: 07 September 2015 Duration: 02 Hours (15h00 – 17h00) Total Marks: 50 FINAL MARK Lecturers: Mr. J.V. OLU OJO % Ms DEIDRE CARBALLO Mr. M. NELENGE % (FT/PT). This paper consists of FIVE pages (including the cover page), and two sections. BOTH sections are compulsory Student Name Mode of Study (Initial & Surname) (full/part time) Student Number Course Registered for (BTECH Acc, HR, etc) Signature Date Group (circle) B H C E G PT QT Good Luck! ST PT RT SECTION A 1. The following seven steps of systems analysis have been placed here in the wrong order: a) evaluation of alternatives b) selecting goals and objectives and defining the problem c) implementing d) generating alternative solutions e) choosing appropriate alternatives f) monitoring performance and reviewing goals and objectives g) system modelling Which sequence of steps is correct? a) B, G, D, A, E, C, F b) B, D, G, A, E, C, F c) B, G, D, A, C, E, F d) B, G, A, D, E, C, F e) B, G, D, A, E, F, C 2. Consumers’ willingness to pay reflects the __________ they place on a product. a) monetary value b) time value c) place utility d) possession utility e) form utility 3. Supply chain management includes all logistics management activities as well as … a) Manufacturing operations and sales (applied marketing). b) Materials management and physical distribution. c) Procurement and sales. d) Procurement and manufacturing operations. e) Manufacturing operations and sales 4. One of the following statements does not form part of the Competitive advantage created by logistics a) Logistics linkages with the value chain b) Value-added role of logistics c) Customer service d) Aspects of competitive advantage and wealth creation through logistic. e) Globally competitive and profitable business that deliver consumer satisfaction. 5 The proven ability, readiness and willingness to effectively handle variations in order and inventory quantities, freight consignment volumes and mass, delivery times and delivery locations–without any significant loss in overall efficiency–is known as … a) Accessibility. b) Goods security. c) Reliability. d) Flexibility. e) Suitability. 6 The competitive environment of organisations has changed drastically in a number of aspects. Which of the following is NOT one of these aspects? a) Customers are more geographically dispersed than before. b) Customers are demanding higher-quality products at lower costs in a shorter time. c) Strategic partners are now incorporated into, and become part of, a supply network structure (suppliers and manufacturers). d) Organisations have reduced their manufacturing operations to single-site manufacturing facilities within one country. e) Businesses are faced with increasing volatility and uncertainty in the economic and competitive playing fields. 7. In aligning the supply chain strategy to the organisational strategy, the supply chain focus needs to start with ... a) The customer and then work backwards through the supply chain scope. b) The supplier and then work forwards through the supply chain scope. c) The production facility as the centre of focus. d) The logistics service providers and their own objectives. e) Environmental pressure groups and their demands. 8. Purchase and make to order is used in industries where … a) Mass customisation is commonplace. b) The raw material content is negligible in relation to the total cost of ownership. c) The raw material inventory levels are normally high. d) The raw material inputs are relatively expensive. e) The customer order penetrates upstream from the finished goods store. 9. Which one of the following quantities is NOT calculated by materials requirements planning? a) Sales requirements b) Manufacturing activity schedules c) Expected shortages d) Surplus components inventory e) Available free capacity 10. Economic value added is: a) The difference between the net operating profit after tax less the cost of capital employed b) Important in the creation of shareholders’ value c) A term that refers to the value that a company adds to a country’s economy d) Important in the creation of economic wealth e) The present value of future market value added Total = 20 marks SECTION B 1. Explain and give examples of what is meant by Corporate Strategy, Business or tactical and operational strategy in the logistic or organisation context. (10) 2. Describe and illustrate where applicable the process to follow for supply chain strategy development and implementation (20)